
Which question converts propene to propan 1-ol?
A.${{H}_{2}}O,{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
B.${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}},{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}},OH$
C.$Hg{{(OAc)}_{2}},NaB{{H}_{4}},{{H}_{2}}O$
D.$Aq.\,KOH$
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: The reagent reacts with the alkenes to give trialkyl bromides. This is now oxidised in the presence of hydrogen peroxide to give us the necessary alcohol. An alkaline medium is used for this reaction.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about the method of preparation of alcohol. Alcohols can be prepared from alkenes by acid reflux followed by hydrolysis. Alkenes react with water in the presence of catalysts. The additional reaction takes place in accordance with Markovnikov’s rule. In this process, the protonation of alkene takes place. The double bond of the alkene reduces and the oxygen of the water forms a positive charge. Now a stable carbocation is formed, where the carbon has a positive charge on it. Now, the free electrons of the oxygen of the water molecule attack the site of the positively charged carbon. A carbon-oxygen bond is formed, where oxygen has positive charge. Finally, it takes up electrons from another water molecule and forms the alcohol.
Protonation of alkene:

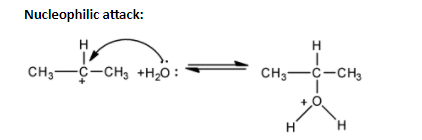
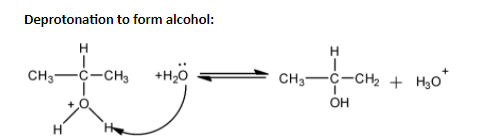
Alcohols can also be produced by hydroboration-oxidation method, where diborane reacts with alkenes to form trialkyl boranes, which is oxidised to alcohol by hydrogen peroxide in an alkaline medium, to give us alcohol. In our question, oxymercuration and demercuration method cannot be used as it converts alkene into alcohols in accordance with Markovnikov’s rule, however there is no rearrangement. Aldehydes and ketones are only reduced to give alcohols, not alkenes. The reducing agents are $Pd/{{H}_{2}},LiAl{{H}_{4}},NaB{{H}_{4}}$. When propene is reacted with ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ along with hydrogen peroxide, then the anti-Markovnikov’s addition takes place and the alcohol group gets attached to the terminal carbon atom.
So, our correct answer is option B.

Note: It is to be noted that during protonation of alkene in the hydrolysis reaction, a less stable carbocation is also formed. However it is the minor product and in that case, some amount of primary alcohol is also formed. In the hydroboration-oxidation reaction, 3 moles of reagent are required.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about the method of preparation of alcohol. Alcohols can be prepared from alkenes by acid reflux followed by hydrolysis. Alkenes react with water in the presence of catalysts. The additional reaction takes place in accordance with Markovnikov’s rule. In this process, the protonation of alkene takes place. The double bond of the alkene reduces and the oxygen of the water forms a positive charge. Now a stable carbocation is formed, where the carbon has a positive charge on it. Now, the free electrons of the oxygen of the water molecule attack the site of the positively charged carbon. A carbon-oxygen bond is formed, where oxygen has positive charge. Finally, it takes up electrons from another water molecule and forms the alcohol.
Protonation of alkene:



Alcohols can also be produced by hydroboration-oxidation method, where diborane reacts with alkenes to form trialkyl boranes, which is oxidised to alcohol by hydrogen peroxide in an alkaline medium, to give us alcohol. In our question, oxymercuration and demercuration method cannot be used as it converts alkene into alcohols in accordance with Markovnikov’s rule, however there is no rearrangement. Aldehydes and ketones are only reduced to give alcohols, not alkenes. The reducing agents are $Pd/{{H}_{2}},LiAl{{H}_{4}},NaB{{H}_{4}}$. When propene is reacted with ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ along with hydrogen peroxide, then the anti-Markovnikov’s addition takes place and the alcohol group gets attached to the terminal carbon atom.
So, our correct answer is option B.

Note: It is to be noted that during protonation of alkene in the hydrolysis reaction, a less stable carbocation is also formed. However it is the minor product and in that case, some amount of primary alcohol is also formed. In the hydroboration-oxidation reaction, 3 moles of reagent are required.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




