
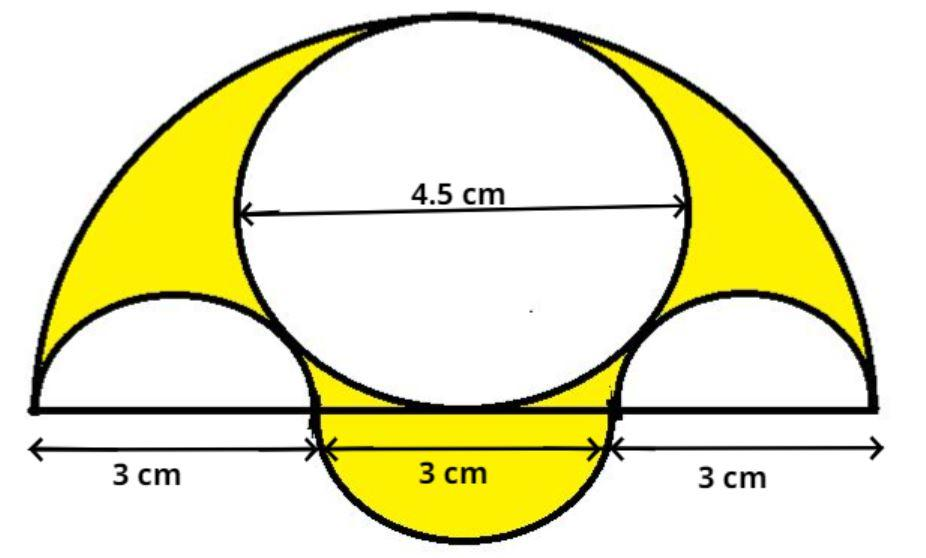
Three semicircles each of diameter 3 cm, a circle of diameter 4.5 cm and semicircle of radius 4.5 cm are drawn in the given figure. Find the area of the shaded region.

Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint – In this area based question we have to find the area of the shaded region. It is clear that the shaded region can easily be obtained by reducing the two smaller inside semicircles and one smaller circle from the larger semicircle and adding this to the area of the outer smaller semicircle. Use this concept along with a basic area formula for the area of semicircles to get the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know that the area (A) of the circle is $\pi {r^2}$ (where r is the radius of the circle).
Now as we know that diameter (d) of a circle is twice the radius.
It is given that the radius of big semicircle is 4.5 cm
So, the diameter of big semicircle is $\left( {2 \times 4.5} \right) = 9$ cm
$\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow d = 2r \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{d}{2} \\
\end{gathered} $
So substitute this value in the formula of area of circle we have
$ \Rightarrow A = \pi {\left( {\dfrac{d}{2}} \right)^2} = \pi \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{4}$
Now the area of the semi-circle (${A_1}$) is half the area of the circle.
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{A}{2} = \dfrac{{\pi \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{4}}}{2} = \pi \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{8}$ Sq. unit.
Now the diameter (${D_1}$) of shaded big semicircle is 9 cm and the diameter (${D_2}$) and (${D_3}$) of smaller unshaded semicircle as well as shaded circle is 3 cm respectively (see figure) and the diameter (${D_4}$) of the smaller unshaded circle is 4.5 cm.
Now in the figure the area (${A_2}$) of shaded region is = Area of big semi-circle having diameter 9 cm + Area of smaller semi-circle having diameter 3 cm – twice multiplied by area of semi-circle having diameter 3 cm – Area of smaller circle having diameter 4.5 cm.
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {{D_1}} \right)}^2}}}{8} + \pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {{D_2}} \right)}^2}}}{8} - 2\pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {{D_3}} \right)}^2}}}{8} - \pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {{D_4}} \right)}^2}}}{4}$
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \pi \dfrac{{{9^2}}}{8} + \pi \dfrac{{{3^2}}}{8} - 2\pi \dfrac{{{3^2}}}{8} - \pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {4.5} \right)}^2}}}{4}$
\[ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \dfrac{\pi }{8}\left[ {{9^2} + {3^2} - 2{{\left( 3 \right)}^2} - 2{{\left( {4.5} \right)}^2}} \right] = \dfrac{\pi }{8}\left( {31.5} \right) = \dfrac{1}{8}\left( {\dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right)\left( {31.5} \right) = \dfrac{{693}}{{56}} = \dfrac{{99}}{8}\] Sq. cm.
As $\left[ {\pi = \dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right]$
Note – Whenever we face such types of problems the key concept is to have the good understanding of the diagrammatic representation of the figure in order to figure out the required shaded region. The good gist of the basic area formula for curves like circle always helps to get on the right track to reach the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know that the area (A) of the circle is $\pi {r^2}$ (where r is the radius of the circle).
Now as we know that diameter (d) of a circle is twice the radius.
It is given that the radius of big semicircle is 4.5 cm
So, the diameter of big semicircle is $\left( {2 \times 4.5} \right) = 9$ cm
$\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow d = 2r \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{d}{2} \\
\end{gathered} $
So substitute this value in the formula of area of circle we have
$ \Rightarrow A = \pi {\left( {\dfrac{d}{2}} \right)^2} = \pi \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{4}$
Now the area of the semi-circle (${A_1}$) is half the area of the circle.
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{A}{2} = \dfrac{{\pi \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{4}}}{2} = \pi \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{8}$ Sq. unit.
Now the diameter (${D_1}$) of shaded big semicircle is 9 cm and the diameter (${D_2}$) and (${D_3}$) of smaller unshaded semicircle as well as shaded circle is 3 cm respectively (see figure) and the diameter (${D_4}$) of the smaller unshaded circle is 4.5 cm.
Now in the figure the area (${A_2}$) of shaded region is = Area of big semi-circle having diameter 9 cm + Area of smaller semi-circle having diameter 3 cm – twice multiplied by area of semi-circle having diameter 3 cm – Area of smaller circle having diameter 4.5 cm.
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {{D_1}} \right)}^2}}}{8} + \pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {{D_2}} \right)}^2}}}{8} - 2\pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {{D_3}} \right)}^2}}}{8} - \pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {{D_4}} \right)}^2}}}{4}$
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \pi \dfrac{{{9^2}}}{8} + \pi \dfrac{{{3^2}}}{8} - 2\pi \dfrac{{{3^2}}}{8} - \pi \dfrac{{{{\left( {4.5} \right)}^2}}}{4}$
\[ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \dfrac{\pi }{8}\left[ {{9^2} + {3^2} - 2{{\left( 3 \right)}^2} - 2{{\left( {4.5} \right)}^2}} \right] = \dfrac{\pi }{8}\left( {31.5} \right) = \dfrac{1}{8}\left( {\dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right)\left( {31.5} \right) = \dfrac{{693}}{{56}} = \dfrac{{99}}{8}\] Sq. cm.
As $\left[ {\pi = \dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right]$
Note – Whenever we face such types of problems the key concept is to have the good understanding of the diagrammatic representation of the figure in order to figure out the required shaded region. The good gist of the basic area formula for curves like circle always helps to get on the right track to reach the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




