
What is the formula of an ammeter?
Answer
505.2k+ views
Hint: In the above question we are basically asked to what is the role of the ammeter in a circuit as well as the formula for the quantity it measures. Ammeter is always connected in series in an electrical circuit. Hence from the above information we will understand the significance of the ammeter as well about the quantity that it measures.
Formula used:
$V=iR$
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the hint we know that an ammeter is always connected in series to the equivalent circuit. This is due to the fact that the electric current in a series circuit is always constant. From this we can imply that the role of the ammeter is to measure the electric current in a circuit.
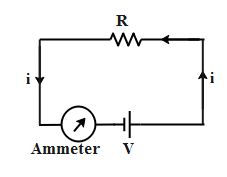
In the above circuit diagram, we can see that the ammeter measures current ‘i’ through the circuit. Let us say the equivalent resistance of the above circuit be ‘R’ which is connected across a potential difference of V. Hence from Ohm’s law we can say that the current in the circuit obeys the relation,
$V=iR$
Therefore the formula for the value of the electric current measured by an ammeter is $i=\dfrac{V}{R}$.
Note:Ohms law states that the current though a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference provided the temperature remains the same. It is to be noted that a galvanometer can also be used as an ammeter. This is basically done by connecting a shunt resistance (very small) parallel to the galvanometer so that the maximum current flows through the shunt and the galvanometer can give desired value of current.
Formula used:
$V=iR$
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the hint we know that an ammeter is always connected in series to the equivalent circuit. This is due to the fact that the electric current in a series circuit is always constant. From this we can imply that the role of the ammeter is to measure the electric current in a circuit.

In the above circuit diagram, we can see that the ammeter measures current ‘i’ through the circuit. Let us say the equivalent resistance of the above circuit be ‘R’ which is connected across a potential difference of V. Hence from Ohm’s law we can say that the current in the circuit obeys the relation,
$V=iR$
Therefore the formula for the value of the electric current measured by an ammeter is $i=\dfrac{V}{R}$.
Note:Ohms law states that the current though a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference provided the temperature remains the same. It is to be noted that a galvanometer can also be used as an ammeter. This is basically done by connecting a shunt resistance (very small) parallel to the galvanometer so that the maximum current flows through the shunt and the galvanometer can give desired value of current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




