
The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation.
(A) True
(B) False
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: The lungs is the organ of the respiration. The respiration takes place in the two stages as the inhalation and the exhalation. The inhalation deals with the breathing in of the oxygen and the exhalation deals with the leaving out of the carbon dioxide as the metabolic waste product.
Complete Answer:
The thoracic pit, or chest cavity maintains the negative pressure which helps in keeping the aviation routes of the lungs open.
During the cycle of inward breath, the lung volume grows because of the constriction of the stomach and intercostal muscles (the muscles that are associated with the rib confine), consequently extending the thoracic cavity.
During this cycle, the diaphragm extends out and away from the lungs. The lungs are flexible; in this way, when air fills the lungs, the versatile force inside the tissues of the lung applies pressure back toward the inside of the lungs. These outward and internal powers contend to swell and empty the lung with each breath. Hence the chest cavity increases.
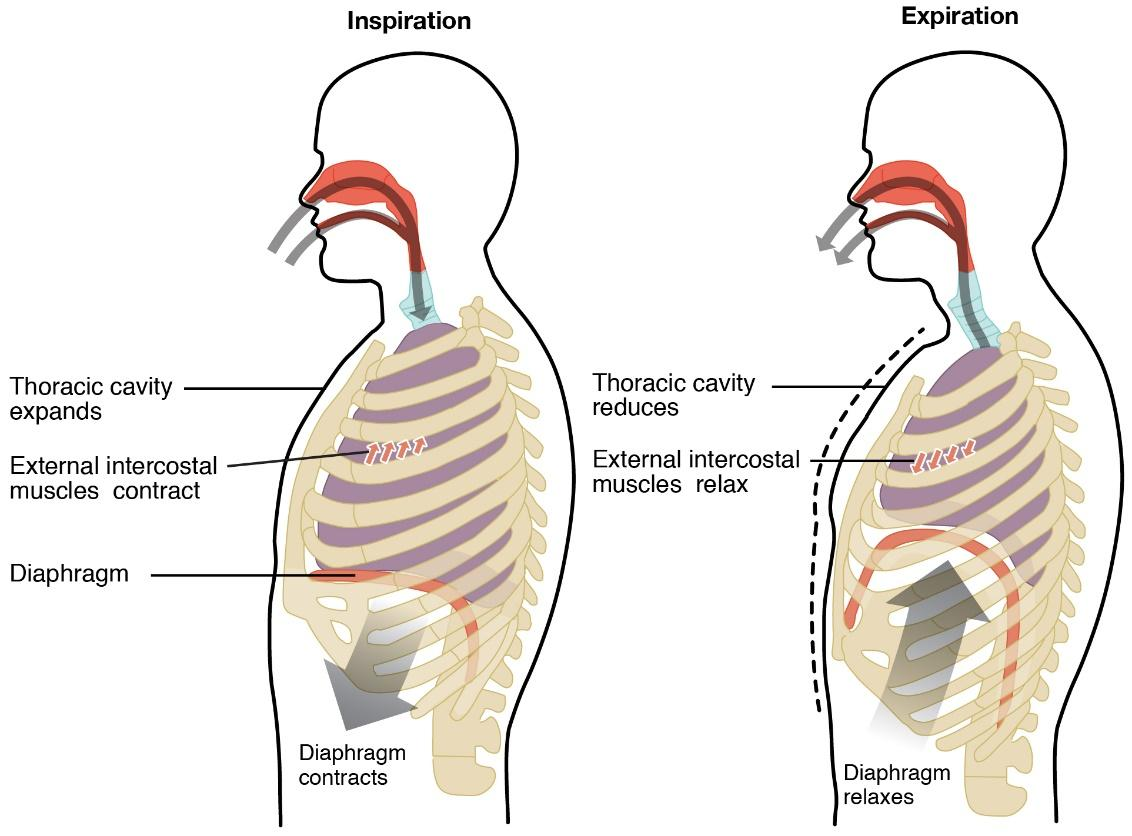
Upon exhalation, the intercostal muscles unwind, restoring the diaphragm to its unique position. During exhalation, the stomach likewise unwinds, moving higher into the thoracic cavity. Air surges out of the lungs because of the weight slope between the thoracic pit and the external environment. This causes the decrease in the area of the chest cavity.
Thus, the option (A) is correct.
Note: During the breathing in of the air, the ribs move upward and outward but during the breathing out the rib cage moves downward and the inward. The exchange of the gases takes place in the balloon like structures in the lungs called alveoli surrounded by the blood capillaries.
Complete Answer:
The thoracic pit, or chest cavity maintains the negative pressure which helps in keeping the aviation routes of the lungs open.
During the cycle of inward breath, the lung volume grows because of the constriction of the stomach and intercostal muscles (the muscles that are associated with the rib confine), consequently extending the thoracic cavity.
During this cycle, the diaphragm extends out and away from the lungs. The lungs are flexible; in this way, when air fills the lungs, the versatile force inside the tissues of the lung applies pressure back toward the inside of the lungs. These outward and internal powers contend to swell and empty the lung with each breath. Hence the chest cavity increases.

Upon exhalation, the intercostal muscles unwind, restoring the diaphragm to its unique position. During exhalation, the stomach likewise unwinds, moving higher into the thoracic cavity. Air surges out of the lungs because of the weight slope between the thoracic pit and the external environment. This causes the decrease in the area of the chest cavity.
Thus, the option (A) is correct.
Note: During the breathing in of the air, the ribs move upward and outward but during the breathing out the rib cage moves downward and the inward. The exchange of the gases takes place in the balloon like structures in the lungs called alveoli surrounded by the blood capillaries.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




