
Which of the following is an allylic halide?
A) 3-bromo-2-methylpropene
B) 3-bromobut-1-ene
C) 3-bromopent-2-ene
D) 4-bromobut-1-ene
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint:. To answer this question, first you should know what allylic halides are. They are the molecules in which the halogen atom is attached to the carbon atom which is further attached to the carbon-carbon double bond. Draw the chemical structures of each compound given in options and examine their structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Allylic halides are the halides in which the halogen atom is bonded to $s{p^3}$- hybridised carbon atom next to carbon-carbon double bond ($C = C$). General chemical structure of allylic halides:
$C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - X$
Here, X is any halogen atom.
Now, let us draw the structure of each given compound to find the allylic halide.
- 3-bromo-2-methylpropene:
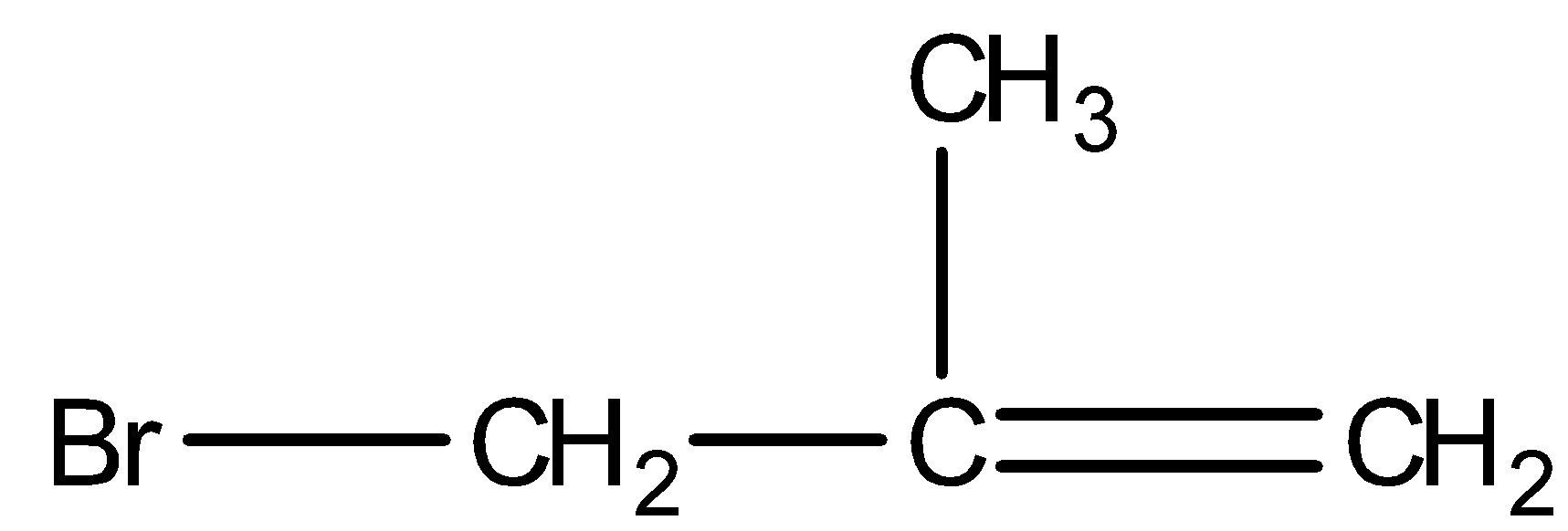
- 3-bromobut-1-ene:
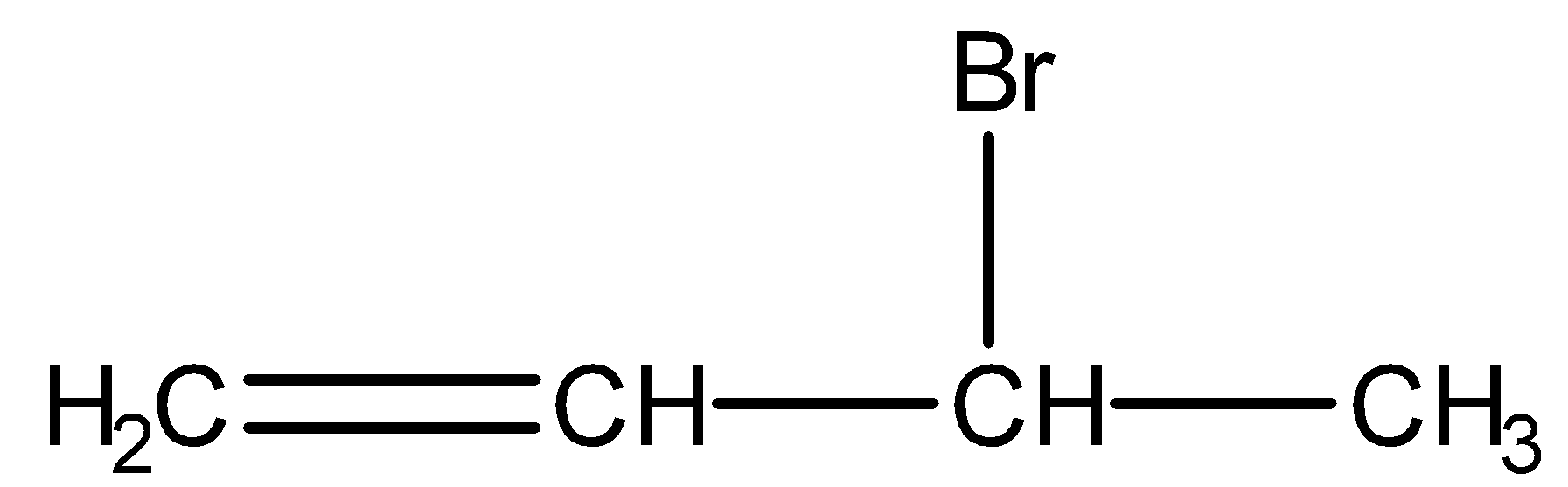
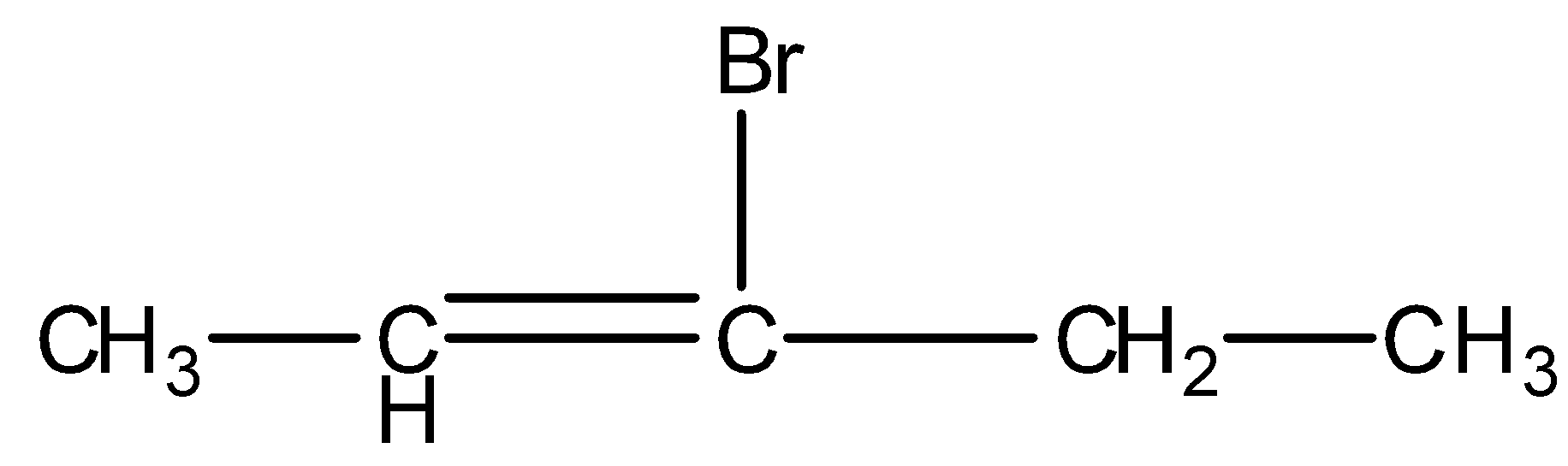
- 3-bromopent-2-ene
- 4-bromobut-1-ene
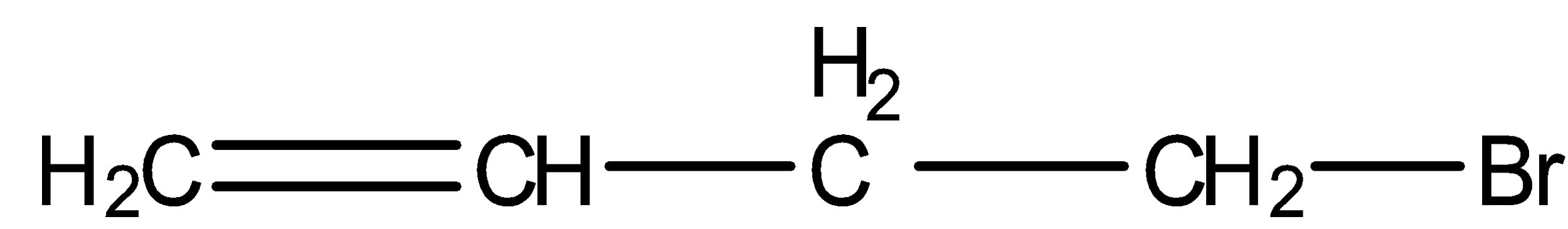
We can see from the above structures that in, 3-bromo-2-methylpropene and 3-bromobut-1-ene, bromine is attached to the $s{p^3}$ -hybridised carbon atom which is next to carbon-carbon double bond or $s{p^2}$ - hybridised carbon. Thus, both 3-bromo-2-methylpropene and 3-bromobut-1-ene are the allylic halides.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and B”.
Additional Information:
One can confuse between allylic halides and vinyl halides. You must know that vinyl halides are the compounds in which the halogen atom is bonded to the carbon atom that is doubly bonded to another carbon atom or we can simply say that, halogen atom is bonded to an $s{p^2}$- hybridised carbon. General formula of vinyl halides is: $C{H_2} = C{H_2} - X$. Here, X is any halogen atom.
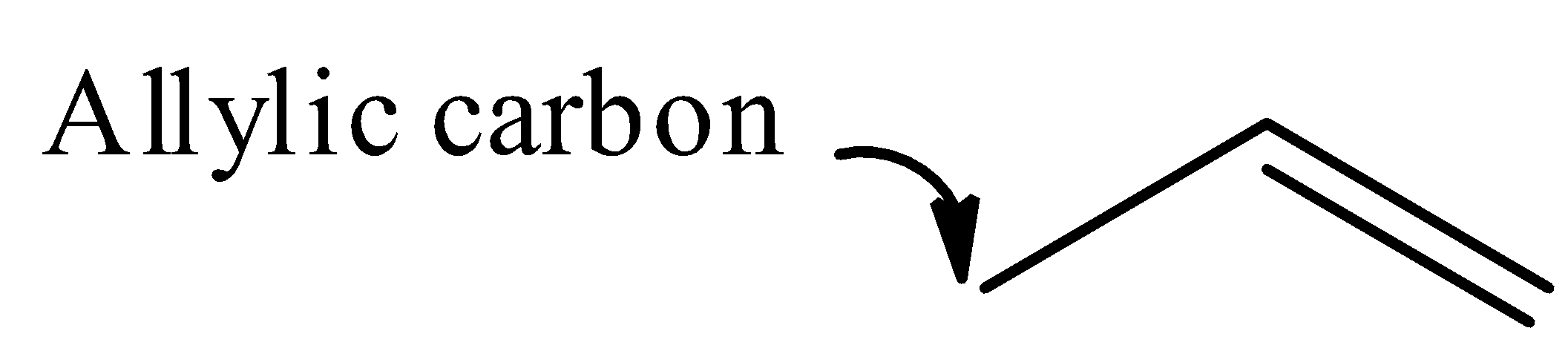
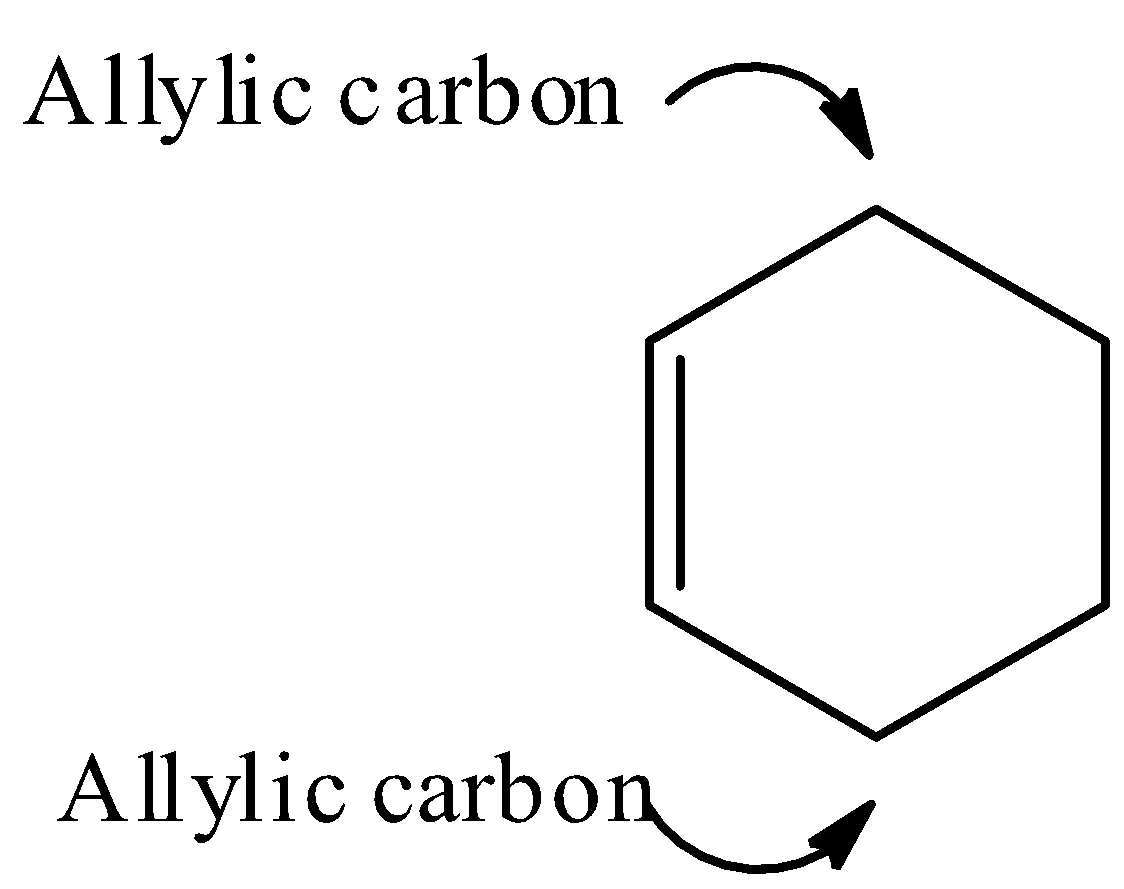
Note: It should be noted that the carbon atom bonded to carbon atom that in turn is doubly bonded to another carbon atom is known as allylic carbon. Examples of allylic carbon:
Complete step by step answer:
Allylic halides are the halides in which the halogen atom is bonded to $s{p^3}$- hybridised carbon atom next to carbon-carbon double bond ($C = C$). General chemical structure of allylic halides:
$C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - X$
Here, X is any halogen atom.
Now, let us draw the structure of each given compound to find the allylic halide.
- 3-bromo-2-methylpropene:

- 3-bromobut-1-ene:

- 3-bromopent-2-ene

- 4-bromobut-1-ene
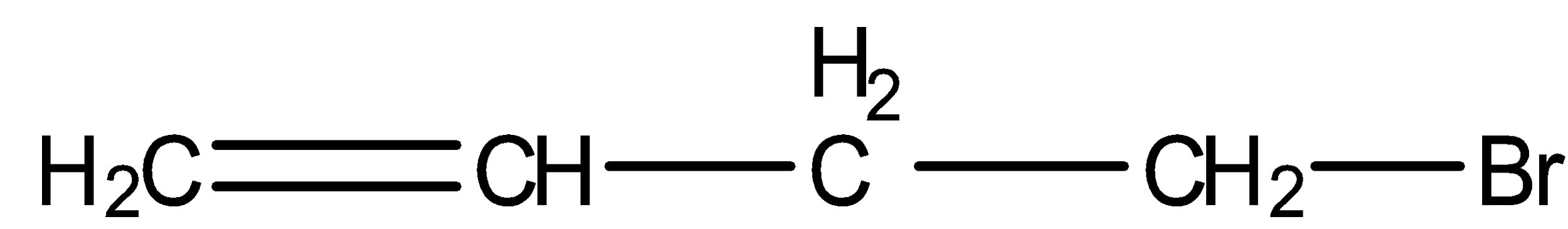
We can see from the above structures that in, 3-bromo-2-methylpropene and 3-bromobut-1-ene, bromine is attached to the $s{p^3}$ -hybridised carbon atom which is next to carbon-carbon double bond or $s{p^2}$ - hybridised carbon. Thus, both 3-bromo-2-methylpropene and 3-bromobut-1-ene are the allylic halides.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and B”.
Additional Information:
One can confuse between allylic halides and vinyl halides. You must know that vinyl halides are the compounds in which the halogen atom is bonded to the carbon atom that is doubly bonded to another carbon atom or we can simply say that, halogen atom is bonded to an $s{p^2}$- hybridised carbon. General formula of vinyl halides is: $C{H_2} = C{H_2} - X$. Here, X is any halogen atom.
Note: It should be noted that the carbon atom bonded to carbon atom that in turn is doubly bonded to another carbon atom is known as allylic carbon. Examples of allylic carbon:


Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




