
How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side of the right triangle with the given measures given c is the hypotenuse and we have a = 3, c = 4?
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint: In this problem we have to use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side of the right triangle with the given measures given c is the hypotenuse and we have a = 3, c = 4. We know that the Pythagoras Theorem is \[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}\]. We can see that, we are already given the value for a and c, which we can substitute in the formula where the missing side is b, which we have to find.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that we have used the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side of the right triangle with the given measures given c is the hypotenuse and we have a = 3, c = 4.
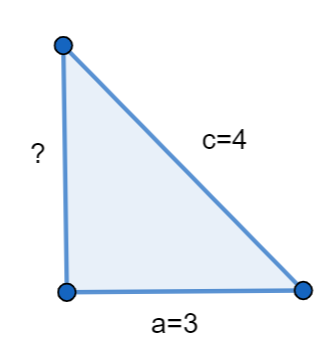
We know that the Pythagoras Theorem is \[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}\].
We can substitute the value a = 3, c = 4 in the above formula, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{3}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}\]
We can now simplify the above step, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}=16-9 \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}=7 \\
\end{align}\]
We can now take square root on both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow b=\sqrt{7}\]
Therefore, the missing side of the given right triangle is \[\sqrt{7}\]units.

Note: Students should remember the Pythagoras theorem formula is \[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}\]. Where the sum of squares of two sides is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. We should also see that the given triangle should be a right angle triangle, where Pythagoras theorem is only applied to right-angled triangles. We can also consider a as the perpendicular and find b as the base as it will lead to the same answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that we have used the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side of the right triangle with the given measures given c is the hypotenuse and we have a = 3, c = 4.

We know that the Pythagoras Theorem is \[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}\].
We can substitute the value a = 3, c = 4 in the above formula, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{3}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}\]
We can now simplify the above step, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}=16-9 \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}=7 \\
\end{align}\]
We can now take square root on both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow b=\sqrt{7}\]
Therefore, the missing side of the given right triangle is \[\sqrt{7}\]units.

Note: Students should remember the Pythagoras theorem formula is \[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}\]. Where the sum of squares of two sides is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. We should also see that the given triangle should be a right angle triangle, where Pythagoras theorem is only applied to right-angled triangles. We can also consider a as the perpendicular and find b as the base as it will lead to the same answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




