
Which isomers of hexane give a maximum number of stereoisomers on monochlorination.
A.n-hexane
B.2-methyl pentane
C.3-methyl pentane
D.2,2-dimethylbutane
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Stereoisomers are those isomers that have the same structural formula but the different relative arrangements of atoms or groups in space and this phenomenon are called stereoisomerism.
Complete step by step solution:
In the case of option A, i.e. n-hexane there are three different carbon atoms present thus it gives three stereoisomers on monochlorination. The three different carbon atoms are shown below:
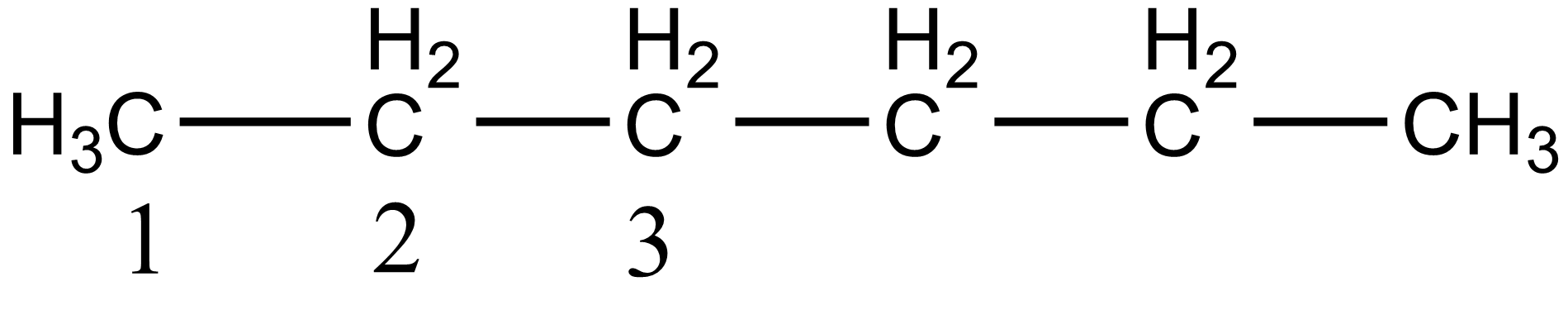
In the case of option B i.e. 2-methyl pentane, there are five different carbon atoms present thus giving five stereoisomers on monochlorination. The five different carbon of 2-methyl pentane is shown below:
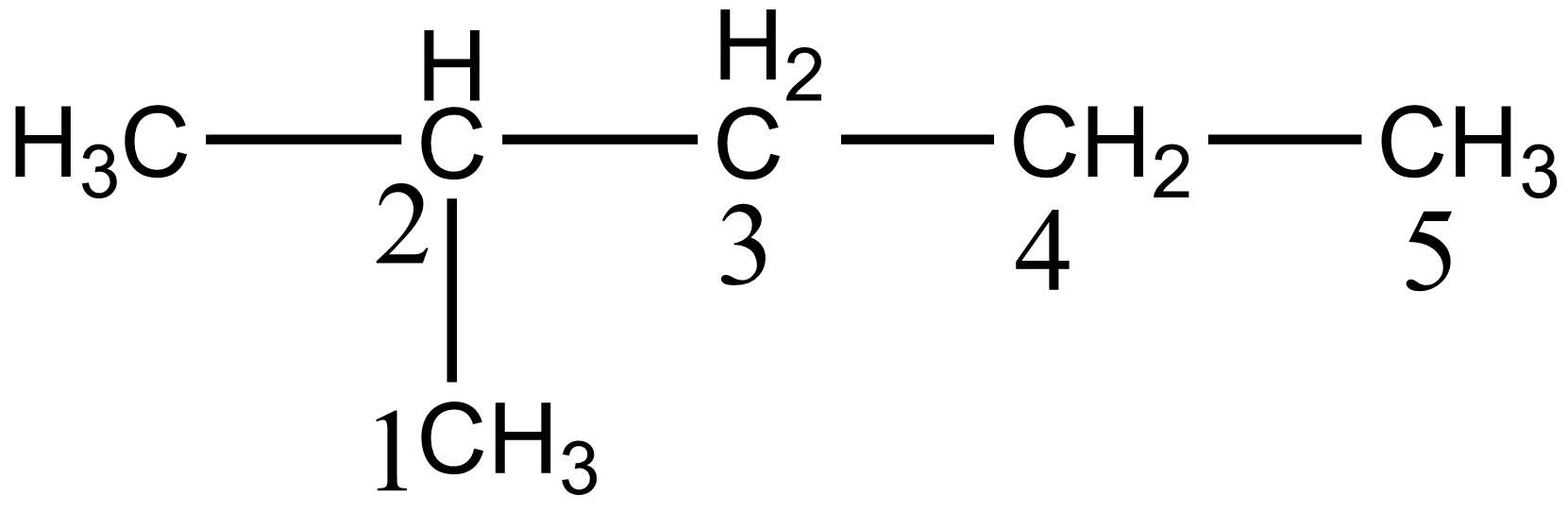
In the case of option C i.e. 3-methyl pentane, there are four different carbon atoms present, thus giving four stereoisomers on monochlorination. The four different carbon of 3-methyl pentane is shown below:
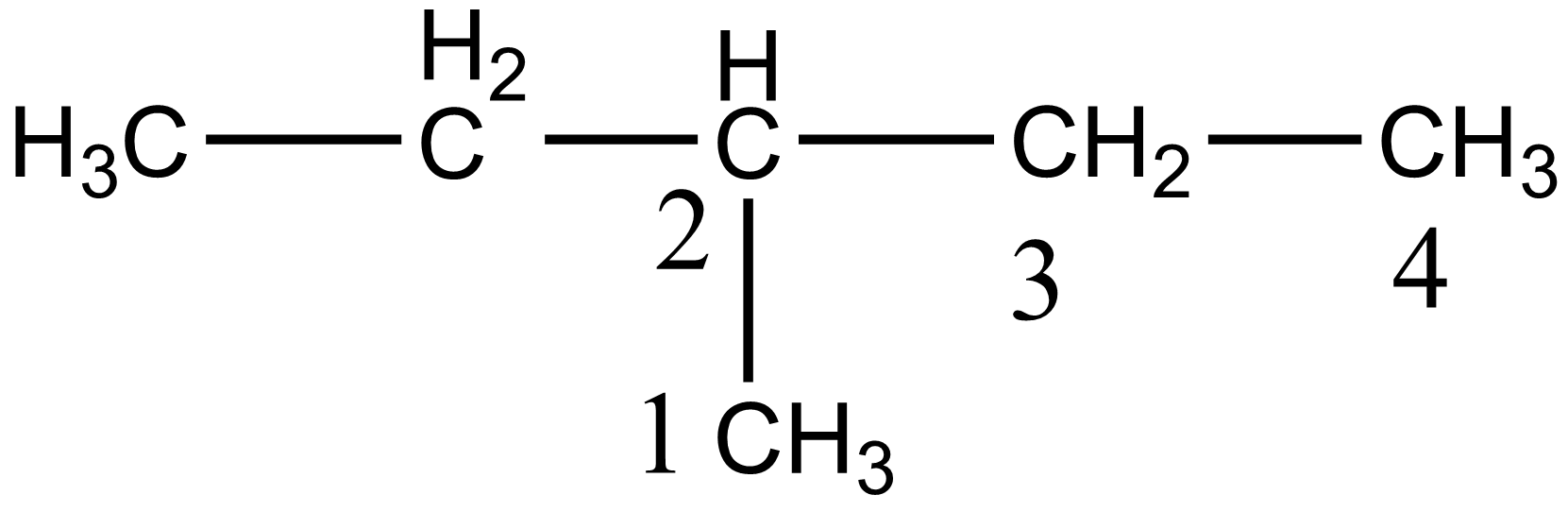
In the case of option D i.e. 2,2-dimethylbutane, there are two different carbon atoms present thus giving two stereoisomers on monochlorination. Hence 2-methyl pentane gives maximum stereoisomers on monochlorination.
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Note:
There are two types of stereoisomers namely:
Conformational isomers: They are the isomers that differ in the relative position of the atom within the molecule and which can be simply interconverted by rotation about sigma bonds. These isomers don’t require making and remaking of covalent bonds at the time of interconversion.
Configurational isomers: The isomers which can be interconverted only by breaking and remaking of covalent bonds and not by simple rotation about sigma bonds are considered as Configurational isomers. These are of two types:
Geometrical isomerism
Optical isomerism.
Complete step by step solution:
In the case of option A, i.e. n-hexane there are three different carbon atoms present thus it gives three stereoisomers on monochlorination. The three different carbon atoms are shown below:
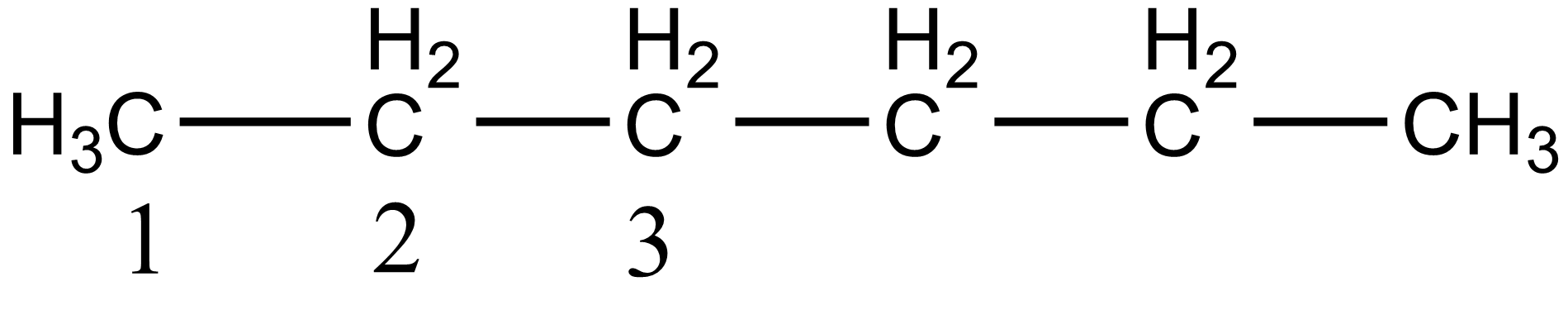
In the case of option B i.e. 2-methyl pentane, there are five different carbon atoms present thus giving five stereoisomers on monochlorination. The five different carbon of 2-methyl pentane is shown below:

In the case of option C i.e. 3-methyl pentane, there are four different carbon atoms present, thus giving four stereoisomers on monochlorination. The four different carbon of 3-methyl pentane is shown below:

In the case of option D i.e. 2,2-dimethylbutane, there are two different carbon atoms present thus giving two stereoisomers on monochlorination. Hence 2-methyl pentane gives maximum stereoisomers on monochlorination.
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Note:
There are two types of stereoisomers namely:
Conformational isomers: They are the isomers that differ in the relative position of the atom within the molecule and which can be simply interconverted by rotation about sigma bonds. These isomers don’t require making and remaking of covalent bonds at the time of interconversion.
Configurational isomers: The isomers which can be interconverted only by breaking and remaking of covalent bonds and not by simple rotation about sigma bonds are considered as Configurational isomers. These are of two types:
Geometrical isomerism
Optical isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




