
The primary origin of magnetism lies in the
(A) Atomic current and intrinsic spin of electrons.
(B) Polar and nonpolar nature of molecules.
(C) Pauli Exclusion Principle.
(D) Electronegative nature of materials.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The magnetic behavior of solids can primarily be explained with the help of electrons of atoms. An electron exhibits both spin and orbital motion. The orbital motion is analogous to current in a loop of wire. Thus the combination of both orbital and spin motion is responsible for magnetism.
Complete step by step answer:
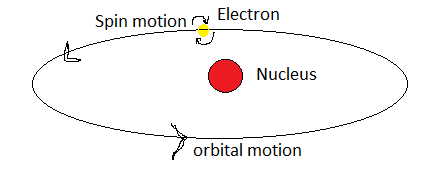
Fig: electron revolving around the nucleus exhibiting both spin and orbital motions.
The electrons exhibit orbital motion of an electron around the nucleus. This orbital motion is analogous to the current in a loop of wire and is measured in terms of Bohr magneton units. Thus, it is known as atomic current. The cause of its atomic current is the orbital motion of the revolving electrons since electrons have an electric charge in them.
There is also a spin magnetic moment associated with a revolving electron and it is due to the electron itself spinning on its own axis. The resultant magnetic moment in an electron is due to both orbital and spin motion.
The orbital motion accounts for the atomic current so the correct option for the origin of magnetism is (A) Atomic current and intrinsic spin of electrons.
Additional Information:
There are many types of magnetisms that are found to exist in nature. The nature of magnetism depends on the alignment of electrons inside the atom.
Note:
In this problem we must understand that the orbital motion of electrons relates to the atomic current and all electrons inside an atom have an intrinsic spin in them. These two reasons primarily account for the origin of magnetism in any material.
Complete step by step answer:

Fig: electron revolving around the nucleus exhibiting both spin and orbital motions.
The electrons exhibit orbital motion of an electron around the nucleus. This orbital motion is analogous to the current in a loop of wire and is measured in terms of Bohr magneton units. Thus, it is known as atomic current. The cause of its atomic current is the orbital motion of the revolving electrons since electrons have an electric charge in them.
There is also a spin magnetic moment associated with a revolving electron and it is due to the electron itself spinning on its own axis. The resultant magnetic moment in an electron is due to both orbital and spin motion.
The orbital motion accounts for the atomic current so the correct option for the origin of magnetism is (A) Atomic current and intrinsic spin of electrons.
Additional Information:
There are many types of magnetisms that are found to exist in nature. The nature of magnetism depends on the alignment of electrons inside the atom.
Note:
In this problem we must understand that the orbital motion of electrons relates to the atomic current and all electrons inside an atom have an intrinsic spin in them. These two reasons primarily account for the origin of magnetism in any material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




