
Velocity of nerve impulse is more in
(a)Medullated nerve fibres
(b)Non-medullated nerve fibres
(c)Equal in both types of nerve fibres
(d)None of the above
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: An impulse is the spread of a wave of depolarisation which travels along the axon membrane. The velocity of nerve impulse increases in saltatory conduction when neurons are covered around by insulating covering.
Complete answer:
The ion channels within the axon membrane are voltage-dependent, which only open when the membrane is depolarised. The propagated nerve impulse moves at a continuing velocity along the axon membrane. Saltatory conduction is a sort of conduction which only occurs when the nerve impulse jumps from one ‘node of Ranvier’ to a different one. This is often due to the axon being myelinated. The results arise within the conduction velocity. During the passage of the impulse the axon will gain Na+ and lose ${{K}^{+}}$, but these ions are re-exchanged by the $N{{a}^{+}}$ / ${{K}^{+}}$ pumps which can actively pump out $N{{a}^{+}}$ and pump ${{K}^{+}}$ into the axon.
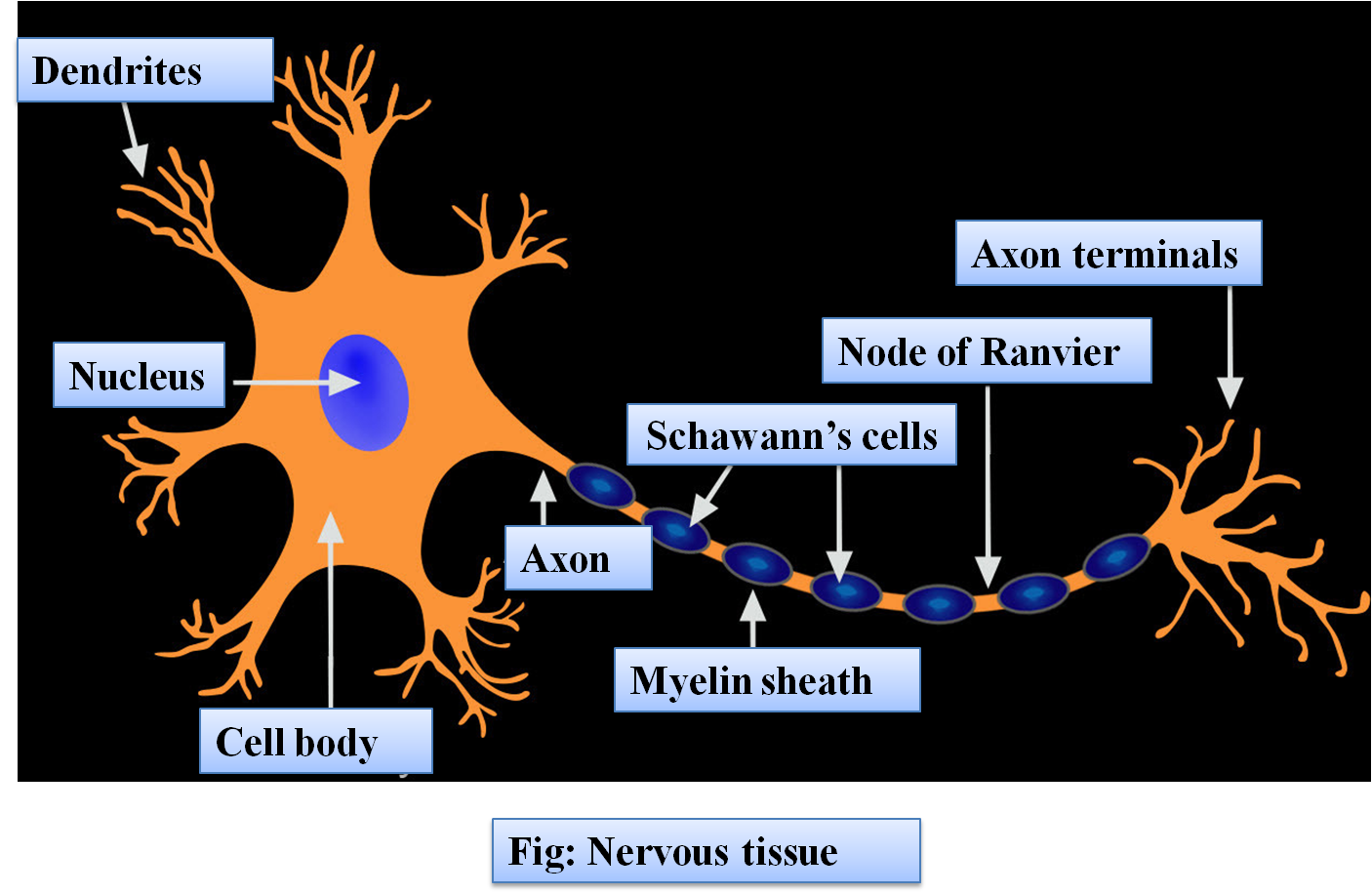
Additional Information:
Steps of conduction of nerve impulse:
-The electric potential of a neuron refers to the state of the neuron before the sending of an impulse.
-The membrane of a neuron maintains an electrical gradient which may be a difference within the electrical charge inside and out of doors of the cell.
-At rest, the membrane maintains an electrical polarization or a difference within the electrical charge of two locations.
-The inside the membrane is slightly negative with reference to the surface approximately -70 millivolts.
-The membrane is selectively permeable by allowing some chemicals to pass more freely than others. -Sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride undergo channels within the membrane.
-When the membrane is at rest sodium channels are closed and potassium channels are partially closed allowing the slow passage of sodium.
-The sodium-potassium pump may be a protein complex that continually pumps three sodium ions out of the cells while drawing two potassium ions into the cell which also helps to take care of the electrical gradient.
-An nerve impulse may be a rapid depolarization of the neuron.
-Stimulation of the neuron past the edge of excitation triggers an impulse or nerve impulse.
-When sodium channels are opened, charged sodium ions rush in and a subsequent impulse occurs.
-After a nerve impulse occurs, sodium channels are quickly closed.
-The neuron is returned to its resting state by the opening of potassium channels and potassium ions diffuse thanks to the concentration gradient and takes with them their charge. The sodium-potassium pump later restores the first distribution of ions.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Medullated nerve fibres.’
Note: -The electric potential remains stable until the neuron is stimulated.
-Hyperpolarization is the increasing polarization or the difference between the electrical charge of two places.
-Depolarization refers to decreasing the polarization towards zero.
-The threshold of pleasure refers to any stimulation beyond a particular level and leads to a huge depolarization.
Complete answer:
The ion channels within the axon membrane are voltage-dependent, which only open when the membrane is depolarised. The propagated nerve impulse moves at a continuing velocity along the axon membrane. Saltatory conduction is a sort of conduction which only occurs when the nerve impulse jumps from one ‘node of Ranvier’ to a different one. This is often due to the axon being myelinated. The results arise within the conduction velocity. During the passage of the impulse the axon will gain Na+ and lose ${{K}^{+}}$, but these ions are re-exchanged by the $N{{a}^{+}}$ / ${{K}^{+}}$ pumps which can actively pump out $N{{a}^{+}}$ and pump ${{K}^{+}}$ into the axon.

Additional Information:
Steps of conduction of nerve impulse:
-The electric potential of a neuron refers to the state of the neuron before the sending of an impulse.
-The membrane of a neuron maintains an electrical gradient which may be a difference within the electrical charge inside and out of doors of the cell.
-At rest, the membrane maintains an electrical polarization or a difference within the electrical charge of two locations.
-The inside the membrane is slightly negative with reference to the surface approximately -70 millivolts.
-The membrane is selectively permeable by allowing some chemicals to pass more freely than others. -Sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride undergo channels within the membrane.
-When the membrane is at rest sodium channels are closed and potassium channels are partially closed allowing the slow passage of sodium.
-The sodium-potassium pump may be a protein complex that continually pumps three sodium ions out of the cells while drawing two potassium ions into the cell which also helps to take care of the electrical gradient.
-An nerve impulse may be a rapid depolarization of the neuron.
-Stimulation of the neuron past the edge of excitation triggers an impulse or nerve impulse.
-When sodium channels are opened, charged sodium ions rush in and a subsequent impulse occurs.
-After a nerve impulse occurs, sodium channels are quickly closed.
-The neuron is returned to its resting state by the opening of potassium channels and potassium ions diffuse thanks to the concentration gradient and takes with them their charge. The sodium-potassium pump later restores the first distribution of ions.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Medullated nerve fibres.’
Note: -The electric potential remains stable until the neuron is stimulated.
-Hyperpolarization is the increasing polarization or the difference between the electrical charge of two places.
-Depolarization refers to decreasing the polarization towards zero.
-The threshold of pleasure refers to any stimulation beyond a particular level and leads to a huge depolarization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




