
The number of $\alpha $-hydrogen atoms present in is:
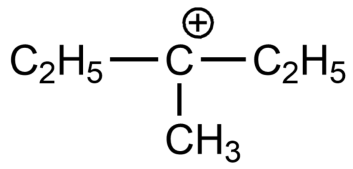
(A)- 6
(B)- 7
(C)- 13
(D)- 9

Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: The first carbon atom in an organic molecule that attaches to a functional group such as carbonyl is known as the alpha carbon and represented as $C\alpha $. The hydrogen atom which is attached to an alpha carbon is called alpha hydrogen and represented as $H\alpha $.
Complete step by step answer:
-The second carbon atom in an organic molecule which attaches to the alpha carbon $(C\alpha )$ is known as the beta carbon and represented as $C\beta $. The hydrogen atom which is attached to a beta carbon is called beta hydrogen and represented as $H\beta $.
-Let us open and draw the structure given in the question and try identifying the alpha hydrogens and alpha carbons in the molecule-
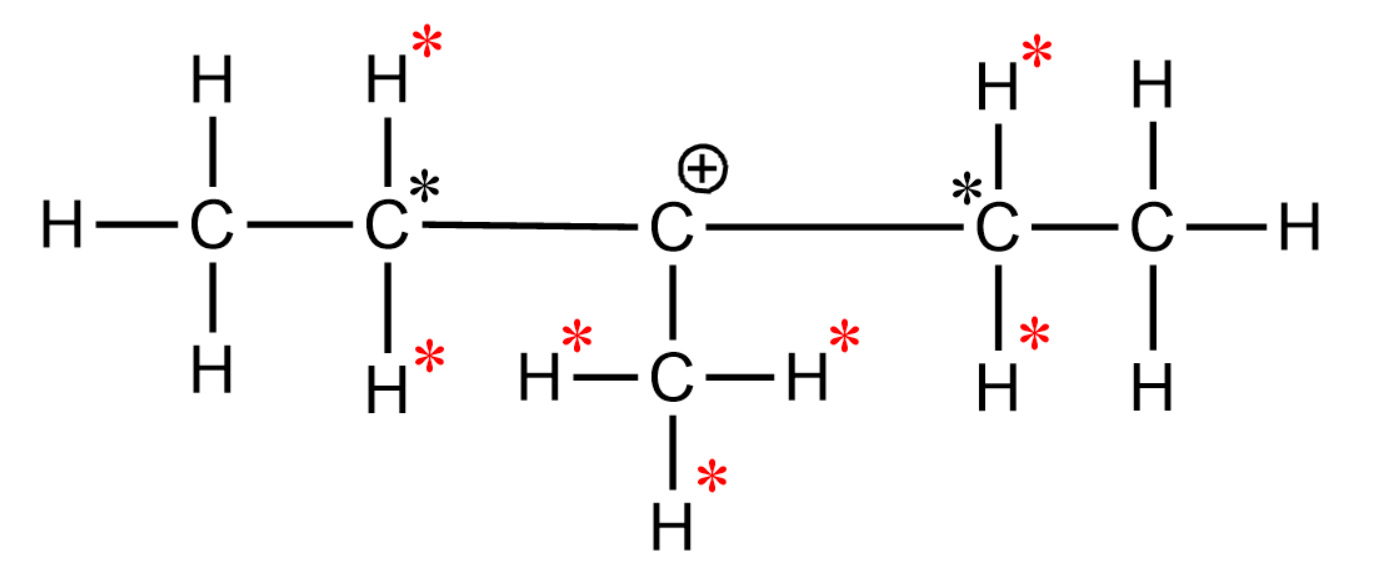
-The carbons marked with black stars are the alpha carbons and the hydrogens attached to $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized alpha carbon which is directly attached to the carbocation are called the alpha hydrogens. The alpha hydrogen in the molecules are marked with red stars.
So, the number of $\alpha $-hydrogen are 7.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: -Alpha carbons are very reactive and hence are responsible for so many reactions.
-Identifying the alpha hydrogens in the molecule helps us in determining the stability of the alkenes or alkynes.
-Due to the acidic nature of alpha hydrogens in aldehydes and ketones, they undergo many reactions. The acidity of alpha hydrogen of ketones or aldehydes is due to the strong electron-withdrawing nature of the carbonyl groups and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
-Some of the important reactions showing the reactivity of alpha hydrogens are given below-
(i) Aldol condensation is the reaction in which $\beta $-hydroxy aldehydes and $\beta $-hydroxy ketones are produced when aldehydes and ketones with at least one alpha hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as a catalyst.
(ii) Cross aldol condensation is the reaction between two different aldehydes and ketones having at least one alpha hydrogen involved in aldol condensation undergoes reaction producing a mixture of four products.
(iii) Cannizaro reaction is the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with at least one alpha hydrogen undergoing self-oxidation and reduction reaction on heating.
Complete step by step answer:
-The second carbon atom in an organic molecule which attaches to the alpha carbon $(C\alpha )$ is known as the beta carbon and represented as $C\beta $. The hydrogen atom which is attached to a beta carbon is called beta hydrogen and represented as $H\beta $.
-Let us open and draw the structure given in the question and try identifying the alpha hydrogens and alpha carbons in the molecule-

-The carbons marked with black stars are the alpha carbons and the hydrogens attached to $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized alpha carbon which is directly attached to the carbocation are called the alpha hydrogens. The alpha hydrogen in the molecules are marked with red stars.
So, the number of $\alpha $-hydrogen are 7.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: -Alpha carbons are very reactive and hence are responsible for so many reactions.
-Identifying the alpha hydrogens in the molecule helps us in determining the stability of the alkenes or alkynes.
-Due to the acidic nature of alpha hydrogens in aldehydes and ketones, they undergo many reactions. The acidity of alpha hydrogen of ketones or aldehydes is due to the strong electron-withdrawing nature of the carbonyl groups and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
-Some of the important reactions showing the reactivity of alpha hydrogens are given below-
(i) Aldol condensation is the reaction in which $\beta $-hydroxy aldehydes and $\beta $-hydroxy ketones are produced when aldehydes and ketones with at least one alpha hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as a catalyst.
(ii) Cross aldol condensation is the reaction between two different aldehydes and ketones having at least one alpha hydrogen involved in aldol condensation undergoes reaction producing a mixture of four products.
(iii) Cannizaro reaction is the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with at least one alpha hydrogen undergoing self-oxidation and reduction reaction on heating.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




