
Which of the following shows somatogenic reproduction?
(a) Paramecium
(b) Amoeba
(c) Hydra
(d) All of these
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Reproduction is one of the features of living organisms and though it may not be essential for survival, it is of immense importance for the continuity of any species. It is two types based on the number of parents involved.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction is also known as somatogenic reproduction. It is named so because it involves the division of somatic or vegetative parts and not the reproductive part.
Examples of somatogenic reproduction are binary fission, fragmentation, budding, spore formation, etc.
Asexual reproduction is uniparental and it involves various methods such as gemmules, binary fission, budding, fragmentation in plants. Paramecium and Amoeba divide by binary fission. Hydra reproduces by budding
Additional Information: Some features of asexual reproduction are:
-Due to the non-participation of germ cells or sex cells, fertilization doesn’t take place and thus no zygote is formed.
-The progeny produced is morphologically and genetically similar to its parent. Thus, their offspring are often referred to as ‘clones.’
-No genetic diversity is observed as no recombination is involved.
-Mutation takes place at a slow rate.
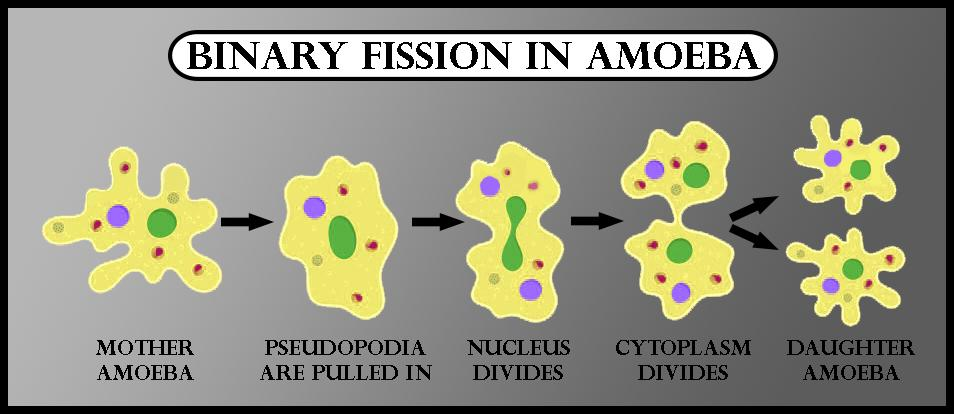
Binary Fission
It is the process of the division of parents into two daughter cells of equal size. During binary fission, the cell elongates, followed by the replication of its genetic material. Later, the nucleus divides into two daughter nuclei which are distributed to two daughter cells through a transverse wall that causes the separation formation from the center to the periphery. Upon separation, the two daughter cells lead a separate life.
Budding:
In this process, the parent cell produces one or more bud-like outgrowths, which upon detachment from the parent cell, grow into a new individual. E.g. Yeasts(fungi) and Hydra(cnidaria).
So, the correct answer is ‘All of these.’
Note: Some other modes of asexual reproduction are:
- Asexual reproduction by gemmules
Gemmules are also known as propagules. They are rich in food and germinate into the new plant on detachment from the parent. E.g. Marchantia.
- Fragmentation:
Upon an accident or through external force, a parent individual breaks down into small pieces or fragments. These pieces later develop into a new individual. fragmentation is usually observed in lower forms like algae, fungi, and lichens during unfavorable conditions.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction is also known as somatogenic reproduction. It is named so because it involves the division of somatic or vegetative parts and not the reproductive part.
Examples of somatogenic reproduction are binary fission, fragmentation, budding, spore formation, etc.
Asexual reproduction is uniparental and it involves various methods such as gemmules, binary fission, budding, fragmentation in plants. Paramecium and Amoeba divide by binary fission. Hydra reproduces by budding
Additional Information: Some features of asexual reproduction are:
-Due to the non-participation of germ cells or sex cells, fertilization doesn’t take place and thus no zygote is formed.
-The progeny produced is morphologically and genetically similar to its parent. Thus, their offspring are often referred to as ‘clones.’
-No genetic diversity is observed as no recombination is involved.
-Mutation takes place at a slow rate.
Binary Fission
It is the process of the division of parents into two daughter cells of equal size. During binary fission, the cell elongates, followed by the replication of its genetic material. Later, the nucleus divides into two daughter nuclei which are distributed to two daughter cells through a transverse wall that causes the separation formation from the center to the periphery. Upon separation, the two daughter cells lead a separate life.
Budding:
In this process, the parent cell produces one or more bud-like outgrowths, which upon detachment from the parent cell, grow into a new individual. E.g. Yeasts(fungi) and Hydra(cnidaria).
So, the correct answer is ‘All of these.’
Note: Some other modes of asexual reproduction are:
- Asexual reproduction by gemmules
Gemmules are also known as propagules. They are rich in food and germinate into the new plant on detachment from the parent. E.g. Marchantia.
- Fragmentation:
Upon an accident or through external force, a parent individual breaks down into small pieces or fragments. These pieces later develop into a new individual. fragmentation is usually observed in lower forms like algae, fungi, and lichens during unfavorable conditions.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




