
The total number of conformations of ethane is:
A.Infinite
B.Two
C.Three
D.Four
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Different spatial arrangements of atoms or groups that can be converted into one another by the rotation around single bonds are called conformations. They are also known as conformational isomers. This phenomenon is termed as ‘conformational isomerism’.
Complete step by step answer:
In ethane, two carbon atoms are bonded together by a single bond and each carbon is bonded to three hydrogen atoms. If one of the carbon atoms of ethane is allowed to undergo rotation around the central bond while the other is kept fixed, an infinite number of conformations depending upon the angle of rotation will be obtained.
All of these conformations differ in the relative spatial arrangements of the hydrogen atoms of one carbon with respect to the hydrogen atoms of the other carbon atom. But, in all these conformations, the various bond angles and bond lengths remain the same.
Of the infinite number of possible conformations of ethane, there are two extreme conformations. They are the eclipsed and the staggered conformations.
In the eclipsed conformation, the tetrahedrally arranged hydrogen atoms of both the carbon atoms are facing each other and the bond pairs of carbon – hydrogen bonds of the two carbon atoms are very close to each other.
In the staggered conformation, the tetrahedrally arranged hydrogen atoms of both the carbon atoms are placed wide apart and the bond pairs of carbon – hydrogen bonds of the two carbon atoms are far away from each other.
The Sawhorse representation of conformation of ethane is shown below.
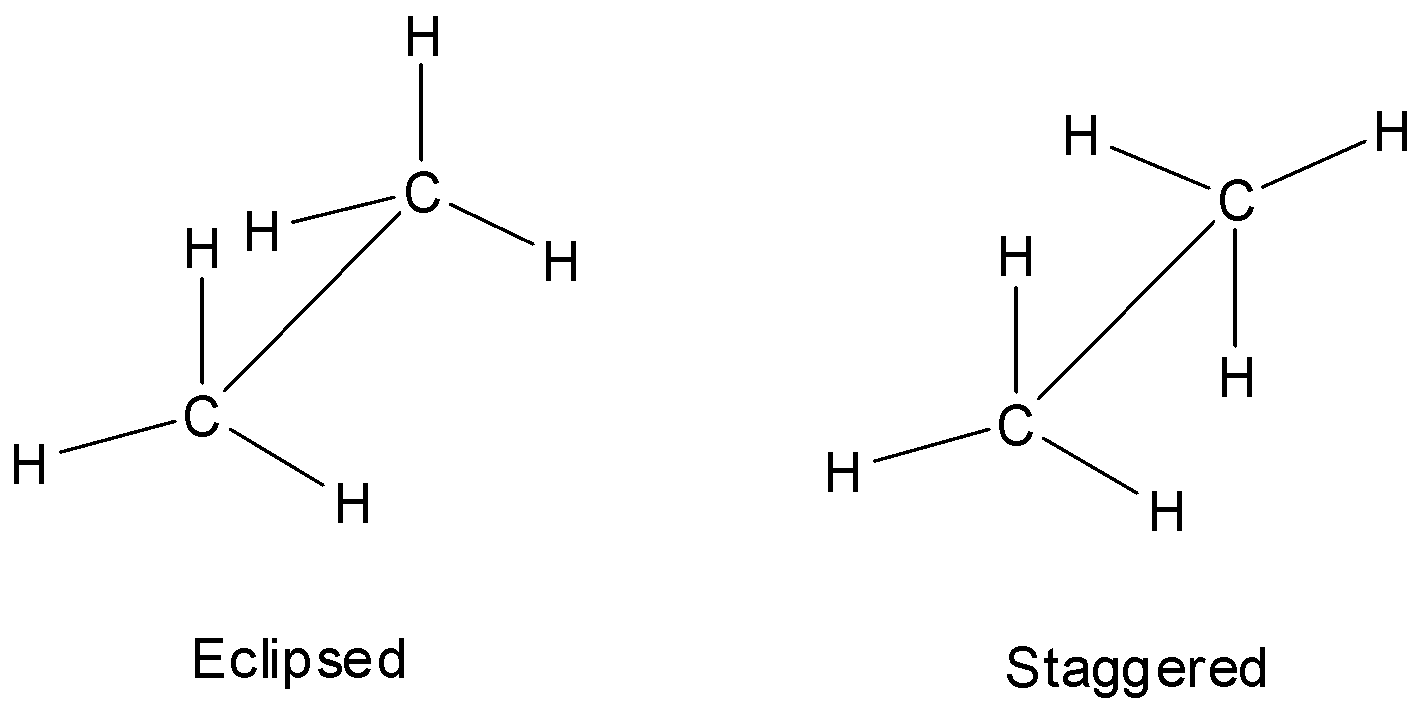
Thus, there are an infinite number of conformations possible and so the correct answer is A.
Note:
Rotation around the single bond is not entirely free and so the potential energy of the molecule changes somewhat with the rotation around the carbon-carbon single bond.
The potential energy of the staggered form, in which the two carbon atoms are far away from each other, is minimum.
It increases with rotation and becomes maximum for eclipsed conformation in which the two carbon atoms are very close to each other.
Complete step by step answer:
In ethane, two carbon atoms are bonded together by a single bond and each carbon is bonded to three hydrogen atoms. If one of the carbon atoms of ethane is allowed to undergo rotation around the central bond while the other is kept fixed, an infinite number of conformations depending upon the angle of rotation will be obtained.
All of these conformations differ in the relative spatial arrangements of the hydrogen atoms of one carbon with respect to the hydrogen atoms of the other carbon atom. But, in all these conformations, the various bond angles and bond lengths remain the same.
Of the infinite number of possible conformations of ethane, there are two extreme conformations. They are the eclipsed and the staggered conformations.
In the eclipsed conformation, the tetrahedrally arranged hydrogen atoms of both the carbon atoms are facing each other and the bond pairs of carbon – hydrogen bonds of the two carbon atoms are very close to each other.
In the staggered conformation, the tetrahedrally arranged hydrogen atoms of both the carbon atoms are placed wide apart and the bond pairs of carbon – hydrogen bonds of the two carbon atoms are far away from each other.
The Sawhorse representation of conformation of ethane is shown below.

Thus, there are an infinite number of conformations possible and so the correct answer is A.
Note:
Rotation around the single bond is not entirely free and so the potential energy of the molecule changes somewhat with the rotation around the carbon-carbon single bond.
The potential energy of the staggered form, in which the two carbon atoms are far away from each other, is minimum.
It increases with rotation and becomes maximum for eclipsed conformation in which the two carbon atoms are very close to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




