
Two circular coils $ X $ and $ Y $ have equal number of turns and carry equal currents in the same sense and subtend the same solid angle at point $ \left( O \right) $ . If the smaller coil $ X $ is midway between $ O $ and $ Y $ , then if we represent magnetic induction due to bigger coil $ Y $ at $ O $ as $ {B_Y} $ , and that due to smaller coil $ X $ at $ O $ as $ {B_X} $ , then
A. $ \dfrac{{{B_Y}}}{{{B_X}}} = 1 $
B. $ \dfrac{{{B_Y}}}{{{B_X}}} = 2 $
C. $ \dfrac{{{B_Y}}}{{{B_X}}} = \dfrac{1}{2} $
D. $ \dfrac{{{B_Y}}}{{{B_X}}} = \dfrac{1}{4} $

Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are given two coils carrying the same current and having the same number of turns. As they subtend the same solid angle at point $ O $ and the smaller coil is midway between the larger coil and point $ O $ . By using geometry we can say, Radius of the larger coil is twice the radius of smaller coil and we can find out the magnetic field due to coil at a distance $ x $ using the formula $ B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{R^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Magnetic field due at the axis of a circular current-carrying coil, $ B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{R^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Where $ B $ is the magnetic field at the axis
$ R $ is the radius of the coil
$ I $ is the current carried by the coil
$ N $ is the number of turns in the coil
$ x $ is the distance from the center of the coil.
Complete step by step answer:
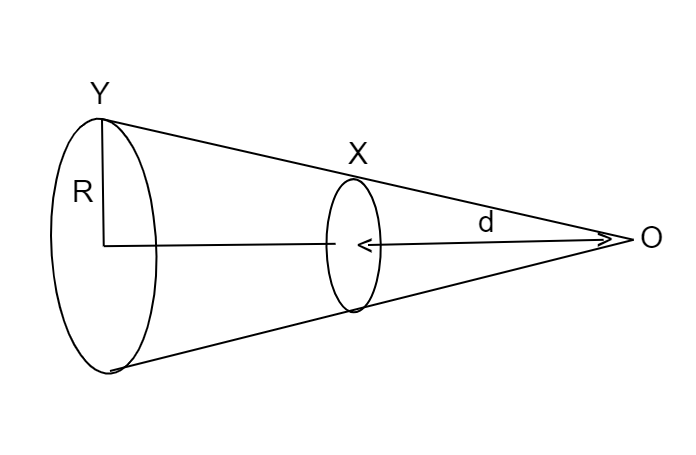
We are given two coils $ X $ and $ Y $ having an equal number of turns $ N $ and carrying an equal amount of current $ I $
Distance of centre of coil $ X $ from the point $ O $ is $ d $
As coil $ X $ is midway between $ Y $ and $ O $ ,
Distance of centre of coil $ Y $ and $ O $ is $ 2d $
Let radius of coil $ Y $ be $ R $ and radius of coil $ X $ be $ r $
Both the coils subtend same angle at point $ O $ thus,
$ \dfrac{r}{d} = \dfrac{R}{{2d}} $
$ \Rightarrow R = 2r $
Now, the magnetic field at point $ O $ due to bigger coil $ Y $ , $ {B_Y} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{R^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{R^2} + {{\left( {2d} \right)}^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Substituting $ R = 2r $ we get,
$ \Rightarrow {B_Y} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI\left( {4{r^2}} \right)}}{{2{{\left( {4{r^2} + 4{d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {B_Y} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI\left( {4{r^2}} \right)}}{{2 \times 8{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {B_Y} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{r^2}}}{{4{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Magnetic field at point $ O $ due to smaller coil $ X $ , $ {B_X} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{r^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Therefore, $ \dfrac{{{B_Y}}}{{{B_X}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{r^2}}}{{4{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}}}}{{\dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{r^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}}}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} $
$ \dfrac{{{B_Y}}}{{{B_X}}} = \dfrac{1}{2} $
Hence, the correct option is option C.
Note:
Magnetic field at the center of the coil is maximum and is equal to $ {B_X} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI}}{{2R}} $ . The magnetic field along the axis of the coil keeps on decreasing as we move away from the center of the coil and at far points, $ x \gg R $ magnetic field becomes, $ B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{R^2}}}{{2{x^3}}} $ .
Magnetic field due at the axis of a circular current-carrying coil, $ B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{R^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Where $ B $ is the magnetic field at the axis
$ R $ is the radius of the coil
$ I $ is the current carried by the coil
$ N $ is the number of turns in the coil
$ x $ is the distance from the center of the coil.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given two coils $ X $ and $ Y $ having an equal number of turns $ N $ and carrying an equal amount of current $ I $
Distance of centre of coil $ X $ from the point $ O $ is $ d $
As coil $ X $ is midway between $ Y $ and $ O $ ,
Distance of centre of coil $ Y $ and $ O $ is $ 2d $
Let radius of coil $ Y $ be $ R $ and radius of coil $ X $ be $ r $
Both the coils subtend same angle at point $ O $ thus,
$ \dfrac{r}{d} = \dfrac{R}{{2d}} $
$ \Rightarrow R = 2r $
Now, the magnetic field at point $ O $ due to bigger coil $ Y $ , $ {B_Y} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{R^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{R^2} + {{\left( {2d} \right)}^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Substituting $ R = 2r $ we get,
$ \Rightarrow {B_Y} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI\left( {4{r^2}} \right)}}{{2{{\left( {4{r^2} + 4{d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {B_Y} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI\left( {4{r^2}} \right)}}{{2 \times 8{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {B_Y} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{r^2}}}{{4{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Magnetic field at point $ O $ due to smaller coil $ X $ , $ {B_X} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{r^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Therefore, $ \dfrac{{{B_Y}}}{{{B_X}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{r^2}}}{{4{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}}}}{{\dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{r^2}}}{{2{{\left( {{r^2} + {d^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}}}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} $
$ \dfrac{{{B_Y}}}{{{B_X}}} = \dfrac{1}{2} $
Hence, the correct option is option C.
Note:
Magnetic field at the center of the coil is maximum and is equal to $ {B_X} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI}}{{2R}} $ . The magnetic field along the axis of the coil keeps on decreasing as we move away from the center of the coil and at far points, $ x \gg R $ magnetic field becomes, $ B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}NI{R^2}}}{{2{x^3}}} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




