
Write about the haplontic and diplontic life cycle with a diagram.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: We had already learned that human beings and other organisms have to undergo a life cycle. In terms of biology, we can say that a succession of variations in the form that an animal experiences, recurring to the preliminary stage, is coined as a biological life cycle. In this duration, they also give life to other creatures of their species. To give experience, they also need to go through specific processes, like meiosis or mitosis.
Complete answer:
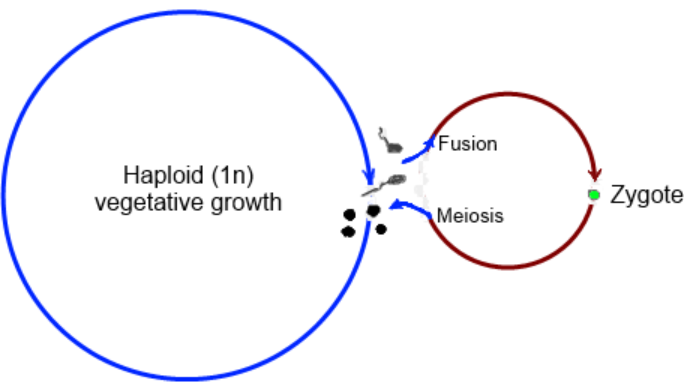
Let’s learn about both the haplontic and diplontic life cycles one after one:
Note: We have perceived that the organisms undergo two types of the biological life cycle. But few microorganisms live in the stage between both kinds of life cycles throughout their lifetime.
A transitional state amid haplontic and diplontic life cycle in which both the sporophyte and gametophyte exist freely and multicellular but have different dominant segments.
For example, Ectocarpus, polyphonic, and kelps.
Complete answer:
Let’s learn about both the haplontic and diplontic life cycles one after one:
| Haplontic life cycle | Diplontic life cycle |
| Such a biological life cycle is seen in microorganisms such as algae (like volvox and spirogyra) etc. | Such type of biological life cycle is observed in plants such as angiosperms and gymnosperms. |
| In this process, the embryo is formed when the zygote undertakes the procedure of meiosis. Besides, the dominant stage in this process is gametophyte. | In this life cycle, the diploid sporophyte is the dominant and independent phase. Moreover, the gametes undergo meiosis. |
| Zygospores are the zygotes that contain a single cell, and they represent the sporophytic phase. | These gametes are haploid, and they are called a gametophyte. The sporophyte is noticeable. |
| On undergoing the process of meiosis, a zygote will lead to the formation of Haploid spores. | Sporophytes are contained by stamens of angiosperms and ovaries. |
| A gametophyte can be formed by every spore, which is in a favorable condition. |

Note: We have perceived that the organisms undergo two types of the biological life cycle. But few microorganisms live in the stage between both kinds of life cycles throughout their lifetime.
A transitional state amid haplontic and diplontic life cycle in which both the sporophyte and gametophyte exist freely and multicellular but have different dominant segments.
For example, Ectocarpus, polyphonic, and kelps.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




