
Which type of lens always forms a virtual image?
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The concave lens is the diverging lens while the convex lens is the converging lens. Properties of the image formed by concave are exactly opposite to properties of image formed by convex. The image formed by convex is real and downward. The virtual image is formed by extending the refracted lens from the lens.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A concave lens is a diverging lens. In the concave lens, there are three types of rays of light. The first type of ray is the ray of light which is parallel to the principal axis after refraction appears to be coming from the focus.
The second type of ray is the ray of light going towards the optical centre of a concave lens goes straight through without being deviated.
The third type of ray is the ray of light going towards the focus after refraction becomes parallel to the principal axis.
The ray diagram given below contains only two types of ray.
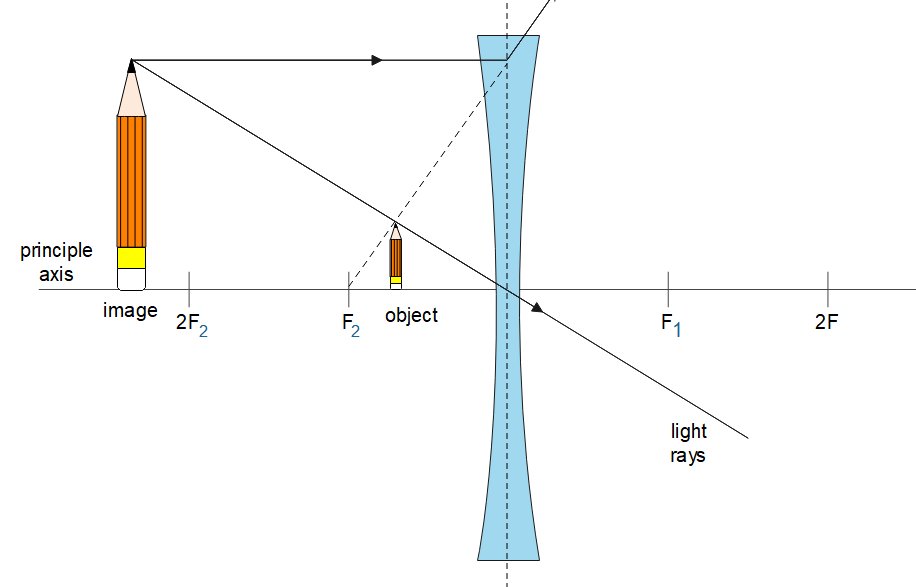
Place a pencil placed in front of a concave lens. First, ray emerges from top of the pencil and on the lens, it refracted and after refraction, it extended towards the backward direction and it appears to come towards a focus that is. Now the ray going toward the optical centre is going straight without being deviated.
The point where the extended ray and second ray meets, there an image of a pencil is formed. The properties of the image are virtual and upright.
Note: The image formed by a concave lens is virtual, upright and diminished. The image is formed between the object and lens. Now if you change the position of an object then you get the image having similar property. So no matter where the object is placed, the property of the image will always be the same i.e. virtual, upright and diminished and it formed between object and lens. But a convex lens has many different cases based on a variety of positions of the object.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A concave lens is a diverging lens. In the concave lens, there are three types of rays of light. The first type of ray is the ray of light which is parallel to the principal axis after refraction appears to be coming from the focus.
The second type of ray is the ray of light going towards the optical centre of a concave lens goes straight through without being deviated.
The third type of ray is the ray of light going towards the focus after refraction becomes parallel to the principal axis.
The ray diagram given below contains only two types of ray.

Place a pencil placed in front of a concave lens. First, ray emerges from top of the pencil and on the lens, it refracted and after refraction, it extended towards the backward direction and it appears to come towards a focus that is. Now the ray going toward the optical centre is going straight without being deviated.
The point where the extended ray and second ray meets, there an image of a pencil is formed. The properties of the image are virtual and upright.
Note: The image formed by a concave lens is virtual, upright and diminished. The image is formed between the object and lens. Now if you change the position of an object then you get the image having similar property. So no matter where the object is placed, the property of the image will always be the same i.e. virtual, upright and diminished and it formed between object and lens. But a convex lens has many different cases based on a variety of positions of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




