
Two charges of $ + 25 \times {10^{ - 9}}$ coulombs and $ - 25 \times {10^{ - 9}}$ coulomb are placed 6m apart. Find the electric field intensity ratio at points 4m from the centre of the electric dipole.
(i) On axial line
(ii) On equatorial line
(A) $\dfrac{{1000}}{{49}}$
(B) $\dfrac{{49}}{{1000}}$
(C) $\dfrac{{500}}{{49}}$
(D) $\dfrac{{49}}{{500}}$
Answer
526.7k+ views
Hint: To find the electric field intensity an axial line or equatorial line due to +q and –q charge we use the point charge formula i.e., $E = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$ and after then acceleration to the direction of electric field we can find the complete solution for axial & equatorial.
Complete step by step solution:
We have to calculate the electric field intensity on the axial line and on the equatorial line.
Case-I
For axial line
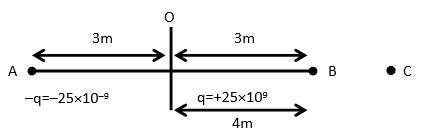
The electric field intensity due to point charge $ - q = \dfrac{{ - kq}}{{{r^2}}}$
For –q charge r is the distance between A & C i.e., $ = 4 + 3 = 7m$
${E_q} = \dfrac{{ - 9 \times {{10}^9} \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{7 \times 7}} = \dfrac{{ - 25 \times 9}}{{49}}$
Now, the electric field intensity due to point charge +q is $ = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$
Here r is distance between B & C i.e., $4 - 3 = 1m$
${E_{ + q}} = \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{1 \times 1}} = 25 \times 9$
Hence the electric field intensity at point C i.e., on axial line is ${E_a} = {E_{ + q}} + {E_{ - q}}$
$ = 25 \times 9 - \dfrac{{25 \times 9}}{{49}} = 25 \times 9\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{{49}}} \right)$
${E_a} = \left( {\dfrac{{48}}{{49}}} \right)(25 \times 9)$
${E_a} = \dfrac{{10,800}}{{49}}$ ……(i)
Case-II
If point C is situated on equatorial line then electric field intensity can be calculated as

Here magnitude of electric field intensity for +q & -q are same i.e., $E = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$
Here r is distance between +q and –q to point C i.e., AC & BC which are equal
So, $AC = BC = r = \sqrt {{{(3)}^2} + {{(4)}^2}} $
$r = 5m$
Then, ${E_{ + q}} = {E_{ - q}} = E = \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{5 \times 5}}$
$E = \dfrac{{25 \times 9}}{{25}} = 9\dfrac{N}{C}$
Now, the total electric field intensity at point C i.e., on equatorial line according to diagram is given as –
${E_{eq}} = {E_{ + q}}\cos \theta + {E_{ - q}}\cos \theta $
$ = 2E\cos \theta $
From diagram $\cos \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}$
${E_{eq}} = 2 \times 9 \times \dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{{54}}{5}$ …..(2)
From equation (1) & (2) we can easily calculate the ratio of ${E_a}$ & ${E_{eq}}$
So, $\dfrac{{(1)}}{{(2)}}$
$\dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{{E_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{10,800}}{{49}} \times \dfrac{5}{{54}}$
$\dfrac{{54,000}}{{49 \times 54}}$
So, ratio of ${E_a}$ & ${E_{eq}}$
${E_a}:{E_{eq}} = 1000:49$
So, the correct answer is (A) $\dfrac{{1000}}{{49}}$
Note: In this type of question basically we use electric field intensity due to point charge separately and then add them. But in many cases of dipole numericals $a < < < r$ i.e., distance from the centre of dipole is very large comparatively the distance between the 2 charges. So, in this case we can directly use 2 formulas which are given as
${E_a} = \dfrac{{2kp}}{{{r^3}}}$
${E_{eq}} = \dfrac{{kr}}{{{r^3}}}$
Where p is dipole moment of electric dipole i.e., $p = qa$
Complete step by step solution:
We have to calculate the electric field intensity on the axial line and on the equatorial line.
Case-I
For axial line

The electric field intensity due to point charge $ - q = \dfrac{{ - kq}}{{{r^2}}}$
For –q charge r is the distance between A & C i.e., $ = 4 + 3 = 7m$
${E_q} = \dfrac{{ - 9 \times {{10}^9} \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{7 \times 7}} = \dfrac{{ - 25 \times 9}}{{49}}$
Now, the electric field intensity due to point charge +q is $ = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$
Here r is distance between B & C i.e., $4 - 3 = 1m$
${E_{ + q}} = \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{1 \times 1}} = 25 \times 9$
Hence the electric field intensity at point C i.e., on axial line is ${E_a} = {E_{ + q}} + {E_{ - q}}$
$ = 25 \times 9 - \dfrac{{25 \times 9}}{{49}} = 25 \times 9\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{{49}}} \right)$
${E_a} = \left( {\dfrac{{48}}{{49}}} \right)(25 \times 9)$
${E_a} = \dfrac{{10,800}}{{49}}$ ……(i)
Case-II
If point C is situated on equatorial line then electric field intensity can be calculated as

Here magnitude of electric field intensity for +q & -q are same i.e., $E = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$
Here r is distance between +q and –q to point C i.e., AC & BC which are equal
So, $AC = BC = r = \sqrt {{{(3)}^2} + {{(4)}^2}} $
$r = 5m$
Then, ${E_{ + q}} = {E_{ - q}} = E = \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{5 \times 5}}$
$E = \dfrac{{25 \times 9}}{{25}} = 9\dfrac{N}{C}$
Now, the total electric field intensity at point C i.e., on equatorial line according to diagram is given as –
${E_{eq}} = {E_{ + q}}\cos \theta + {E_{ - q}}\cos \theta $
$ = 2E\cos \theta $
From diagram $\cos \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}$
${E_{eq}} = 2 \times 9 \times \dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{{54}}{5}$ …..(2)
From equation (1) & (2) we can easily calculate the ratio of ${E_a}$ & ${E_{eq}}$
So, $\dfrac{{(1)}}{{(2)}}$
$\dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{{E_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{10,800}}{{49}} \times \dfrac{5}{{54}}$
$\dfrac{{54,000}}{{49 \times 54}}$
So, ratio of ${E_a}$ & ${E_{eq}}$
${E_a}:{E_{eq}} = 1000:49$
So, the correct answer is (A) $\dfrac{{1000}}{{49}}$
Note: In this type of question basically we use electric field intensity due to point charge separately and then add them. But in many cases of dipole numericals $a < < < r$ i.e., distance from the centre of dipole is very large comparatively the distance between the 2 charges. So, in this case we can directly use 2 formulas which are given as
${E_a} = \dfrac{{2kp}}{{{r^3}}}$
${E_{eq}} = \dfrac{{kr}}{{{r^3}}}$
Where p is dipole moment of electric dipole i.e., $p = qa$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




