
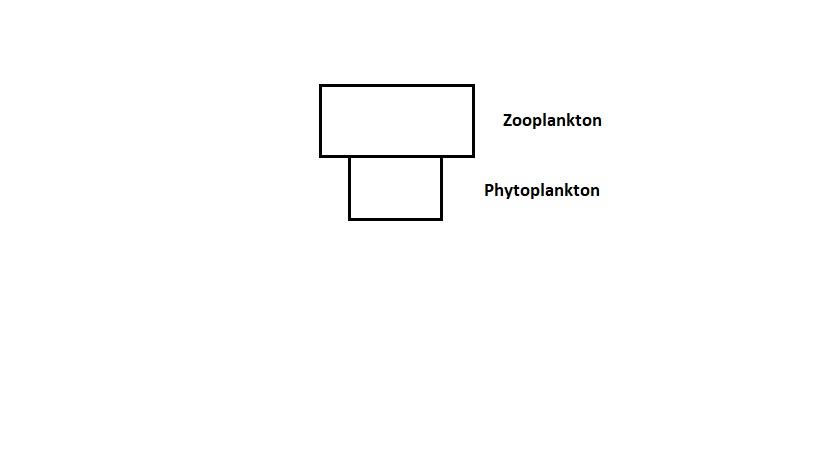
The pyramid shows the relative biomass of zooplankton and phytoplankton in a marine ecosystem. The biomass of the zooplankton is higher than that of the phytoplankton because
A. The zooplanktons convert energy more efficiently
B. The zooplanktons have a shorter life cycle than the phytoplankton
C. The phytoplankton are individually much smaller than the zooplanktons
D. The phytoplankton have an extremely high turnover rate

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Organisms that live in large water bodies such as the pelagic ocean zones, seas, and freshwater, and cannot swim against the water current are called planktons. They are a diverse group of organisms and include algae, protozoa, bacteria, archaea, floaters, and drifters. Large aquatic organisms and animals such as fishes, whales, and bivalves derive their food and energy from plankton species.
Complete answer:Though planktons are a diverse group of organisms they can be classified under zooplanktons and phytoplanktons. Heterotrophic types of plankton are called zooplankton. They range in size from microscopic organisms to large-sized species such as the jellyfish. These are ecologically important drifters and are found in large water bodies such as the oceans and freshwater bodies. Crustaceans, chordates, cnidarians, radiolarians, foraminiferans, dinoflagellates, and mollusks are some of the most crucial types of zooplanktons. Examples of zooplanktons include Krill, Crabs, Lobster, Jellyfish, Corals, Conger eel, segmented worm, copepod, etc. to name a few.

Another plankton microscopic organism is the phytoplankton. Phytoplanktons also inhabit salty and freshwater environments or water-bodies. Phytoplanktons mostly are single-celled organisms such as bacteria and some protists. Cyanobacteria, green algae, dinoflagellates, chalk- coated coccolithophores, and silica-encased diatoms are some of the most common varieties of phytoplankton. Phytoplankton has the ability to photosynthesize as they have chlorophyll. They capture the sunlight through photosynthesis and convert it into chemical energy. They have the ability to produce oxygen by the consumption of carbon dioxide. They can also generate extra additional energy by consuming other microorganisms. Carbon dioxide, sunlight, essential nutrients such as phosphate, silicate, calcium, and nitrate, are required for the growth of phytoplankton. Though some phytoplankton possesses the ability to synthesize nitrogen and can prosper and grow in regions with relatively low nitrate concentrations. Factors such as water depth, temperature, salinity, wind, predators feeding on them, can contribute an influence on the growth of phytoplankton. Phytoplanktons happen to be the primary source of food for the zooplankton.

The pyramid showcases the biomass of the zooplankton to be higher than the biomass of the phytoplankton. Biomass can be defined as the total weight or quantity of the organisms in a given region. The biomass of zooplanktons is higher than that of phytoplankton because zooplanktons have a low weight and are smaller in size. They furthermore live in the depths of water bodies away from sunlight and swim to the surface to feed on phytoplankton during the night time. Phytoplankton depends on photosynthesis for their food. Zooplanktons not only feed on phytoplankton but also feed on other zooplankton, bacteria, and other plant matters. Phytoplankton has a shorter life span when compared to zooplankton. Also, they reproduce and die quickly.
Note: Phytoplankton contributes to half of the world’s oxygen. They produce oxygen by consuming carbon dioxide. These microorganisms safeguard the Earth’s atmosphere. They also form a marine food chain basis.
Complete answer:Though planktons are a diverse group of organisms they can be classified under zooplanktons and phytoplanktons. Heterotrophic types of plankton are called zooplankton. They range in size from microscopic organisms to large-sized species such as the jellyfish. These are ecologically important drifters and are found in large water bodies such as the oceans and freshwater bodies. Crustaceans, chordates, cnidarians, radiolarians, foraminiferans, dinoflagellates, and mollusks are some of the most crucial types of zooplanktons. Examples of zooplanktons include Krill, Crabs, Lobster, Jellyfish, Corals, Conger eel, segmented worm, copepod, etc. to name a few.

Another plankton microscopic organism is the phytoplankton. Phytoplanktons also inhabit salty and freshwater environments or water-bodies. Phytoplanktons mostly are single-celled organisms such as bacteria and some protists. Cyanobacteria, green algae, dinoflagellates, chalk- coated coccolithophores, and silica-encased diatoms are some of the most common varieties of phytoplankton. Phytoplankton has the ability to photosynthesize as they have chlorophyll. They capture the sunlight through photosynthesis and convert it into chemical energy. They have the ability to produce oxygen by the consumption of carbon dioxide. They can also generate extra additional energy by consuming other microorganisms. Carbon dioxide, sunlight, essential nutrients such as phosphate, silicate, calcium, and nitrate, are required for the growth of phytoplankton. Though some phytoplankton possesses the ability to synthesize nitrogen and can prosper and grow in regions with relatively low nitrate concentrations. Factors such as water depth, temperature, salinity, wind, predators feeding on them, can contribute an influence on the growth of phytoplankton. Phytoplanktons happen to be the primary source of food for the zooplankton.

The pyramid showcases the biomass of the zooplankton to be higher than the biomass of the phytoplankton. Biomass can be defined as the total weight or quantity of the organisms in a given region. The biomass of zooplanktons is higher than that of phytoplankton because zooplanktons have a low weight and are smaller in size. They furthermore live in the depths of water bodies away from sunlight and swim to the surface to feed on phytoplankton during the night time. Phytoplankton depends on photosynthesis for their food. Zooplanktons not only feed on phytoplankton but also feed on other zooplankton, bacteria, and other plant matters. Phytoplankton has a shorter life span when compared to zooplankton. Also, they reproduce and die quickly.
Note: Phytoplankton contributes to half of the world’s oxygen. They produce oxygen by consuming carbon dioxide. These microorganisms safeguard the Earth’s atmosphere. They also form a marine food chain basis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




