
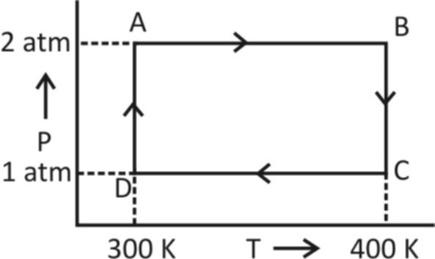
Two moles of helium gas undergo a cyclic process as shown in figure. Assuming the gas to be ideal. The net work done by the gas is
A. $200R\,\,\operatorname{I} n2$
B. $100R\,\,\operatorname{I} n2$
C. $300R\,\,\operatorname{I} n2$
D. $400R\,\,\operatorname{I} n2$

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: Concept of work done in case of isothermal process and isobaric process. As the processes AB and CD occur at constant pressure so it is barbaric while processes BC and DA occur at constant temperature so isothermal
Formula used:
1. Work done in an isobaric process
$W = P\Delta V = nR\Delta T$
2. Work done in an isothermal process
$ = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\dfrac{{\,{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
1. Isobaric Process – A process which occurs under constant pressure is called isobaric process.
2. Isothermal Process- A process which occurs for the same temperature is called isotherm process.
3. Isochoric Process- A process for which volume remains constant is called isochoric process.
4. Adiabatic Process- A process which involves no exchange of heat is called adiabatic from now, from the given figure, it is clear that both AB and CD processes involve no change in pressure. So, AB and CD represent isobaric processes.
Work done $ = $$P\Delta V = nR\Delta T$
Where is pressure, R is gas constant, n is number of moles, $\Delta \to $change, V is volume, T is temperature.
Now, work done for AB is given by
${W_{AB}} = nR\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)$
$ \implies {W_{AB}} = nR\left( {400 - 300} \right)\,\,\,\,\left[ {as{T_1} = 300K,\,{T_2} = 400K} \right] $
${W_{AB}} = nR\,\,100\,\,.........\left( 1 \right)$
Work done for CD is given by
\[{W_{CD}} = nR\,\,\Delta T\]
$ \implies {W_{CD}} = nR\left( {{T_1} - {T_2}} \right) $
Putting the values of temperatures
\[{W_{CD}} = nR\,\left( {300 - 400} \right)\]
$ \implies {W_{CD}} = nR\,\,100\,\,.......\left( 2 \right) $
Now, the process BC and DA occur at a constant temperature. So BC and DA represent isothermal process and the work done by an isothermal process is given by
$W = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\,\dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}}$
Where ${P_1}$ is the initial pressure
${P_2}$ is the final pressure
Now, work done for isothermal process BC is given by
\[{W_{BC}} = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\,\dfrac{{{P_2}}}{{{P_1}}}\]
$ \implies {W_{BC}} = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\dfrac{1}{2}\,\,\left( {as\,\,here\,\,{P_1} = 2atm,{P_2} = 1atm} \right) $
$ \implies{W_{BC}} = 400nR\,\,\ell n\,\dfrac{1}{2}\,\,\left( {as\,\,here\,\,T = 400K} \right) $
$ \implies{W_{BC}} = 400nR\,\left( {\ell n\,1 - \ell n\,2} \right)\, $
On solving this we get
\[{W_{BC}} = 400nR\,\left( {0 - \ell n\,2} \right)\,\]
$ \implies {W_{BC}} = 400nR\,\,\ell n\,2..........\left( 3 \right)\, $
Now, work done for isothermal process DA is
\[{W_{DA}} = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\,\dfrac{2}{1}\,\]
$ \implies{W_{DA}} = 300nR\,\,\ell n\,2\,\,........\left( 4 \right)\, $
Total work done $ = {W_{AB}} + {W_{BC}} + {W_{CD}} + {W_{DA}}$
$ = 100nR - 400nR\ell n2 - 100nR + 300nR\ell n2$
$ = - 100nR\,\,\ell n2$
Here number of moles, $n = 2$
So, Net work done $ = - 100 \times 2\,\,R\,\,\ell n2$
$ = - 200R\,\,\ell n2$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Remember $\ell n\left( {\dfrac{a}{b}} \right) = \ell n\,\,a - \ell n\,\,b$ and $\ell n\,\,\left( {ab} \right) = \ell n\,\,a\, + \ell n\,\,b$
So, $\ell n\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = \ell n1 - \ell n2$that is basic formulas of logarithms are used.
Formula used:
1. Work done in an isobaric process
$W = P\Delta V = nR\Delta T$
2. Work done in an isothermal process
$ = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\dfrac{{\,{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
1. Isobaric Process – A process which occurs under constant pressure is called isobaric process.
2. Isothermal Process- A process which occurs for the same temperature is called isotherm process.
3. Isochoric Process- A process for which volume remains constant is called isochoric process.
4. Adiabatic Process- A process which involves no exchange of heat is called adiabatic from now, from the given figure, it is clear that both AB and CD processes involve no change in pressure. So, AB and CD represent isobaric processes.
Work done $ = $$P\Delta V = nR\Delta T$
Where is pressure, R is gas constant, n is number of moles, $\Delta \to $change, V is volume, T is temperature.
Now, work done for AB is given by
${W_{AB}} = nR\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)$
$ \implies {W_{AB}} = nR\left( {400 - 300} \right)\,\,\,\,\left[ {as{T_1} = 300K,\,{T_2} = 400K} \right] $
${W_{AB}} = nR\,\,100\,\,.........\left( 1 \right)$
Work done for CD is given by
\[{W_{CD}} = nR\,\,\Delta T\]
$ \implies {W_{CD}} = nR\left( {{T_1} - {T_2}} \right) $
Putting the values of temperatures
\[{W_{CD}} = nR\,\left( {300 - 400} \right)\]
$ \implies {W_{CD}} = nR\,\,100\,\,.......\left( 2 \right) $
Now, the process BC and DA occur at a constant temperature. So BC and DA represent isothermal process and the work done by an isothermal process is given by
$W = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\,\dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}}$
Where ${P_1}$ is the initial pressure
${P_2}$ is the final pressure
Now, work done for isothermal process BC is given by
\[{W_{BC}} = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\,\dfrac{{{P_2}}}{{{P_1}}}\]
$ \implies {W_{BC}} = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\dfrac{1}{2}\,\,\left( {as\,\,here\,\,{P_1} = 2atm,{P_2} = 1atm} \right) $
$ \implies{W_{BC}} = 400nR\,\,\ell n\,\dfrac{1}{2}\,\,\left( {as\,\,here\,\,T = 400K} \right) $
$ \implies{W_{BC}} = 400nR\,\left( {\ell n\,1 - \ell n\,2} \right)\, $
On solving this we get
\[{W_{BC}} = 400nR\,\left( {0 - \ell n\,2} \right)\,\]
$ \implies {W_{BC}} = 400nR\,\,\ell n\,2..........\left( 3 \right)\, $
Now, work done for isothermal process DA is
\[{W_{DA}} = nRT\,\,\ell n\,\,\dfrac{2}{1}\,\]
$ \implies{W_{DA}} = 300nR\,\,\ell n\,2\,\,........\left( 4 \right)\, $
Total work done $ = {W_{AB}} + {W_{BC}} + {W_{CD}} + {W_{DA}}$
$ = 100nR - 400nR\ell n2 - 100nR + 300nR\ell n2$
$ = - 100nR\,\,\ell n2$
Here number of moles, $n = 2$
So, Net work done $ = - 100 \times 2\,\,R\,\,\ell n2$
$ = - 200R\,\,\ell n2$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Remember $\ell n\left( {\dfrac{a}{b}} \right) = \ell n\,\,a - \ell n\,\,b$ and $\ell n\,\,\left( {ab} \right) = \ell n\,\,a\, + \ell n\,\,b$
So, $\ell n\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = \ell n1 - \ell n2$that is basic formulas of logarithms are used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




