
What is microsporangium?
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: It is the structure that houses the pollen grains in a flower. The microspores develop inside the microsporangium.
Complete answer:
- All flowering plants show sexual reproduction. A flower is the reproductive structure of a plant that contains the male and female gametophytes. The male reproductive structure is the androecium, represented by a whorl of stamens and the female reproductive structure is the gynoecium.
- Stamens are structures that contain pollen in terminal sac-like structures called microsporangia or anthers, also known as microsporophylls. Typically, an angiosperm anther is bilobed meaning each lobe is made up of two theca. Each anther is made up of four structures containing four microsporangia, two in each lobe, situated at the corners. The microsporangium appears nearly spherical in outline.
- It typically consists of four wall layers, namely, the epidermis, endothecium, middle layers and the tapetum. The three outer wall layers play protective roles and help release the pollen in anther dehiscence. The tapetum is the innermost wall layer and provides nourishment to the developing pollen grains. The tapetum cells generally consist of more than a single nucleus with a dense cytoplasm.
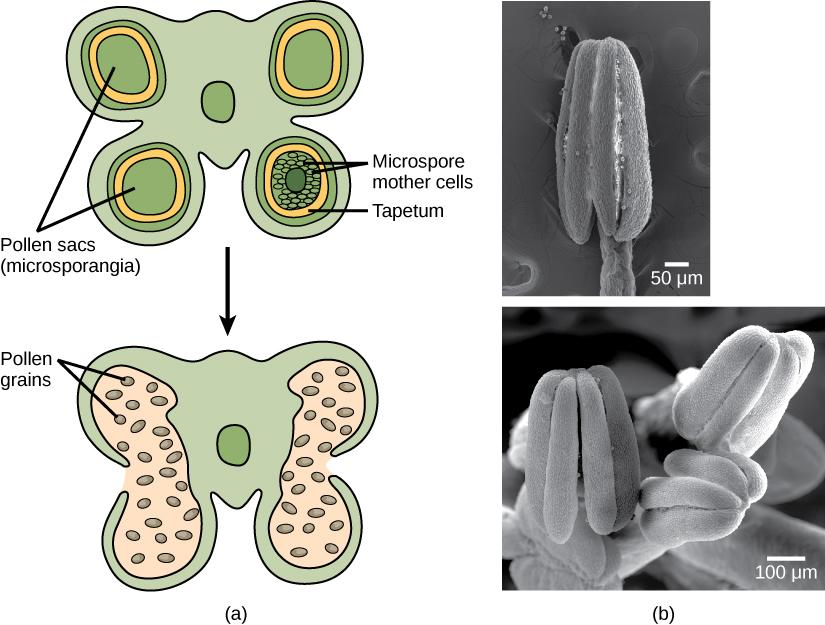
Fig: Microsporangia
- Microsporangia develop further into pollen sacs. They extend throughout the anther's length and are filled with pollen grains. A young anther has a cluster of compactly organised homogeneous cells known as sporogenous tissue in the middle of each microsporangium. The microspores separate and grow into pollen grains as the anthers mature and dehydrate.
Note: Microsporogenesis is the process of the production of microspores through a pollen mother cell by the process of meiosis. The microspores are found arranged in a four-cell cluster called the microspore tetrad.
Complete answer:
- All flowering plants show sexual reproduction. A flower is the reproductive structure of a plant that contains the male and female gametophytes. The male reproductive structure is the androecium, represented by a whorl of stamens and the female reproductive structure is the gynoecium.
- Stamens are structures that contain pollen in terminal sac-like structures called microsporangia or anthers, also known as microsporophylls. Typically, an angiosperm anther is bilobed meaning each lobe is made up of two theca. Each anther is made up of four structures containing four microsporangia, two in each lobe, situated at the corners. The microsporangium appears nearly spherical in outline.
- It typically consists of four wall layers, namely, the epidermis, endothecium, middle layers and the tapetum. The three outer wall layers play protective roles and help release the pollen in anther dehiscence. The tapetum is the innermost wall layer and provides nourishment to the developing pollen grains. The tapetum cells generally consist of more than a single nucleus with a dense cytoplasm.

Fig: Microsporangia
- Microsporangia develop further into pollen sacs. They extend throughout the anther's length and are filled with pollen grains. A young anther has a cluster of compactly organised homogeneous cells known as sporogenous tissue in the middle of each microsporangium. The microspores separate and grow into pollen grains as the anthers mature and dehydrate.
Note: Microsporogenesis is the process of the production of microspores through a pollen mother cell by the process of meiosis. The microspores are found arranged in a four-cell cluster called the microspore tetrad.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




