
What is Curie temperature?
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Before understanding Curie temperature, we must know that, as temperature increases, the randomization of magnetic moments increases. This results in changes in properties of magnetic materials. Curie temperature is such a point.
Complete solution:
Now we will discuss more about Curie temperature and temperature dependence on susceptibility of materials.
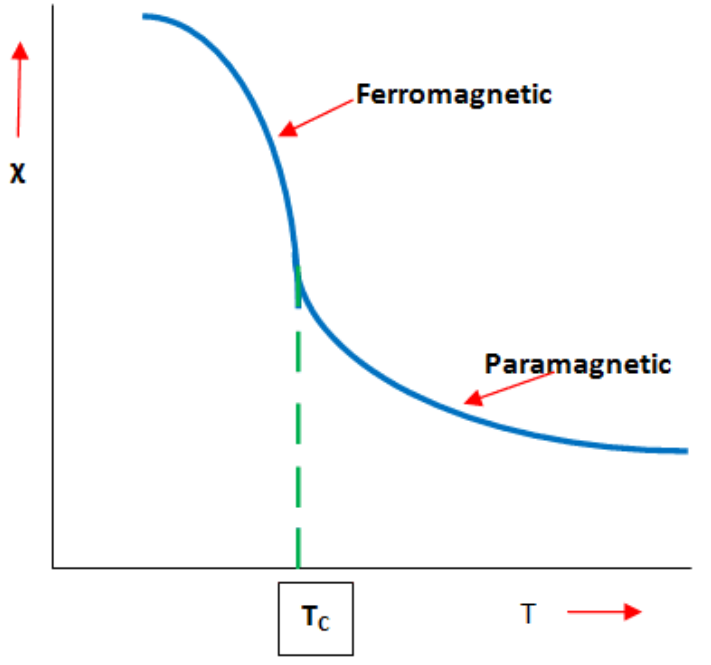
Curie temperature: it is the temperature at which a ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic in nature. That is, the temperature at which a magnetic material completely loses its magnetic property.
When temperature increases, randomization of magnetic moments increases which leads to decrease in magnetization \[I\]. So, the resulting magnetic field \[B\] decreases.
That means \[\chi \](susceptibility) decreases as \[T\] increases.
Curie's law states that “susceptibility of a paramagnetic substance is inversely proportional to temperature.”
i.e., \[\chi =\dfrac{c}{T}\]
In this equation, \[c\] is called Curies constant.
Now, let’s take the case of a ferromagnetic material. A ferromagnetic material has magnetic properties as its magnetic moments are aligned in a certain direction. As temperature increases, this alignment randomizes and it loses magnetic property and turns into a paramagnetic material at a certain temperature. This temperature is known as Curie temperature.
After Curie temperature, we can see the susceptibility varies as, \[\chi =\dfrac{c}{T-{{T}_{C}}}\]
Where \[{{T}_{C}}\] is a Curie temperature.
Note: We must be aware that every material has different construction of intrinsic magnetic moments that depend on temperature. So Curie temperature varies according to materials as temperature required for different materials differs.
Complete solution:
Now we will discuss more about Curie temperature and temperature dependence on susceptibility of materials.
Curie temperature: it is the temperature at which a ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic in nature. That is, the temperature at which a magnetic material completely loses its magnetic property.
When temperature increases, randomization of magnetic moments increases which leads to decrease in magnetization \[I\]. So, the resulting magnetic field \[B\] decreases.
That means \[\chi \](susceptibility) decreases as \[T\] increases.
Curie's law states that “susceptibility of a paramagnetic substance is inversely proportional to temperature.”
i.e., \[\chi =\dfrac{c}{T}\]
In this equation, \[c\] is called Curies constant.
Now, let’s take the case of a ferromagnetic material. A ferromagnetic material has magnetic properties as its magnetic moments are aligned in a certain direction. As temperature increases, this alignment randomizes and it loses magnetic property and turns into a paramagnetic material at a certain temperature. This temperature is known as Curie temperature.
After Curie temperature, we can see the susceptibility varies as, \[\chi =\dfrac{c}{T-{{T}_{C}}}\]
Where \[{{T}_{C}}\] is a Curie temperature.

Note: We must be aware that every material has different construction of intrinsic magnetic moments that depend on temperature. So Curie temperature varies according to materials as temperature required for different materials differs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




