
Write the free radical mechanism for the polymerisation of ethene.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: In polymerisation, the type of same monomer or different monomers add together to form a polymer. This process is called polymerisation. However, the free radical addition or chain growth polymerisation is the most common way. The monomer is $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}=\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ or ethene.
Complete answer:
The polymerisation leads to an increase in chain length that can take place through the formation of free radicals. Let us discuss the definition of free radical mechanism and its process and steps involved:
Free radical mechanism: In this, alkenes and its derivatives are polymerized in the presence of a free radical generating initiator like benzoyl peroxide and tert-butyl peroxide. Like, the polymerisation of ethene to polythene occurs by heating a mixture of ethene with a small amount of benzoyl peroxide initiator.
The process occurs in three steps of the alkene chains where the initial step is the chain initiation step, followed by the chain propagation step and at last chain termination step. The sequence of the formation of polythene is:
Step (1): Chain initiation steps: The sequence starts with generating free radical of phenyl formed by the peroxide to the ethene double bond, which breaks the radical thus generating a new free radical and this is called chain initiation step. This takes place like
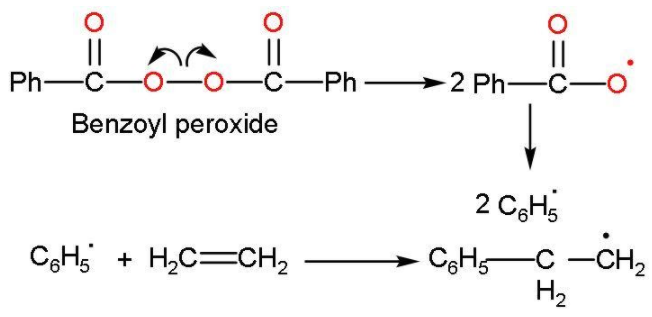
Step (2): Chain propagation step: Now, the radical formed reacts with another molecule of ethene forming a bigger size of radical. The repetition of this sequence with new and bigger radicals carries the following reaction forward. This step is followed as:
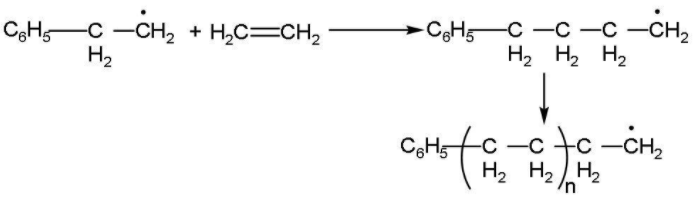
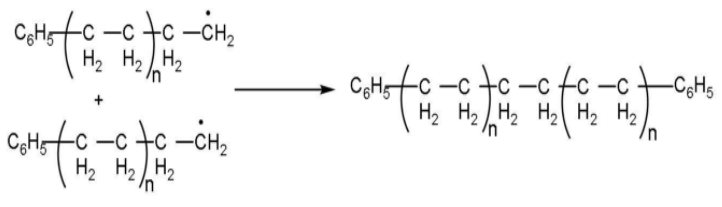
Step (3): Chain terminating step: The product radical thus formed reacts with another radical to form the polymerized product and step is called the chain terminating step. In the termination step, these free radicals can combine in different ways to form polythene. One way of termination of chain is:
Note:
There are two types of polythene formed depending on the type of initiator, catalysts, pressure and temperature.
At high pressure of 1000-2000 atm at temperature 350K-570K in the presence of traces of dioxygen, low density polythene is formed.
At low pressure of 6-7 atm at temperature 333K-343K in the presence of triethyl aluminium and titanium tetrachloride (Ziegler-Natta catalyst), high density polythene is formed.
Complete answer:
The polymerisation leads to an increase in chain length that can take place through the formation of free radicals. Let us discuss the definition of free radical mechanism and its process and steps involved:
Free radical mechanism: In this, alkenes and its derivatives are polymerized in the presence of a free radical generating initiator like benzoyl peroxide and tert-butyl peroxide. Like, the polymerisation of ethene to polythene occurs by heating a mixture of ethene with a small amount of benzoyl peroxide initiator.
The process occurs in three steps of the alkene chains where the initial step is the chain initiation step, followed by the chain propagation step and at last chain termination step. The sequence of the formation of polythene is:
Step (1): Chain initiation steps: The sequence starts with generating free radical of phenyl formed by the peroxide to the ethene double bond, which breaks the radical thus generating a new free radical and this is called chain initiation step. This takes place like

Step (2): Chain propagation step: Now, the radical formed reacts with another molecule of ethene forming a bigger size of radical. The repetition of this sequence with new and bigger radicals carries the following reaction forward. This step is followed as:

Step (3): Chain terminating step: The product radical thus formed reacts with another radical to form the polymerized product and step is called the chain terminating step. In the termination step, these free radicals can combine in different ways to form polythene. One way of termination of chain is:

Note:
There are two types of polythene formed depending on the type of initiator, catalysts, pressure and temperature.
At high pressure of 1000-2000 atm at temperature 350K-570K in the presence of traces of dioxygen, low density polythene is formed.
At low pressure of 6-7 atm at temperature 333K-343K in the presence of triethyl aluminium and titanium tetrachloride (Ziegler-Natta catalyst), high density polythene is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




