
What is dichotomous branching?
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: It is the basic form of branching which occurs in non-vascular and non-seeded vascular plants. It is a characteristic feature particularly in liverworts like Marchantia, Riccia. It is also known as fork branching.
Complete answer:
Dichotomous branching or fork branching is the typical feature of liverworts. In this, the apical meristem divides into two independently functioning axes. In the case of angiosperms, it is like a primary growth form in several families.
The branches are formed by the equal division of the terminal buds into two. These buds are not formed from the axillary buds but are present anywhere in the plant. Some of the angiosperms which show this type of branching are cacti.
There are two types of dichotomous branching-
i) Monopodial branching- In this type, continuous growth is seen in the central axes and the lateral branches remain ungrown. Example beech trees. These plants appear pyramidal in shape.
ii) Sympodial branching- In this type the growth of the terminal bud gets arrested. The axillary bud becomes the new shoot and is known as the renewal shoot. Example- Joshua. It generally resembles candelabra.
The figure below shows Aspergillus species with dichotomous branching.
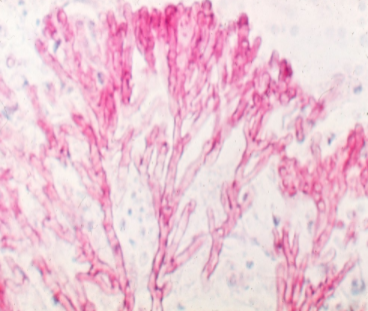
This branching is very complex as the plant has to maintain the division of the meristem properly and accurately.
Note: Dichotomous branching is a primitive kind of branching. In liverworts, the body of the plant is reduced to thallus which is flat, dorsiventral and shows dichotomous branching. The dichotomous branching is also seen in the hyphae of the fungus. Several species of the genus Aspergillus show dichotomous branching. In this apical branching takes place along with the extension of hyphae.
Complete answer:
Dichotomous branching or fork branching is the typical feature of liverworts. In this, the apical meristem divides into two independently functioning axes. In the case of angiosperms, it is like a primary growth form in several families.
The branches are formed by the equal division of the terminal buds into two. These buds are not formed from the axillary buds but are present anywhere in the plant. Some of the angiosperms which show this type of branching are cacti.
There are two types of dichotomous branching-
i) Monopodial branching- In this type, continuous growth is seen in the central axes and the lateral branches remain ungrown. Example beech trees. These plants appear pyramidal in shape.
ii) Sympodial branching- In this type the growth of the terminal bud gets arrested. The axillary bud becomes the new shoot and is known as the renewal shoot. Example- Joshua. It generally resembles candelabra.
The figure below shows Aspergillus species with dichotomous branching.

This branching is very complex as the plant has to maintain the division of the meristem properly and accurately.
Note: Dichotomous branching is a primitive kind of branching. In liverworts, the body of the plant is reduced to thallus which is flat, dorsiventral and shows dichotomous branching. The dichotomous branching is also seen in the hyphae of the fungus. Several species of the genus Aspergillus show dichotomous branching. In this apical branching takes place along with the extension of hyphae.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




