
The number of chiral carbon atom present in open chain and cyclic form glucose is:
A)3,2
B)4,5
C)5,5
D)6,5
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: A chiral carbon atom has four different types of atoms attached to it. In a molecule for each chiral carbon, there exists two optical isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the open chain form of glucose as follows,
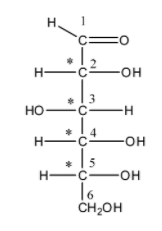
In this structure, we can see that there are four chiral centres C-2, C-3, C-4, and C-5. These four carbons have four different groups attached to it. Hence, they are considered as chiral carbon. The open-chain isomer D-glucose has four isomers: $\alpha$-D-glucopyranose, $\beta$-D-glucofuranose, $\beta$-D-glucopyranose and $\alpha$-D-glucofuranose. These five isomers exist in equilibrium and they can interconvert. The interconversion of the isomers becomes more rapid on acid catalysis.
We can draw the close chain form of glucose as follows,

In this structure, we can see that there are five chiral centres C-2, C-3, C-4, C-5 and C-6 marked by stars. These five carbons have four different groups attached to it. Hence, they are considered as chiral carbon.
So, out of the given four options, B is the correct option.
Note: Students may get confused while determining the number of chiral carbons in the open chain and cyclic form of glucose. The open chain contains four chiral carbons and the cyclic form of glucose contains five chiral carbons. To identify a chiral carbon, we must see the groups attached to it. If all the four groups attached to the carbon atom are different, then we can identify that carbon atom as a chiral carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the open chain form of glucose as follows,

In this structure, we can see that there are four chiral centres C-2, C-3, C-4, and C-5. These four carbons have four different groups attached to it. Hence, they are considered as chiral carbon. The open-chain isomer D-glucose has four isomers: $\alpha$-D-glucopyranose, $\beta$-D-glucofuranose, $\beta$-D-glucopyranose and $\alpha$-D-glucofuranose. These five isomers exist in equilibrium and they can interconvert. The interconversion of the isomers becomes more rapid on acid catalysis.
We can draw the close chain form of glucose as follows,

In this structure, we can see that there are five chiral centres C-2, C-3, C-4, C-5 and C-6 marked by stars. These five carbons have four different groups attached to it. Hence, they are considered as chiral carbon.
So, out of the given four options, B is the correct option.
Note: Students may get confused while determining the number of chiral carbons in the open chain and cyclic form of glucose. The open chain contains four chiral carbons and the cyclic form of glucose contains five chiral carbons. To identify a chiral carbon, we must see the groups attached to it. If all the four groups attached to the carbon atom are different, then we can identify that carbon atom as a chiral carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




