
The most acidic among the following is:
(A) p-cresol
(B) o-cresol
(C) p-nitrophenol
(D) p-chlorophenol
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: To solve the above question we will have to consider various inductive effects and resonance effects present in substituted phenols. Consider the effect of electron withdrawing and electron releasing groups.
Complete step by step solution: The structures of different substituted phenols as shown below:
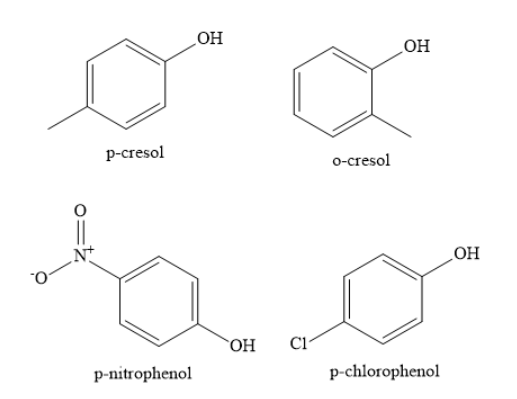
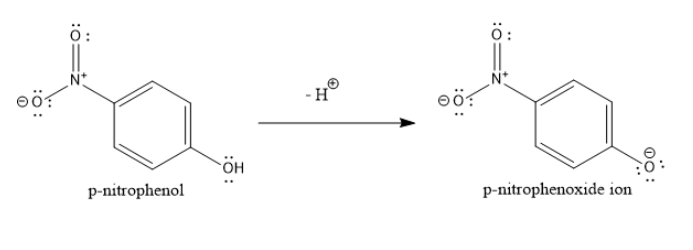
When phenols lose a proton, they form phenoxide ions. These phenoxide ions are resonance stabilized. The lone pair of electrons on the negatively charged oxygen atom of phenoxide ion are delocalized over the entire aromatic nucleus.
If you can decrease the extent of this resonance delocalization, then you slightly destabilize the phenoxide ion. To do so, you can introduce an electron releasing group such as alkyl group or alkoxy group in the ortho or para position. This will slightly reduce the dispersion of the negative charge of the oxygen atom of phenoxide ion and decrease its acidity.
On the other hand, if you can increase the extent of this resonance delocalization, then you further stabilize the phenoxide ion. To do so, you can introduce an electron withdrawing group such as nitro or chloro group in the ortho or para position. This will further disperse the negative charge of the oxygen atom of phenoxide ion and increase its acidity.
The resonance structures for the p-nitrophenol are shown below.
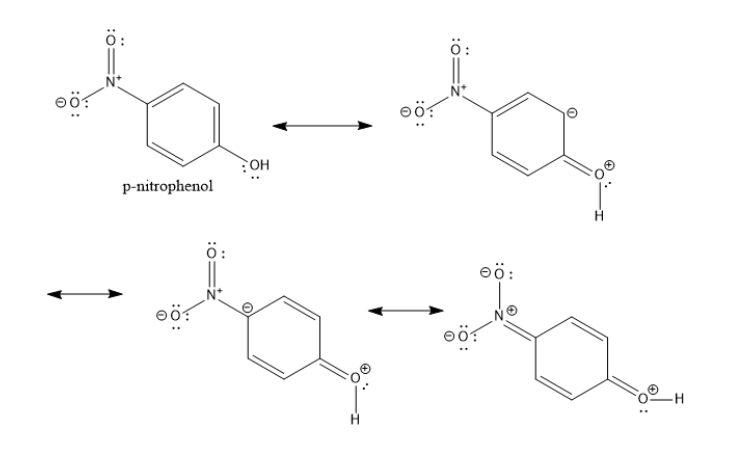
The electron withdrawing power of the nitro group is greater than that of the chloro group. Hence, among the given options, p-nitrophenol is the most acidic.
Hence, the option (C) is the correct option.
Note: Phenols are weak acids. They react with sodium hydroxide but they do not react with sodium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate. Sodium hydroxide is a strong base but sodium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate is a weak base. Thus, phenols react with strong bases but they do not react with weak bases.
Complete step by step solution: The structures of different substituted phenols as shown below:

When phenols lose a proton, they form phenoxide ions. These phenoxide ions are resonance stabilized. The lone pair of electrons on the negatively charged oxygen atom of phenoxide ion are delocalized over the entire aromatic nucleus.
If you can decrease the extent of this resonance delocalization, then you slightly destabilize the phenoxide ion. To do so, you can introduce an electron releasing group such as alkyl group or alkoxy group in the ortho or para position. This will slightly reduce the dispersion of the negative charge of the oxygen atom of phenoxide ion and decrease its acidity.
On the other hand, if you can increase the extent of this resonance delocalization, then you further stabilize the phenoxide ion. To do so, you can introduce an electron withdrawing group such as nitro or chloro group in the ortho or para position. This will further disperse the negative charge of the oxygen atom of phenoxide ion and increase its acidity.
The resonance structures for the p-nitrophenol are shown below.

The electron withdrawing power of the nitro group is greater than that of the chloro group. Hence, among the given options, p-nitrophenol is the most acidic.
Hence, the option (C) is the correct option.

Note: Phenols are weak acids. They react with sodium hydroxide but they do not react with sodium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate. Sodium hydroxide is a strong base but sodium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate is a weak base. Thus, phenols react with strong bases but they do not react with weak bases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




