
The order of basicity among the following compounds is
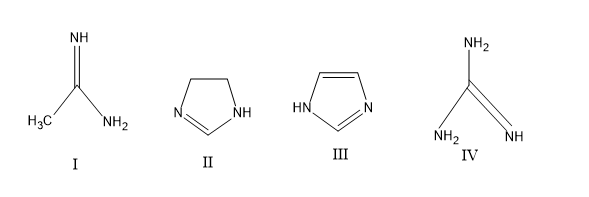
A) $II\rangle I\rangle IV\rangle III$
B) $IV\rangle II\rangle III\rangle I$
C)$IV\rangle I\rangle II\rangle III$
D) $I\rangle IV\rangle III\rangle II$

Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Basicity is the tendency of the molecule to donate electron pairs.
Lone pairs play a very important role in the basicity of the molecules.
Complete answer:
Basicity can be said as the measure for power of the donating lone pairs.
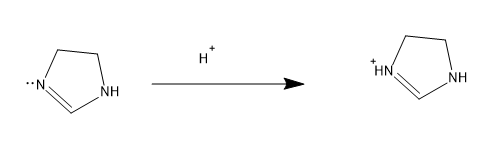
The more number of lone pairs donated, more is the basic character .If the basic is strong then it will easily donate the lone pairs, so stronger the base the easiness for donating electrons increases. Lone pairs have a concentration of negative charge and to reduce the negative charge and to stabilize the molecule the lone pair is donated and comes in conjugation to yield a stable form. So now let’s compare the structures, first let’s check the open chain structures with more lone pairs and then move to aromatic rings, as for aromatic rings they possess extra stability by the resonance factor. For structure IV, it contains more number of lone pairs and it comes in conjugation and increase the electron density in N in =NH, the mechanism is as follows,
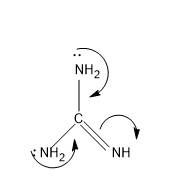
The electron density in N in =NH is more and hence this is the most basic molecule from the above given structures. The conjugate acid stabilizes with resonance with the $N{{H}_{2}}$ groups present
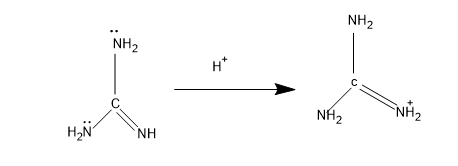
Then comes the structure I, the lone pair comes in conjugation and the mechanism is,
The stabilized form of the conjugate acid, and is stabilized with one $N{{H}_{2}}$group.
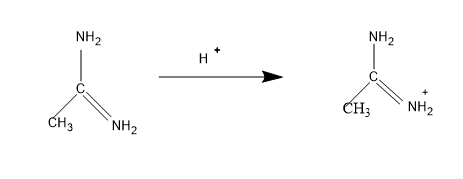
So the electron density of N in N=NH will be less than the structure IV
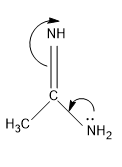
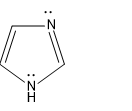
For structure II, the mechanism of the transfer of lone pair is,
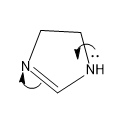
Here the lone pair is in available in this case as it is not involved in the aromatic sextet
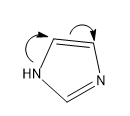
Then comes the last structure, Structure III, here lone pair is involved in the aromaticity so the lone pair is not available, hence this is the least structure.
Note: The valency of the structure should be satisfied while drawing the structure and the arrows should be put from the lone pair to the nearby atom. Arrows should be properly marked then only we could trace the electron charge density.
Lone pairs play a very important role in the basicity of the molecules.
Complete answer:
Basicity can be said as the measure for power of the donating lone pairs.
The more number of lone pairs donated, more is the basic character .If the basic is strong then it will easily donate the lone pairs, so stronger the base the easiness for donating electrons increases. Lone pairs have a concentration of negative charge and to reduce the negative charge and to stabilize the molecule the lone pair is donated and comes in conjugation to yield a stable form. So now let’s compare the structures, first let’s check the open chain structures with more lone pairs and then move to aromatic rings, as for aromatic rings they possess extra stability by the resonance factor. For structure IV, it contains more number of lone pairs and it comes in conjugation and increase the electron density in N in =NH, the mechanism is as follows,

The electron density in N in =NH is more and hence this is the most basic molecule from the above given structures. The conjugate acid stabilizes with resonance with the $N{{H}_{2}}$ groups present

Then comes the structure I, the lone pair comes in conjugation and the mechanism is,

The stabilized form of the conjugate acid, and is stabilized with one $N{{H}_{2}}$group.

So the electron density of N in N=NH will be less than the structure IV
For structure II, the mechanism of the transfer of lone pair is,

Here the lone pair is in available in this case as it is not involved in the aromatic sextet

Then comes the last structure, Structure III, here lone pair is involved in the aromaticity so the lone pair is not available, hence this is the least structure.


Note: The valency of the structure should be satisfied while drawing the structure and the arrows should be put from the lone pair to the nearby atom. Arrows should be properly marked then only we could trace the electron charge density.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




