
Vernier constant is the:
(A). Value if one MSD divided by total number of divisions on the main scale
(B). Value of one VSD divided by total number of divisions on the main scale
(C). Total number of divisions on the main scale divided by total number of divisions on the Vernier scale
(D). Difference between the value of one main scale division and one Vernier scale division
Answer
609.3k+ views
- Hint: Vernier constant or the least count of a Vernier caliper is the least distance that can be measured by the scale.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Vernier caliper is an assistive tool, used to take accurate reading between two markings (graduation) of a main scale. It is a subsidiary scale that increases the resolution of measurement.
In a Vernier caliper, 10 divisions of the Vernier scale coincide with 9 divisions of the main scale. Now the Vernier scale is shifted such that its first marking coincides with the first marking of the main scale. In this situation the difference between the zeroth marking of each scale gives the smallest length that the Vernier caliper can measure. Since, the first marking is coinciding, the required length is the difference between 1 main scale division (msd) (1 msd = 1 mm) and 1 Vernier scale division (vsd).
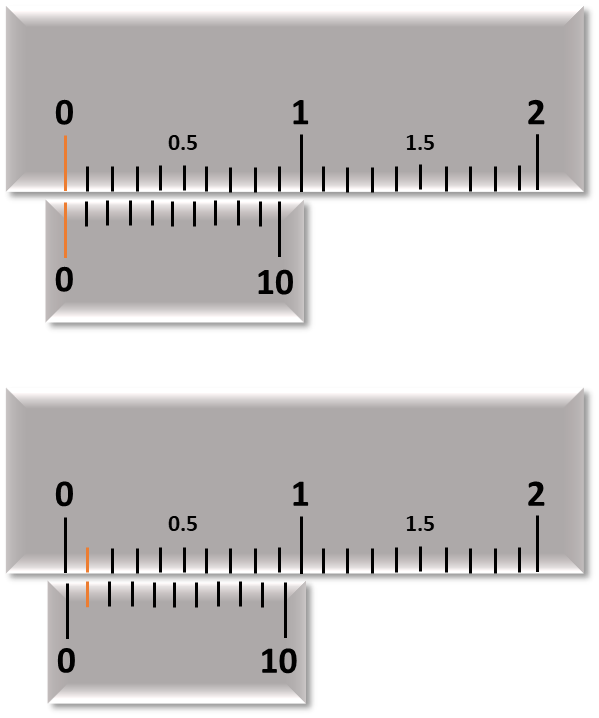
Now, since
$10 vsd = 9 msd$
$1 vsd = \dfrac{9}{10} msd$
$1 vsd = \dfrac{9}{10} mm$
Hence, the required length or the Vernier constant (VC) is given by,
$VC = 1 msd – 1vsd$
$VC = 1 mm - \dfrac{9}{10} mm $
$VC = \dfrac{1}{10} mm $
Hence, Vernier constant is the difference between the value of one main scale division and one Vernier scale division.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: It is easy to remember that the least count is equal to the least count of the main scale divided by the number of divisions in the Vernier scale. The same logic applies for screw gauge.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Vernier caliper is an assistive tool, used to take accurate reading between two markings (graduation) of a main scale. It is a subsidiary scale that increases the resolution of measurement.
In a Vernier caliper, 10 divisions of the Vernier scale coincide with 9 divisions of the main scale. Now the Vernier scale is shifted such that its first marking coincides with the first marking of the main scale. In this situation the difference between the zeroth marking of each scale gives the smallest length that the Vernier caliper can measure. Since, the first marking is coinciding, the required length is the difference between 1 main scale division (msd) (1 msd = 1 mm) and 1 Vernier scale division (vsd).

Now, since
$10 vsd = 9 msd$
$1 vsd = \dfrac{9}{10} msd$
$1 vsd = \dfrac{9}{10} mm$
Hence, the required length or the Vernier constant (VC) is given by,
$VC = 1 msd – 1vsd$
$VC = 1 mm - \dfrac{9}{10} mm $
$VC = \dfrac{1}{10} mm $
Hence, Vernier constant is the difference between the value of one main scale division and one Vernier scale division.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: It is easy to remember that the least count is equal to the least count of the main scale divided by the number of divisions in the Vernier scale. The same logic applies for screw gauge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




