
Three Centre two electron bond is present in:
(A).$N{{H}_{3}}$
(B).${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$
(C).$BC{{l}_{3}}$
(D).$AlC{{l}_{3}}$
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: In a three center two electron bond the two electrons are shared by three separate nuclei. .Elements that are able to form electron deficient bonds are involved.In banana bond, the probability of distribution of this bond is in shape of banana.
Complete answer:
- A three-center two-electron ($3c–2e$) bond is an electron-deficient chemical bond where three atoms share two electrons.
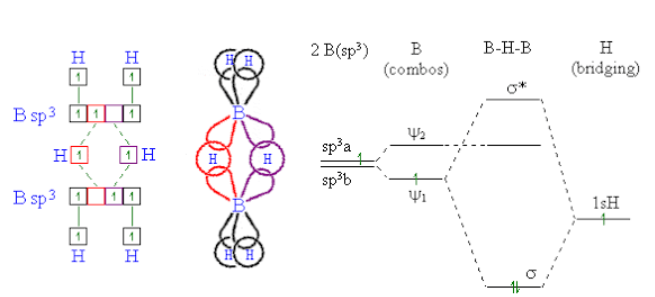
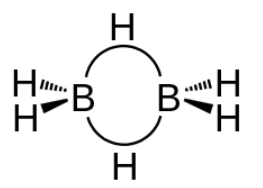
-As boron atom has an empty p-orbital so the monomer $B{{H}_{3}}$ is unstable.when a boron atom shares electrons with a $B−H$ bond on another boron atom, $A B−H−B$ 3-center-2-electron bond is formed . across three internuclear spaces, the two electrons (corresponding to one bond) in a $B−H−B$ bonding molecular orbital are spread out .In diborane (${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ ), two $H$ atoms bridge the two $B$ atoms, leaving two additional H atoms in ordinary $B−H$ bonds on each .There are two such $3c-2e$ bonds: As each boron atom participates in a total of four bonds and there is filling of all bonding molecular orbitals and two of the four bonds are 3-centre $B−H−B$ bonds, so the molecule is stable.
Option B is the correct answer.
Note:
In trimethylaluminum, this Three Centre two electron bonding pattern is seen, which leads to formation of a dimer. $A{{l}_{2}}{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}$ involving bridges with the carbon atoms of two of the methyl groups . This type of bond also occurs in carbon compounds, which is referred to as hyperconjugation.
Complete answer:
- A three-center two-electron ($3c–2e$) bond is an electron-deficient chemical bond where three atoms share two electrons.

-As boron atom has an empty p-orbital so the monomer $B{{H}_{3}}$ is unstable.when a boron atom shares electrons with a $B−H$ bond on another boron atom, $A B−H−B$ 3-center-2-electron bond is formed . across three internuclear spaces, the two electrons (corresponding to one bond) in a $B−H−B$ bonding molecular orbital are spread out .In diborane (${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ ), two $H$ atoms bridge the two $B$ atoms, leaving two additional H atoms in ordinary $B−H$ bonds on each .There are two such $3c-2e$ bonds: As each boron atom participates in a total of four bonds and there is filling of all bonding molecular orbitals and two of the four bonds are 3-centre $B−H−B$ bonds, so the molecule is stable.
Option B is the correct answer.

Note:
In trimethylaluminum, this Three Centre two electron bonding pattern is seen, which leads to formation of a dimer. $A{{l}_{2}}{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}$ involving bridges with the carbon atoms of two of the methyl groups . This type of bond also occurs in carbon compounds, which is referred to as hyperconjugation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




