
Three spheres of the first layer and three spheres of the second layer enclose a site at the centre in a close packing arrangement, this site is called?
A. Interstitial void
B. tetrahedral void
C. octahedral void
D. cubic void
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The type of void is decided on the basis of the number of spheres forming that void. The tetrahedral void is formed by four spheres. The octahedral void is formed by six spheres. The cubic void is formed by eight spheres.
Complete answer:
Interstitial void simply means the space between the spheres. It does not specify any regular arrangement of spheres so, option (A) is incorrect.
When two similar two-dimensional close-packed layers are placed as such, the spheres of the second layer get positioned above the void of the first layer, two types of voids form.
One type of void, in which a sphere of second layer is placed just above the void of the first layer and the second type of the void, in which three spheres of the second layer are placed just above the three spheres of the first layer,
The arrangement of spheres in all type of voids is shown follows:
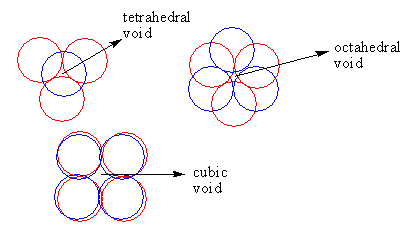
So, when three spheres of the first layer and one sphere of the second layer enclose a site at the centre in a close packing arrangement, this site is called tetrahedral void so option (B) is incorrect.
So, when three spheres of the first layer and three-sphere of the second layer enclose a site at the centre in a close packing arrangement, this site is called an octahedral void so option (C) is correct.
When four spheres of the first layer and four spheres of the second layer enclose a site at the centre in a close packing arrangement, this site is called a cubic void. So, option (D) is incorrect.
Therefore the correct option is (C).
Note: On joining the centres of the four spheres a tetrahedral forms so the void is known as tetrahedral void. On joining the centres of these six spheres octahedron forms so, the void is known as octahedral void and on joining the centres of the eight spheres a cube forms so, the void is known as cubic void.
Complete answer:
Interstitial void simply means the space between the spheres. It does not specify any regular arrangement of spheres so, option (A) is incorrect.
When two similar two-dimensional close-packed layers are placed as such, the spheres of the second layer get positioned above the void of the first layer, two types of voids form.
One type of void, in which a sphere of second layer is placed just above the void of the first layer and the second type of the void, in which three spheres of the second layer are placed just above the three spheres of the first layer,
The arrangement of spheres in all type of voids is shown follows:

So, when three spheres of the first layer and one sphere of the second layer enclose a site at the centre in a close packing arrangement, this site is called tetrahedral void so option (B) is incorrect.
So, when three spheres of the first layer and three-sphere of the second layer enclose a site at the centre in a close packing arrangement, this site is called an octahedral void so option (C) is correct.
When four spheres of the first layer and four spheres of the second layer enclose a site at the centre in a close packing arrangement, this site is called a cubic void. So, option (D) is incorrect.
Therefore the correct option is (C).
Note: On joining the centres of the four spheres a tetrahedral forms so the void is known as tetrahedral void. On joining the centres of these six spheres octahedron forms so, the void is known as octahedral void and on joining the centres of the eight spheres a cube forms so, the void is known as cubic void.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




