
Which of the following gas is responsible for 'Global-Warming'?
(a) Methane
(b) Ozone
(c) Carbon-dioxide
(d) Nitrogen
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: Many variables affect global temperatures, including the reflection of solar radiation by cloud cover, minor changes in the Sun’s intensity, airborne particulate matter from volcanic activity and sulphate aerosol.
Complete answer:
Carbon-dioxide is responsible for 'Global-Warming’.
A layer of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ in the atmosphere traps the infrared radiation coming from earth's surface. These trapped radiations heat the earth's atmosphere and result in greenhouse effect and global warming.
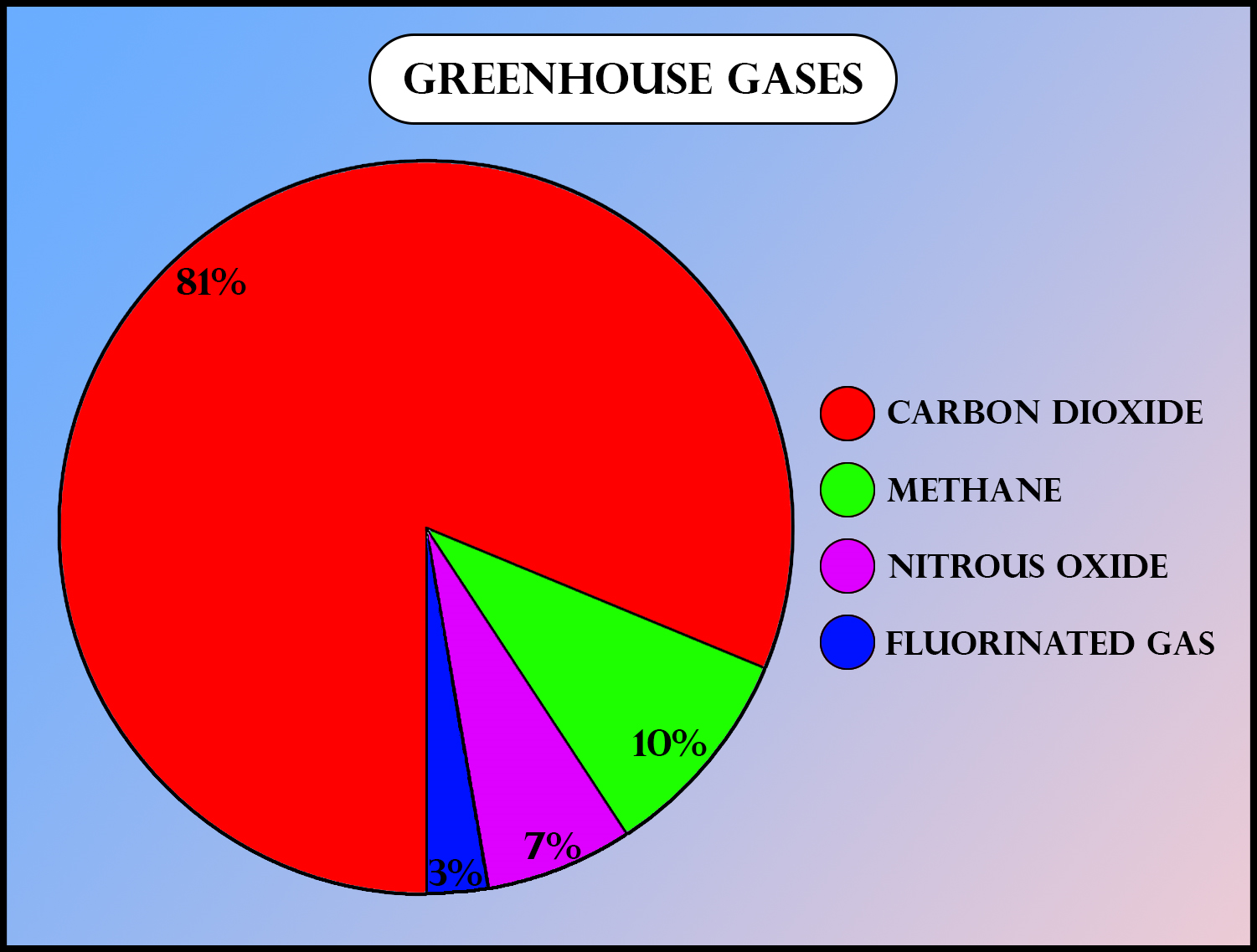
The relative contribution of various greenhouse gases to total global warming is as follows:
${ CO }_{ 2 }=60\%$
${CH}_{4} =20\%$
$CFC =14\%$
${ N }_{ 2 }O=6\%$
Additional information:
Global temperature is on the rise, an effect known as global warming. A trend that coincides with the observed rise in greenhouse gases and the strong correlation between temperature and greenhouse gases from the past is impressive. When respiration predominates (during late fall through spring), ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ levels rise; when photosynthesis predominates (during late spring through early fall), ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ levels fall. As of early 2001, atmospheric ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ levels were over 370ppm, 35% higher than they were before the Industrial Revolution. The phenomenon has been observed since pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900).
So, the correct answer is ‘Carbon-dioxide’.
Note:
- Several other gases absorb infrared radiation and add to the insulating effect of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$.
- Warming will seriously affect rainfall and agriculture. The present-day difference between temperatures at the poles and those at the equator is a major driving force for atmospheric circulation.
- Climate change can not be stopped but it can be slowed.
Complete answer:
Carbon-dioxide is responsible for 'Global-Warming’.
A layer of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ in the atmosphere traps the infrared radiation coming from earth's surface. These trapped radiations heat the earth's atmosphere and result in greenhouse effect and global warming.
The relative contribution of various greenhouse gases to total global warming is as follows:
${ CO }_{ 2 }=60\%$
${CH}_{4} =20\%$
$CFC =14\%$
${ N }_{ 2 }O=6\%$

Additional information:
Global temperature is on the rise, an effect known as global warming. A trend that coincides with the observed rise in greenhouse gases and the strong correlation between temperature and greenhouse gases from the past is impressive. When respiration predominates (during late fall through spring), ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ levels rise; when photosynthesis predominates (during late spring through early fall), ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ levels fall. As of early 2001, atmospheric ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ levels were over 370ppm, 35% higher than they were before the Industrial Revolution. The phenomenon has been observed since pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900).
So, the correct answer is ‘Carbon-dioxide’.
Note:
- Several other gases absorb infrared radiation and add to the insulating effect of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$.
- Warming will seriously affect rainfall and agriculture. The present-day difference between temperatures at the poles and those at the equator is a major driving force for atmospheric circulation.
- Climate change can not be stopped but it can be slowed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




