
Which of the following compound(s) show dipole moment \[?\]
A.$1,4 - $dichlorobenzene
B.$1,2 - $dichlorobenzene
C.$1,3 - $dichlorobenzene
D.trans $ - 2,3 - $ dichloro $ - 2 - $ butene
Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: Dipole moment $(\mu )$ of a molecule arises due to separation of charges. The magnitude of charge and distance between them determines the polarity of the bond. Here, to find the molecules that show dipole moment, first we must draw their structures. The net dipole moment of the molecule can be found out by knowing the direction of the dipole moment of each bond.
Complete answer: Dipole moment is a vector quantity. It depends upon the difference in electronegativity between the atoms or molecules. Chlorine is an electronegative atom. Polarity arises mainly due to the difference in electronegativity of $C - Cl$ bond of the given molecules. Now, let us check which of the following compounds show dipole moment.
A.$1,4 - $dichlorobenzene
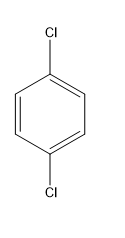
In this case, the dipole moments are in the opposite directions and they cancel out. Therefore, the net dipole moment is zero due to the symmetry of the molecule.
B.$1,2 - $dichlorobenzene
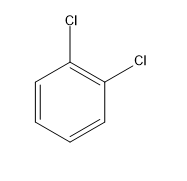
There is a resultant dipole moment for the molecule. The dipole moment is the vector sum of individual dipole moments of $C - Cl$ bonds. The angle between them is around ${60^ \circ }$ .
C.$1,3 - $dichlorobenzene

The two chlorine atoms are meta to each other and the molecule shows a resultant dipole moment. The individual dipole moments are at an angle of ${120^ \circ }$ to each other and their vector sum gives the net dipole moment of the compound.
D.trans $ - 2,3 - $ dichloro $ - 2 - $ butene
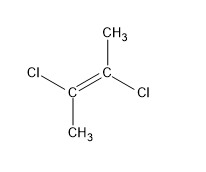
This is similar to (a). The dipole moment by identical chlorine atoms cancels out each other since they are in opposite directions. There is a center of symmetry at $C = C$ and thus the net dipole moment is zero.
Therefore, the compounds that show dipole moment are :
(b) $1,2 - $dichlorobenzene
(c) $1,3 - $dichlorobenzene
Note:
Dipole moment is a measure of polarity of a molecule. Non polar molecules have zero net dipole moment. Symmetric molecules will have net dipole moment zero as their individual dipole moments cancel out in opposite directions. Cis molecules will have more dipole moment than trans molecules.
Complete answer: Dipole moment is a vector quantity. It depends upon the difference in electronegativity between the atoms or molecules. Chlorine is an electronegative atom. Polarity arises mainly due to the difference in electronegativity of $C - Cl$ bond of the given molecules. Now, let us check which of the following compounds show dipole moment.
A.$1,4 - $dichlorobenzene

In this case, the dipole moments are in the opposite directions and they cancel out. Therefore, the net dipole moment is zero due to the symmetry of the molecule.
B.$1,2 - $dichlorobenzene

There is a resultant dipole moment for the molecule. The dipole moment is the vector sum of individual dipole moments of $C - Cl$ bonds. The angle between them is around ${60^ \circ }$ .
C.$1,3 - $dichlorobenzene

The two chlorine atoms are meta to each other and the molecule shows a resultant dipole moment. The individual dipole moments are at an angle of ${120^ \circ }$ to each other and their vector sum gives the net dipole moment of the compound.
D.trans $ - 2,3 - $ dichloro $ - 2 - $ butene

This is similar to (a). The dipole moment by identical chlorine atoms cancels out each other since they are in opposite directions. There is a center of symmetry at $C = C$ and thus the net dipole moment is zero.
Therefore, the compounds that show dipole moment are :
(b) $1,2 - $dichlorobenzene
(c) $1,3 - $dichlorobenzene
Note:
Dipole moment is a measure of polarity of a molecule. Non polar molecules have zero net dipole moment. Symmetric molecules will have net dipole moment zero as their individual dipole moments cancel out in opposite directions. Cis molecules will have more dipole moment than trans molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




