
What is micropropagation?
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: Micropropagation is significant in several aspects on account of its economic importance and also by virtue of its role in crop improvement. The advantage of the micro population is the production of many plants that are clones of each other. Micropropagation can be used to produce disease-free plants. It requires only a limited and short duration for carrying out the whole process. It can be carried out all- year- round, irrespective of changing seasons.
Complete answer:
Micropropagation is also called micro cloning or clonal propagation, is the vegetative propagation of plants by tissue culture techniques, using cells, tissues, organs, etc. Essentially, it involves the regeneration of plants from isolated meristematic or somatic cells or tissues. It provides a rapid and reliable means for the mass production of genetically similar and disease-free plants through the culture of the shoot – apices, axillary buds, and meristems. It can be best used for the large- scale production of crop plants, ornamental plants, medicinal plants,etc.which are difficult to propagate sexually.
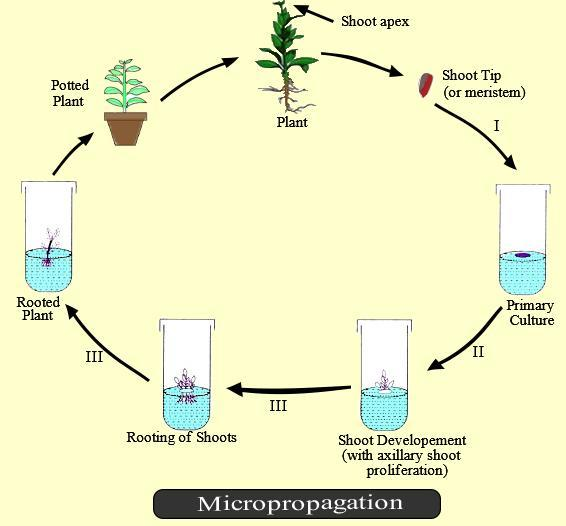
It is often used for the propagation of exclusively vegetative species whose multiplication rate is very lowland also for mass multiplication of superior varieties of hybrids as an alternative to seed propagation. Micropropagation is most ideal for those dioecious species whose males are economically undesirable. It is one of the most important applications of tissue culture for commercial plant propagation. Currently, it is very important in the commercial multiplication of banana, apple, strawberry, pear. Orchids, and so on. The production of genetically identical plants by the vegetative or sexual method is called clonal propagation.
Additional information:
The progeny or population of genetically identical members, obtained by vegetative or asexual multiplication of one and the same parent plant is called a clone. Micropropagation is essentially in vitro clonal propagation.
- In contrast to conventional methods of vegetative Propagation, it results in the mass multiplication of the members of elite species, preserving their genetic identity and uniformity.
- it is significant that it involves the utilization of most plant parts such as shoot tip leaf petiole, nodal tissue, anther, pollen, ovary, ovule, immature embryo, cotyledon, etc., as source material for the production of millions of plantlets in a short period of time.
- This is mainly due to the totipotency of plant cells. By micropropagation, suitable explants from angiosperms, gymnosperms, and pteridophytes can be cultured in vitro and induced to develop into adventitious
Note:
- Micropropagation is advantageous in that only a small amount of plant tissue is needed as the source material for the production of millions of clonal plants in a relatively short period of time.
- It enables the cost-effective multiplication of desired varieties of plants to produce clones of genetically uniform members.
- Also, it enables the multiplication of plants that are difficult to propagate by other methods. It tremendously increases the rate of multiplication of plants.
Complete answer:
Micropropagation is also called micro cloning or clonal propagation, is the vegetative propagation of plants by tissue culture techniques, using cells, tissues, organs, etc. Essentially, it involves the regeneration of plants from isolated meristematic or somatic cells or tissues. It provides a rapid and reliable means for the mass production of genetically similar and disease-free plants through the culture of the shoot – apices, axillary buds, and meristems. It can be best used for the large- scale production of crop plants, ornamental plants, medicinal plants,etc.which are difficult to propagate sexually.

It is often used for the propagation of exclusively vegetative species whose multiplication rate is very lowland also for mass multiplication of superior varieties of hybrids as an alternative to seed propagation. Micropropagation is most ideal for those dioecious species whose males are economically undesirable. It is one of the most important applications of tissue culture for commercial plant propagation. Currently, it is very important in the commercial multiplication of banana, apple, strawberry, pear. Orchids, and so on. The production of genetically identical plants by the vegetative or sexual method is called clonal propagation.
Additional information:
The progeny or population of genetically identical members, obtained by vegetative or asexual multiplication of one and the same parent plant is called a clone. Micropropagation is essentially in vitro clonal propagation.
- In contrast to conventional methods of vegetative Propagation, it results in the mass multiplication of the members of elite species, preserving their genetic identity and uniformity.
- it is significant that it involves the utilization of most plant parts such as shoot tip leaf petiole, nodal tissue, anther, pollen, ovary, ovule, immature embryo, cotyledon, etc., as source material for the production of millions of plantlets in a short period of time.
- This is mainly due to the totipotency of plant cells. By micropropagation, suitable explants from angiosperms, gymnosperms, and pteridophytes can be cultured in vitro and induced to develop into adventitious
Note:
- Micropropagation is advantageous in that only a small amount of plant tissue is needed as the source material for the production of millions of clonal plants in a relatively short period of time.
- It enables the cost-effective multiplication of desired varieties of plants to produce clones of genetically uniform members.
- Also, it enables the multiplication of plants that are difficult to propagate by other methods. It tremendously increases the rate of multiplication of plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




