
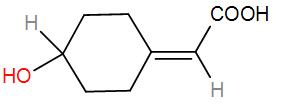
Two possible stereoisomers of the above molecules are:
[A] Enantiomers
[B] Diastereomers
[C] Conformers
[D] Rotamers

Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Here, this compound has 1 chiral centre thus it will have 2 stereoisomers. The stereoisomers will be non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Complete answer:
We know that stereoisomers are compounds having the same formula and composition but they differ in the spatial orientation of those parts in space i.e. the same molecule is attached to the same atom but their orientations will change.
Now we will discuss the types of stereoisomers.
The isomers which are mirror images of each other are known as enantiomers. We generally found enantiomers of compounds having a chiral centre and are asymmetric. The mirror images are non-superimposable.
The stereoisomers which are not mirror images of each other are diastereomers. They are neither superimposable non mirror images of each other. Generally, compounds having two or more stereo-centres are diastereomers.
Conformers are the stereoisomers which can be interconverted into one another by rotation of a single or more bonds and rotamers are also stereoisomers which can be interconverted into one another by rotation of a bond but there will be a restricted rotation around a single bond strictly.
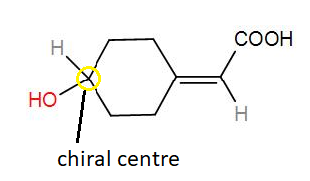
We know that a chiral centre is a carbon centre to which four different types of molecules are present. To find the number of stereoisomers, we can use the formula, $X={{2}^{n}}$, where n is the number of stereoisomers.
In the given compound, we have 1 chiral centre.
Therefore, it will have 2 stereoisomers –
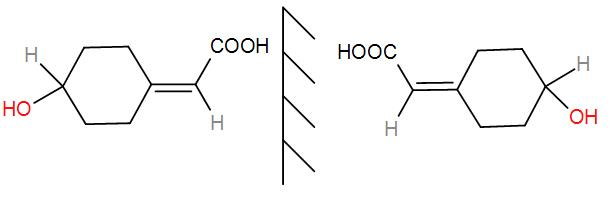
As we can see, we get two non-superimposable mirror images i.e. placing one on top of another will not give us the same compound, thus they are enantiomers.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [A] Enantiomers.
Note:
The number of stereoisomers depends on the number of chiral centres present on the molecule. If a compound has a superimposable image i.e. we get the same molecule on placing them on top of each other, such molecules are called homomers. They are not mirror images of each other.
Complete answer:
We know that stereoisomers are compounds having the same formula and composition but they differ in the spatial orientation of those parts in space i.e. the same molecule is attached to the same atom but their orientations will change.
Now we will discuss the types of stereoisomers.
The isomers which are mirror images of each other are known as enantiomers. We generally found enantiomers of compounds having a chiral centre and are asymmetric. The mirror images are non-superimposable.
The stereoisomers which are not mirror images of each other are diastereomers. They are neither superimposable non mirror images of each other. Generally, compounds having two or more stereo-centres are diastereomers.
Conformers are the stereoisomers which can be interconverted into one another by rotation of a single or more bonds and rotamers are also stereoisomers which can be interconverted into one another by rotation of a bond but there will be a restricted rotation around a single bond strictly.
We know that a chiral centre is a carbon centre to which four different types of molecules are present. To find the number of stereoisomers, we can use the formula, $X={{2}^{n}}$, where n is the number of stereoisomers.
In the given compound, we have 1 chiral centre.

Therefore, it will have 2 stereoisomers –

As we can see, we get two non-superimposable mirror images i.e. placing one on top of another will not give us the same compound, thus they are enantiomers.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [A] Enantiomers.
Note:
The number of stereoisomers depends on the number of chiral centres present on the molecule. If a compound has a superimposable image i.e. we get the same molecule on placing them on top of each other, such molecules are called homomers. They are not mirror images of each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




