
The point on the stress-strain curve, on which point strain begins to increase even without increase in stress is called as
(A) Elastic point
(B) Yield point
(C) Breaking point
(D) None of these
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: Stress-strain curves display the deformation of a material in response to a tensile, compressive, or torsional load. Based on the material being tested, a stress-strain curve may indicate the properties of the material including its elastic region, plastic region, yield point, and ultimate tensile strength. The definitions of the given options have to be known to find the answer.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the definition of the given options.
Option (A) Elastic point:
The elastic point of a material is the highest stress that can be applied to it without causing permanent deformation. When a material is stressed to a point below its elastic limit, it will go back to its initial length when the stress is removed.
Option (B) Yield point:
The yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that denotes the limit of the elastic form and the beginning of deformation. Below this point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the stress is removed. At this point, the strain increases even if the strain does not increase.
Option (C) Breaking point:
The breaking point is the point where the strength of a material stops or breaks. The stress corresponding to this point is known as breaking strength. You can see the same in the below graph of stress and strain.
The stress and strain curve will look as shown below:
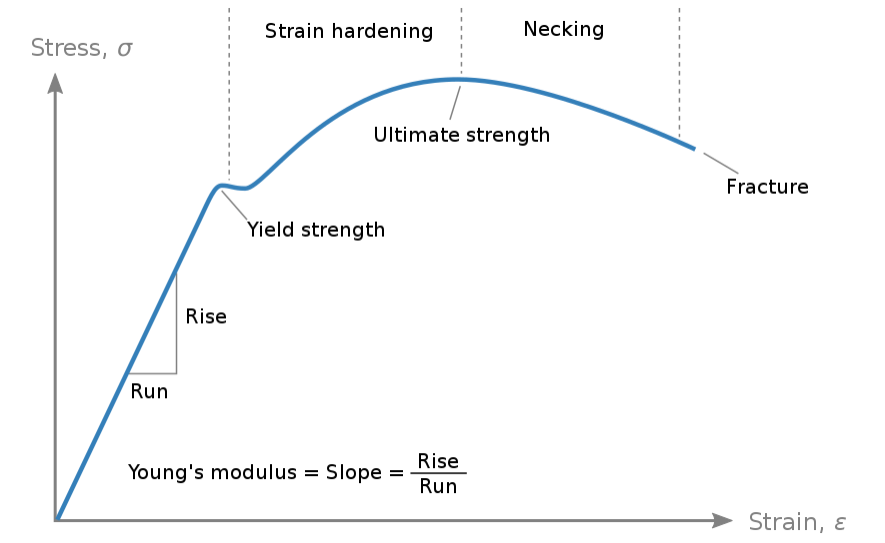
Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Note:
A stress-strain curve is used to state the relationship between the stress and strain of material. A stress-strain curve can be built from data gained in any mechanical test where the load is applied to a material and rapid measurements of stress and strain are made simultaneously. The stress-strain curve gives the design of a long list of important parameters needed for application design. A stress-strain graph provides many mechanical entities such as strength, toughness, elasticity, yield point, strain energy, resilience, and elongation when the load is applied.
Ultimate stress is the highest stress that a material can take and bear. The value of stress associated with the peak point on the stress-strain curve for mild steel is the ultimate stress.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the definition of the given options.
Option (A) Elastic point:
The elastic point of a material is the highest stress that can be applied to it without causing permanent deformation. When a material is stressed to a point below its elastic limit, it will go back to its initial length when the stress is removed.
Option (B) Yield point:
The yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that denotes the limit of the elastic form and the beginning of deformation. Below this point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the stress is removed. At this point, the strain increases even if the strain does not increase.
Option (C) Breaking point:
The breaking point is the point where the strength of a material stops or breaks. The stress corresponding to this point is known as breaking strength. You can see the same in the below graph of stress and strain.
The stress and strain curve will look as shown below:

Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Note:
A stress-strain curve is used to state the relationship between the stress and strain of material. A stress-strain curve can be built from data gained in any mechanical test where the load is applied to a material and rapid measurements of stress and strain are made simultaneously. The stress-strain curve gives the design of a long list of important parameters needed for application design. A stress-strain graph provides many mechanical entities such as strength, toughness, elasticity, yield point, strain energy, resilience, and elongation when the load is applied.
Ultimate stress is the highest stress that a material can take and bear. The value of stress associated with the peak point on the stress-strain curve for mild steel is the ultimate stress.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




