
Write the definition of wavefront.
Answer
528.2k+ views
Hint: When some wave is generated from some source and starts travelling in a particular direction then different points of the wave have different phases. The definition of wavefront arises from the same phase condition for some particular wave.
Complete answer:
Wavefront is defined as the imaginary surface constructed by the locus of all points of a wave that have the same phase, i.e. have the identical path length from the source of that wave.
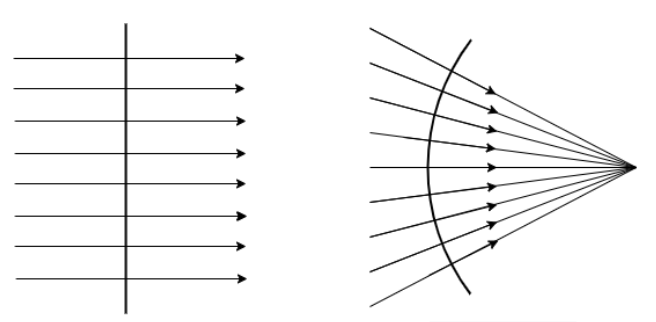
Fig is of Plane wavefront and spherical wavefront
Properties and Explanation:
Wavefront has some interesting properties:
- For an electromagnetic(EM) wave, the wavefront surface is always perpendicular to the ray which denotes the direction of propagation of the EM wave.
- At every point the plane containing electric and magnetic field vectors for an EM wave, is tangential to the wavefront.
- Wavefront is not a stationary object. It propagates along the direction of propagation of the wave with a velocity same as that of the wave.
The nature of the wavefront depends upon the nature of the rays of the wave. For parallel rays, the wavefront is a plane surface, whereas for diverging or converging rays, the wavefront is spherical. If the rays have some varying divergence or convergence, the waveform takes another shape like ellipsoidal or parabolic, depending upon the nature of the source.
Note: Although, wavefront has a definite direction of propagation, it’s not a vector quantity. Rather it’s a time varying function that denotes a surface. The propagation of wavefront can be predicted using Huygens' principle.
Complete answer:
Wavefront is defined as the imaginary surface constructed by the locus of all points of a wave that have the same phase, i.e. have the identical path length from the source of that wave.

Fig is of Plane wavefront and spherical wavefront
Properties and Explanation:
Wavefront has some interesting properties:
- For an electromagnetic(EM) wave, the wavefront surface is always perpendicular to the ray which denotes the direction of propagation of the EM wave.
- At every point the plane containing electric and magnetic field vectors for an EM wave, is tangential to the wavefront.
- Wavefront is not a stationary object. It propagates along the direction of propagation of the wave with a velocity same as that of the wave.
The nature of the wavefront depends upon the nature of the rays of the wave. For parallel rays, the wavefront is a plane surface, whereas for diverging or converging rays, the wavefront is spherical. If the rays have some varying divergence or convergence, the waveform takes another shape like ellipsoidal or parabolic, depending upon the nature of the source.
Note: Although, wavefront has a definite direction of propagation, it’s not a vector quantity. Rather it’s a time varying function that denotes a surface. The propagation of wavefront can be predicted using Huygens' principle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




