
How do you write the orbital diagram for carbon?
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint:. Orbital diagram is the filling of the electrons into different orbitals according to the number of electrons present in an atom and an orbital consists of a maximum of two electrons. Keep in mind that the electrons in an orbital are first singly filled before pairing occurs. Now you can easily draw the orbital diagram for a carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:
- First of let’s discuss the orbital diagram. Orbital diagram involves the distribution of the electrons in the orbitals i.e. s, p , d and f-subshells.
- An orbital can have a maximum of two electrons and the electrons are filled in the orbitals according to the Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity and Pauli’s exclusion principle.
- According to the Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity, electrons are first singly filled in the orbitals before pairing starts i.e. pairing of electrons occurs only after each orbital has been singly filled with the electron.
- On the other hand, according to the Pauli’s exclusion principle, two electrons in an orbital cannot have the same spin quantum number i.e. if one electron is having positive spin i.e. in clockwise direction , then other electron will have negative spin value i.e. in anticlockwise direction.
Now considering the statement:
- Carbon is a non-metal which belongs to the p-block of the periodic table. It occupies the 14th group and 2nd period of the periodic table.
- The atomic number of carbon atoms is 6 and the mass number of oxygen atoms is 12.
- The electronic configuration of carbon atom is as: $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}p_{x}^{1}p_{y}^{1}$.
- The orbital diagram for carbon is as:
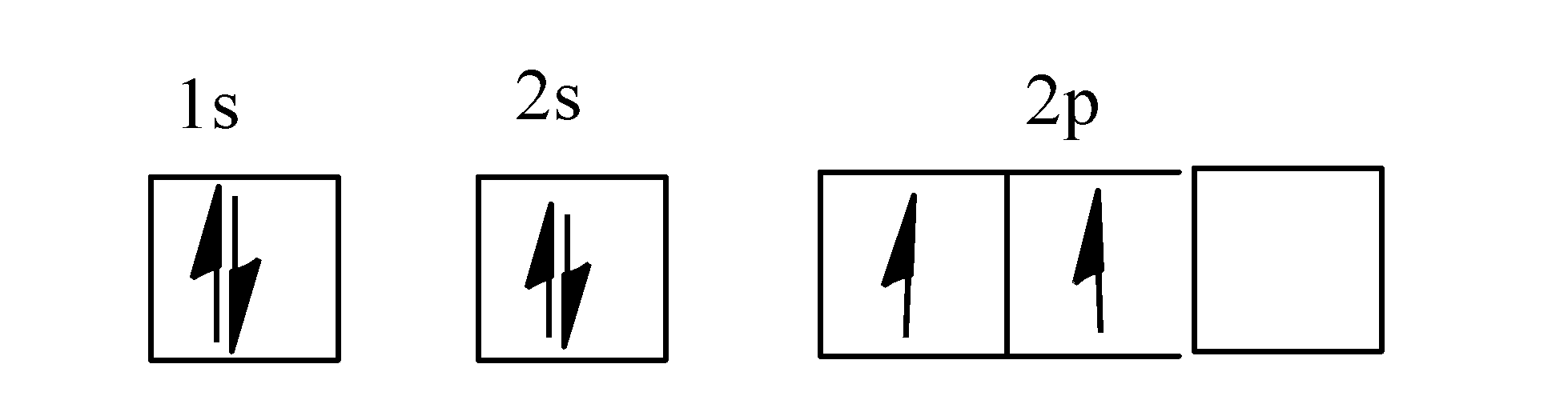
Note: Orbital is the three-dimensional space around the nucleus where probability of finding the electrons is maximum and an orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
- First of let’s discuss the orbital diagram. Orbital diagram involves the distribution of the electrons in the orbitals i.e. s, p , d and f-subshells.
- An orbital can have a maximum of two electrons and the electrons are filled in the orbitals according to the Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity and Pauli’s exclusion principle.
- According to the Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity, electrons are first singly filled in the orbitals before pairing starts i.e. pairing of electrons occurs only after each orbital has been singly filled with the electron.
- On the other hand, according to the Pauli’s exclusion principle, two electrons in an orbital cannot have the same spin quantum number i.e. if one electron is having positive spin i.e. in clockwise direction , then other electron will have negative spin value i.e. in anticlockwise direction.
Now considering the statement:
- Carbon is a non-metal which belongs to the p-block of the periodic table. It occupies the 14th group and 2nd period of the periodic table.
- The atomic number of carbon atoms is 6 and the mass number of oxygen atoms is 12.
- The electronic configuration of carbon atom is as: $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}p_{x}^{1}p_{y}^{1}$.
- The orbital diagram for carbon is as:

Note: Orbital is the three-dimensional space around the nucleus where probability of finding the electrons is maximum and an orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




