
What is Schottky defect?
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: It is a type of vacancy, point and stoichiometric defect as well. The defect does not change the electrical neutrality of the crystal and decreases the density as well.
Complete step by step answer:
-A Schottky defect is a type of vacancy defect which is found in ionic solids. It is a stoichiometry defect (thermodynamic defect), which means that such defects do not change or distort the stoichiometry of the solid. In this type of vacancy defect there are cations and anions missing from the solid, but since the number of missing cations and anions are the same the electrical neutrality of the solid is maintained.
-This defect was first discovered by a German physicist named Walter H. Schottky. In his model he said that this defect occurs when in ionic solids/crystals the oppositely charged ions (cations and anions) leave their lattice sites, thus creating vacancies. These vacancies are furthermore created in order to maintain a neutral charge in the solid/crystal.
-It is also a point defect since vacant positions are generated by the leaving cations and anions.
-This defect causes decrease in the density of the ionic crystal due to decrease in the mass and such defects are found quite often in ionic solids. Another important thing is that for any ionic solid to show this defect the size of its cation and anion should be similar.
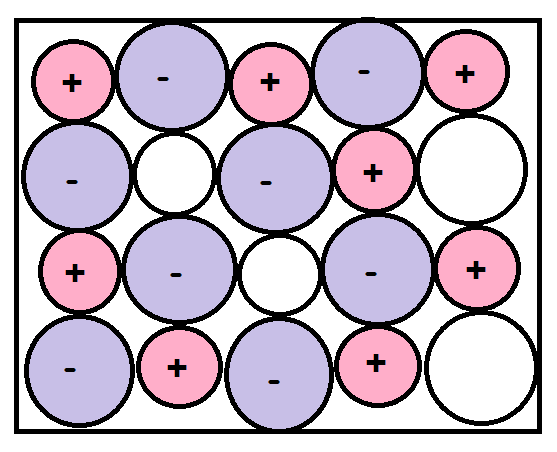
-In short some distinct characteristics of this defect are:
(1)Cation and anion both leave the solid such that electrical neutrality is maintained.
(2)They leave the solid permanently.
(3)The cation and anion are similar in size.
(4)Density of the crystal decreases.
-This defect is shown by compounds like: AgBr, NaCl, CsCl, KCl, KBr, etc.
Note: Do not confuse Schottky defect with Frenkel defect. In Schottky defect the ions permanently leave the solid crystal, while in Frenkel defect the ions leave their positions (to occupy interstitial sites) but stay within the solid crystal.
Complete step by step answer:
-A Schottky defect is a type of vacancy defect which is found in ionic solids. It is a stoichiometry defect (thermodynamic defect), which means that such defects do not change or distort the stoichiometry of the solid. In this type of vacancy defect there are cations and anions missing from the solid, but since the number of missing cations and anions are the same the electrical neutrality of the solid is maintained.
-This defect was first discovered by a German physicist named Walter H. Schottky. In his model he said that this defect occurs when in ionic solids/crystals the oppositely charged ions (cations and anions) leave their lattice sites, thus creating vacancies. These vacancies are furthermore created in order to maintain a neutral charge in the solid/crystal.
-It is also a point defect since vacant positions are generated by the leaving cations and anions.
-This defect causes decrease in the density of the ionic crystal due to decrease in the mass and such defects are found quite often in ionic solids. Another important thing is that for any ionic solid to show this defect the size of its cation and anion should be similar.

-In short some distinct characteristics of this defect are:
(1)Cation and anion both leave the solid such that electrical neutrality is maintained.
(2)They leave the solid permanently.
(3)The cation and anion are similar in size.
(4)Density of the crystal decreases.
-This defect is shown by compounds like: AgBr, NaCl, CsCl, KCl, KBr, etc.
Note: Do not confuse Schottky defect with Frenkel defect. In Schottky defect the ions permanently leave the solid crystal, while in Frenkel defect the ions leave their positions (to occupy interstitial sites) but stay within the solid crystal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




