
The structure of a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose is given below. Identify anomeric carbon atoms in monosaccharide units.
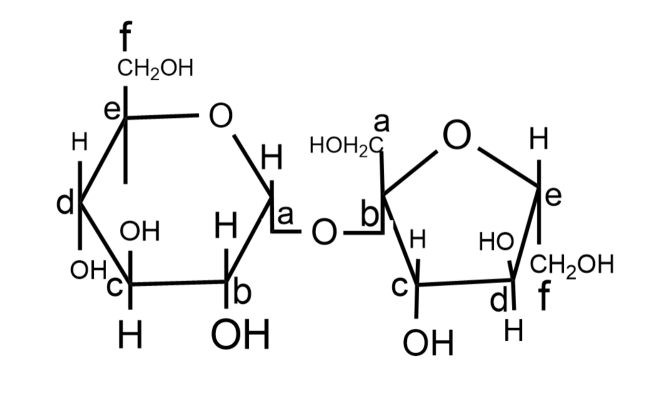
(A) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘a’ carbon of fructose
(B) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘e’ carbon of fructose
(C) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘b’ carbon of fructose
(D) ‘f’ carbon of glucose and ‘f’ carbon of fructose
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The carbon derived the carbonyl carbon compound (maybe a ketone or aldehyde functional group) of the open-chain form of the carbohydrate molecule is known as an anomeric carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
-The cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, differing from each other in the configuration of ${{C}_{1}}$ carbon if they are aldoses or in the configuration at ${{C}_{2}}$carbon if they are ketoses are known as anomers.
-An epimer at the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon in a cyclic sugar is an anomer, and the atom is called anomeric carbon.
-The process of conversion of one anomer to another anomer is known as anomerization.
-According to the configurational relationship between the anomic centre and the anomeric reference atom between the two anomers, they are denoted as alpha or beta anomers.
-If the exocyclic oxygen atom in the cyclic Fischer projection at the anomeric centre is cis to the exocyclic oxygen attached to the anomeric reference atom (in the OH group), then the anomer is referred as alpha $(\alpha )$ anomer.
- If the exocyclic oxygen atom in the cyclic Fischer projection at the anomeric centre is trans to the exocyclic oxygen attached to the anomeric reference atom (in the OH group), the anomeric is referred as beta $(\beta )$ anomer.
-In this molecule, the ‘a’ carbon atom of glucose and ‘b’ carbon atom of the fructose molecule is adjacent to oxygen atoms in the cyclic structures, hence they are anomeric carbons.
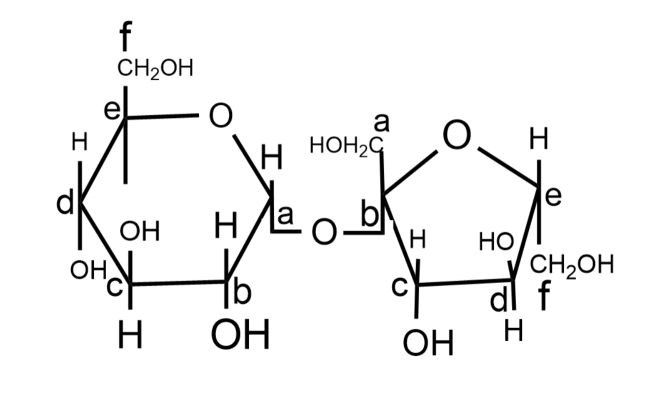
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Two different anomers will differ from each other in their physical properties, melting points as well as in specific rotations. Since anomers show the difference in their physical properties and thus have different stabilizing and destabilizing effects from each other. The anomer that has an electron-withdrawing group (typically oxygen or a nitrogen atom) in axial orientation on the ring is said to exhibit an anomeric effect. Hydrogen bonds if present between the anomeric groups or on the other groups within the ring leads to the stabilization of the anomer. Dipolar repulsions between the anomeric group or in the other groups present on the ring cause the destabilization of the anomer.
Complete step by step answer:
-The cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, differing from each other in the configuration of ${{C}_{1}}$ carbon if they are aldoses or in the configuration at ${{C}_{2}}$carbon if they are ketoses are known as anomers.
-An epimer at the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon in a cyclic sugar is an anomer, and the atom is called anomeric carbon.
-The process of conversion of one anomer to another anomer is known as anomerization.
-According to the configurational relationship between the anomic centre and the anomeric reference atom between the two anomers, they are denoted as alpha or beta anomers.
-If the exocyclic oxygen atom in the cyclic Fischer projection at the anomeric centre is cis to the exocyclic oxygen attached to the anomeric reference atom (in the OH group), then the anomer is referred as alpha $(\alpha )$ anomer.
- If the exocyclic oxygen atom in the cyclic Fischer projection at the anomeric centre is trans to the exocyclic oxygen attached to the anomeric reference atom (in the OH group), the anomeric is referred as beta $(\beta )$ anomer.
-In this molecule, the ‘a’ carbon atom of glucose and ‘b’ carbon atom of the fructose molecule is adjacent to oxygen atoms in the cyclic structures, hence they are anomeric carbons.

So, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Two different anomers will differ from each other in their physical properties, melting points as well as in specific rotations. Since anomers show the difference in their physical properties and thus have different stabilizing and destabilizing effects from each other. The anomer that has an electron-withdrawing group (typically oxygen or a nitrogen atom) in axial orientation on the ring is said to exhibit an anomeric effect. Hydrogen bonds if present between the anomeric groups or on the other groups within the ring leads to the stabilization of the anomer. Dipolar repulsions between the anomeric group or in the other groups present on the ring cause the destabilization of the anomer.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




