
What is a repressible operon?
Answer
480.9k+ views
Hint: Operon is a bacterial and viral genetic regulation mechanism in which genes coding for functionally similar proteins are grouped along the DNA. Protein synthesis can be coordinated in response to the cell's needs and functions.
Complete answer:
The Tryptophan (trp) operon is often called the repressible operon. The trp operon is a type of operon which codes for the components for tryptophan synthesis. E. Coli (rod-shaped bacteria) can generate tryptophan by utilising enzymes produced by five structural genes in the trp operon, which are positioned close to one another.
Image showing Tryptophan (trp) Operon
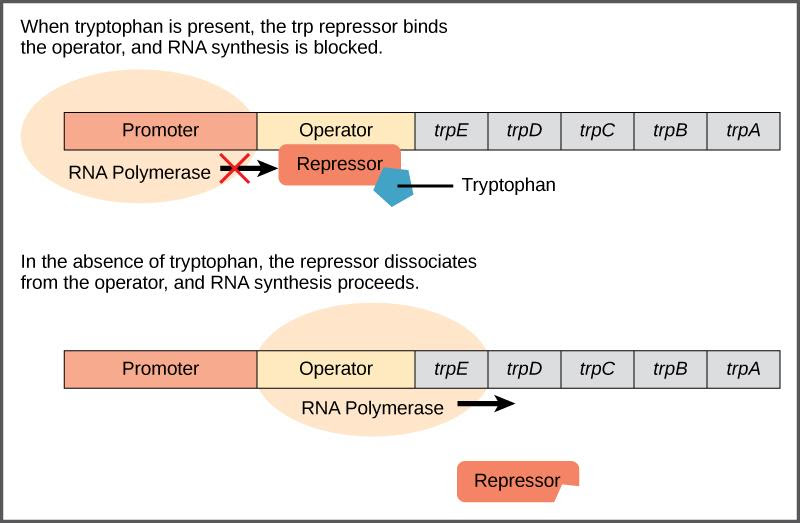
The operon is activated when tryptophan levels in the environment are low. This indicates that when the transcription begins, the genes are exposed which leads to the production of tryptophan. The trp operon, on the other hand, is turned off if tryptophan is present in the environment. This leads to no transcription, which ultimately leads to no production of tryptophan.
The repressor does not attach to the operator when the tryptophan is not present in the cell, leading the operon to become active and also leads to the eventual production of tryptophan. When tryptophan levels rise in the cell, two tryptophan molecules attach to the trp repressor, causing it to change form by enabling it to get linked to the trp operator. The active form of the trp repressor binds to the operator, preventing RNA polymerase from replicating the structural genes and therefore inhibiting operon production. As a result, the operon's expression is regulated by the actual product of the biosynthetic pathway regulated by the operon.
Note:
In general, there are two types of operons such as the prokaryotic operons and eukaryotic operons. Repressible operons and inducible operons are two types of prokaryotic operons. Genes encoding enzymes essential for a metabolic process are often found in repressible operons, such as the tryptophan (trp) operon. Inducible operons, such as E. coli's lac operon, generally contain genes generating enzymes in a system which is involved in the biosynthesis of a specific substrate such as the lactose. Since these enzymes are only essential and required when the substrate is present, expression of the operon is normally activated only when the substrate is present.
Complete answer:
The Tryptophan (trp) operon is often called the repressible operon. The trp operon is a type of operon which codes for the components for tryptophan synthesis. E. Coli (rod-shaped bacteria) can generate tryptophan by utilising enzymes produced by five structural genes in the trp operon, which are positioned close to one another.
Image showing Tryptophan (trp) Operon

The operon is activated when tryptophan levels in the environment are low. This indicates that when the transcription begins, the genes are exposed which leads to the production of tryptophan. The trp operon, on the other hand, is turned off if tryptophan is present in the environment. This leads to no transcription, which ultimately leads to no production of tryptophan.
The repressor does not attach to the operator when the tryptophan is not present in the cell, leading the operon to become active and also leads to the eventual production of tryptophan. When tryptophan levels rise in the cell, two tryptophan molecules attach to the trp repressor, causing it to change form by enabling it to get linked to the trp operator. The active form of the trp repressor binds to the operator, preventing RNA polymerase from replicating the structural genes and therefore inhibiting operon production. As a result, the operon's expression is regulated by the actual product of the biosynthetic pathway regulated by the operon.
Note:
In general, there are two types of operons such as the prokaryotic operons and eukaryotic operons. Repressible operons and inducible operons are two types of prokaryotic operons. Genes encoding enzymes essential for a metabolic process are often found in repressible operons, such as the tryptophan (trp) operon. Inducible operons, such as E. coli's lac operon, generally contain genes generating enzymes in a system which is involved in the biosynthesis of a specific substrate such as the lactose. Since these enzymes are only essential and required when the substrate is present, expression of the operon is normally activated only when the substrate is present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




