
Which type of follicle will rupture to release the egg during ovulation?
Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint: The rupture and release of the dominant follicle from the ovary into the fallopian tube, where it has the potential to become fertilised, is referred to as ovulation. Fluctuating gonadotropic hormone (FSH/LH) levels control the ovulation process. Within the greater Uterine Cycle, ovulation is the third phase (i.e. Menstrual Cycle).
Complete answer:
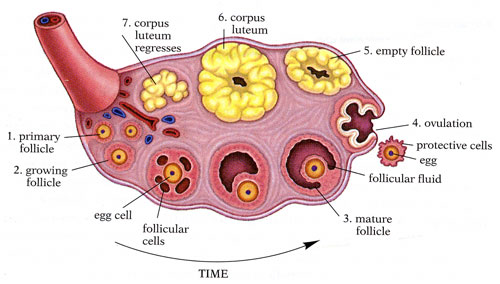
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In humans, this process happens when the ovarian follicles burst and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. During the luteal phase, after ovulation, the egg is ready to be fertilised by sperm. In addition, the endometrium (uterine lining) thickens in order to accommodate a fertilised egg. The uterine lining, as well as blood, will be shed during menstruation if there is no pregnancy.
An oocyte (immature egg cell) will be discharged into the uterine tube after a spike of luteinizing hormone (LH), where it will be fertilised by a male's sperm within 12 hours. Ovulation signifies the end of the ovarian cycle's follicular phase and the beginning of the luteal phase.
The pituitary gland, located in the brain, releases a hormone once a month. This hormone instructs the ovaries to create a number of follicles, which are fluid-filled cysts. The hormone oestrogen is secreted by the follicles as they expand. In order to prepare for pregnancy, oestrogen thickens the uterine wall.
Except for one, the follicles stop growing on day seven of your cycle. This follicle continues to grow and nurture an oocyte (maturing egg).
A blast of oestrogen is released into the bloodstream on day 12 by the growing follicle. The hormone oestrogen circulates in your bloodstream. When oestrogen reaches your brain's pituitary gland, the pituitary gland responds by releasing luteinising hormone. This hormone causes a rapid growth spike in the follicle.
The egg inside the follicle detaches itself just before ovulation. The follicle begins to emit chemicals that cause the neighbouring fallopian tube to close in on the follicle and surround it.
The follicle expands to the point that it bursts open, ejecting the egg and fluid into the abdomen.
Fimbriae, or small finger-like protrusions at the fallopian tube's end, sweep across the burst follicle and pick up the egg. The egg is delivered to the fallopian tube's opening. Muscle contractions propel the egg gently towards the uterus once it is inside the fallopian tube's walls.
On its way through the fallopian tube, the egg will either encounter sperm and fertilise, or it will arrive in the uterus unfertilized and be absorbed back into the body.
Note:-
The pituitary gland in the brain, the ovaries, and the uterus all work together to provide the ideal environment for ovulation (the release of an egg), sperm and egg meeting, and the fertilised egg implanting itself in the uterus. The female reproductive system is a fascinatingly intricate mechanism that involves constant communication between the brain and the ovary. The messengers that govern the monthly cycle are hormones secreted by the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovary.
Complete answer:
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In humans, this process happens when the ovarian follicles burst and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. During the luteal phase, after ovulation, the egg is ready to be fertilised by sperm. In addition, the endometrium (uterine lining) thickens in order to accommodate a fertilised egg. The uterine lining, as well as blood, will be shed during menstruation if there is no pregnancy.
An oocyte (immature egg cell) will be discharged into the uterine tube after a spike of luteinizing hormone (LH), where it will be fertilised by a male's sperm within 12 hours. Ovulation signifies the end of the ovarian cycle's follicular phase and the beginning of the luteal phase.
The pituitary gland, located in the brain, releases a hormone once a month. This hormone instructs the ovaries to create a number of follicles, which are fluid-filled cysts. The hormone oestrogen is secreted by the follicles as they expand. In order to prepare for pregnancy, oestrogen thickens the uterine wall.
Except for one, the follicles stop growing on day seven of your cycle. This follicle continues to grow and nurture an oocyte (maturing egg).
A blast of oestrogen is released into the bloodstream on day 12 by the growing follicle. The hormone oestrogen circulates in your bloodstream. When oestrogen reaches your brain's pituitary gland, the pituitary gland responds by releasing luteinising hormone. This hormone causes a rapid growth spike in the follicle.
The egg inside the follicle detaches itself just before ovulation. The follicle begins to emit chemicals that cause the neighbouring fallopian tube to close in on the follicle and surround it.
The follicle expands to the point that it bursts open, ejecting the egg and fluid into the abdomen.
Fimbriae, or small finger-like protrusions at the fallopian tube's end, sweep across the burst follicle and pick up the egg. The egg is delivered to the fallopian tube's opening. Muscle contractions propel the egg gently towards the uterus once it is inside the fallopian tube's walls.
On its way through the fallopian tube, the egg will either encounter sperm and fertilise, or it will arrive in the uterus unfertilized and be absorbed back into the body.

Note:-
The pituitary gland in the brain, the ovaries, and the uterus all work together to provide the ideal environment for ovulation (the release of an egg), sperm and egg meeting, and the fertilised egg implanting itself in the uterus. The female reproductive system is a fascinatingly intricate mechanism that involves constant communication between the brain and the ovary. The messengers that govern the monthly cycle are hormones secreted by the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




