
Which of the following compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
A) $1 - $phenyl$ - 2 - $butene
B) $3 - $phenyl$ - 1 - $butene
C) $2 - $phenyl$ - 1 - $butene
D) $1,1 - $diphenyl$ - 1 - $propane
Answer
524.5k+ views
Hint: Geometrical isomers are the compounds that have the same number and same type of atoms but they differ with each other in their spatial (an arrangement which is related to the space-based activity of atoms) arrangement of atoms around a double bond. The drawing of structure will help to identify the isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
1) The first condition to have geometrical isomers in a molecule is it must have a double bond.
2) The second condition is that different atoms or molecules must be attached on each side of the carbon in \[C = C\] bond.
3) Based on the atoms or groups attached to carbon on each side with respect to the double bond they are differentiated in two types such as cis isomers and trans-isomers.
4) When highest priority atoms or groups are present on the same side with respect to the double bond then they are called ‘cis’ isomers. When highest priority atoms or groups are present on the different sides with respect to double bonds then they are called ‘trans’ isomers.
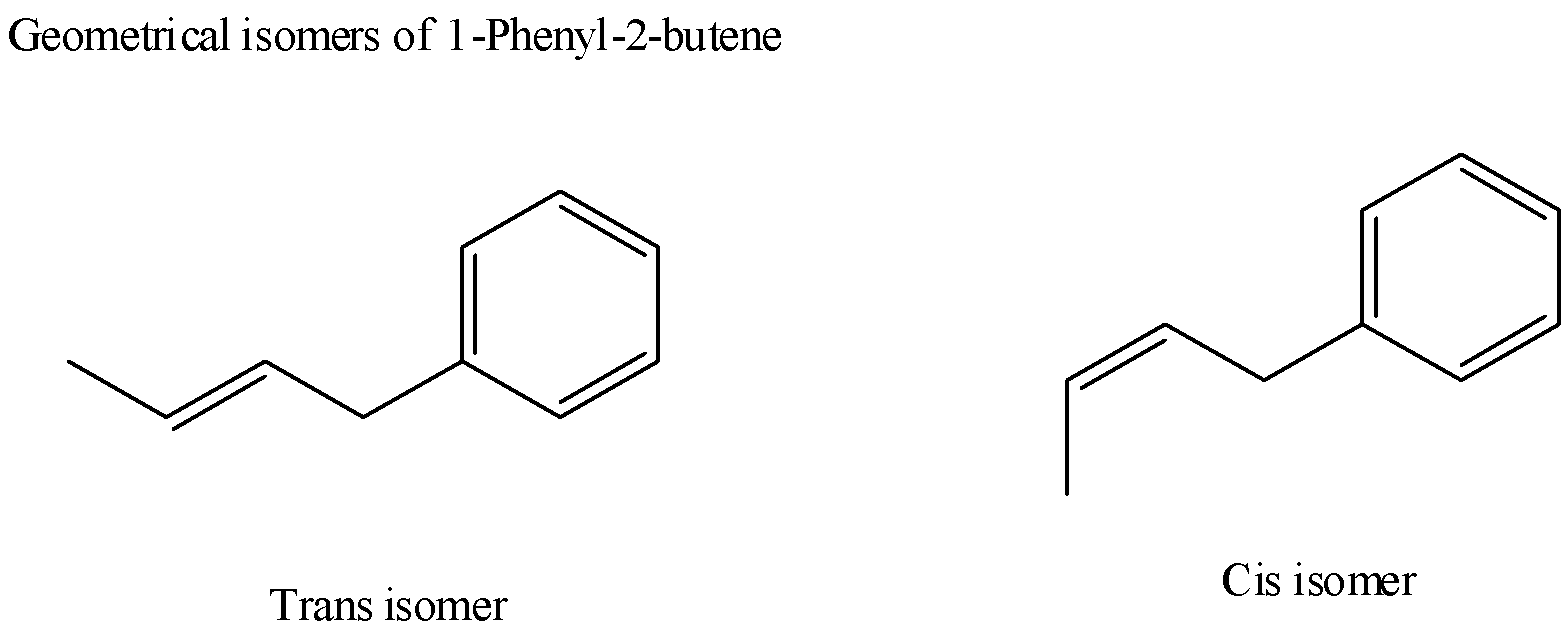
5) By analyzing the above options based on conditions that just learned, the structure $1 - $phenyl$ - 2 - $butane shows two geometrical isomers shown as below,
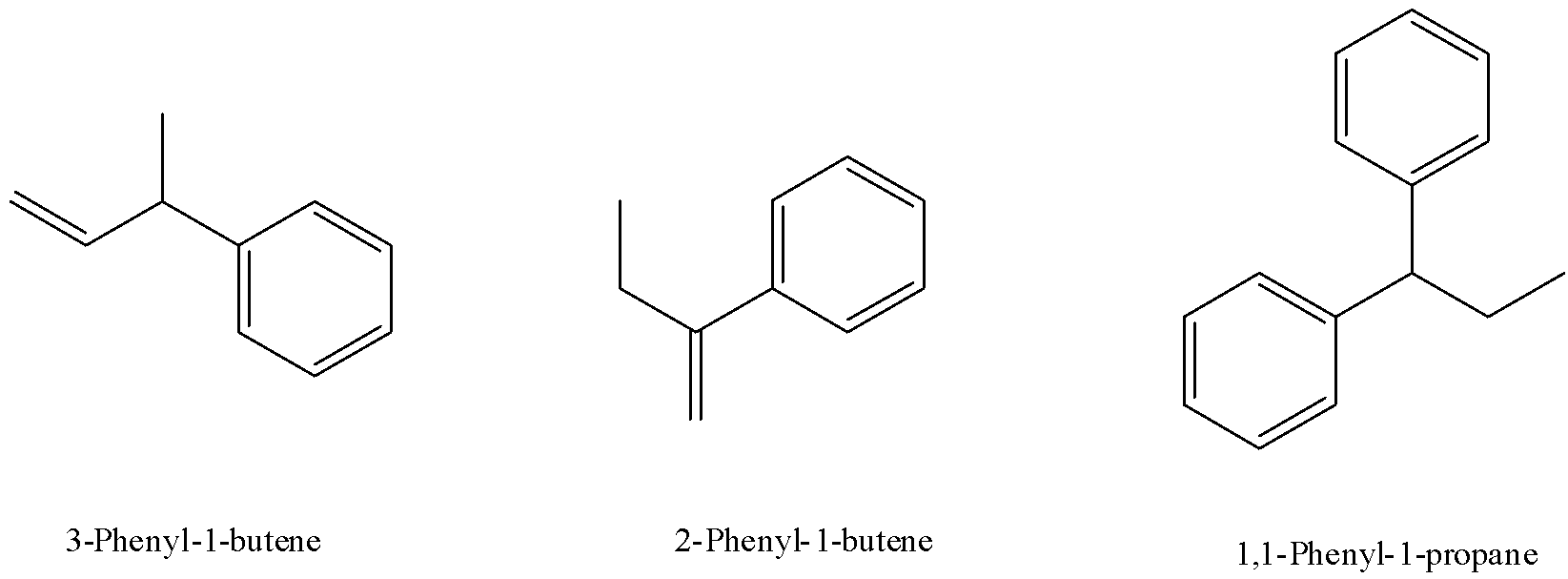
6) The other structures in the option don’t follow the conditions discussed above. Their structure is given below to better analyze them based on conditions for geometrical isomers.
Note:
When the same atoms or groups are present on the same carbon atom of a double bond then the structure will not show geometrical isomerism. The double bond is planar so there is always $180^\circ $ rotation during the conversion of cis to trans and vice-versa.
Complete step by step answer:
1) The first condition to have geometrical isomers in a molecule is it must have a double bond.
2) The second condition is that different atoms or molecules must be attached on each side of the carbon in \[C = C\] bond.
3) Based on the atoms or groups attached to carbon on each side with respect to the double bond they are differentiated in two types such as cis isomers and trans-isomers.
4) When highest priority atoms or groups are present on the same side with respect to the double bond then they are called ‘cis’ isomers. When highest priority atoms or groups are present on the different sides with respect to double bonds then they are called ‘trans’ isomers.
5) By analyzing the above options based on conditions that just learned, the structure $1 - $phenyl$ - 2 - $butane shows two geometrical isomers shown as below,

6) The other structures in the option don’t follow the conditions discussed above. Their structure is given below to better analyze them based on conditions for geometrical isomers.

Note:
When the same atoms or groups are present on the same carbon atom of a double bond then the structure will not show geometrical isomerism. The double bond is planar so there is always $180^\circ $ rotation during the conversion of cis to trans and vice-versa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




