
Write the resonance structures for $S{{O}_{3}},N{{O}_{2}},N{{O}_{3}}^{-}$
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: All non-metals form metal oxides with oxygen, which reacts with water that will form acids or with bases forms salts. Most nonmetals form oxoacids from their acidic oxides. Oxides such as sulfur trioxide ( $S{{O}_{3}}$ ) and dinitrogen pentoxide ( ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$ ) are similar to common oxidation numbers, which are known as acidic anhydrides. A set of two or Lewis structures collectively describes the electronic bonding of a single polyatomic species including fractional charges are resonance structures.
Complete step by step answer:
Based on resonance structures of single polyatomic species are capable of describing delocalized electrons that cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula with an integer number of covalent bonds.
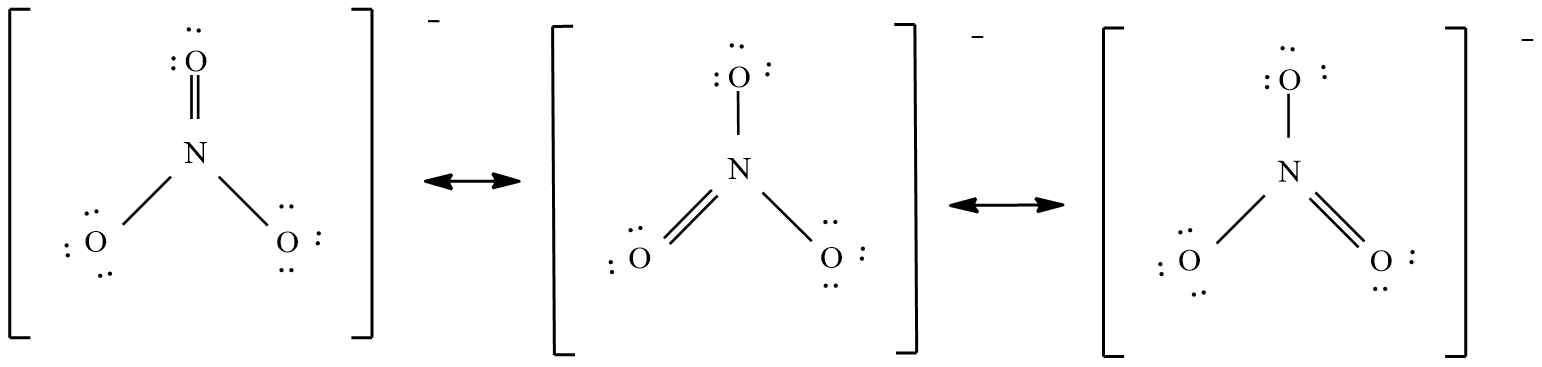
The nitrate ( $N{{O}_{3}}^{-}$ ) ion:
Count the valence electrons
= no of nitrogen atoms x 5 electrons + no of oxygen atoms x 6 electrons + one electron.
= 1 x 5 + 3 x 6 + 1 = 24 electrons
The below diagram shows the bond connectivity and octet electrons to the atoms bonded to the central atom which is the trigonal planar.
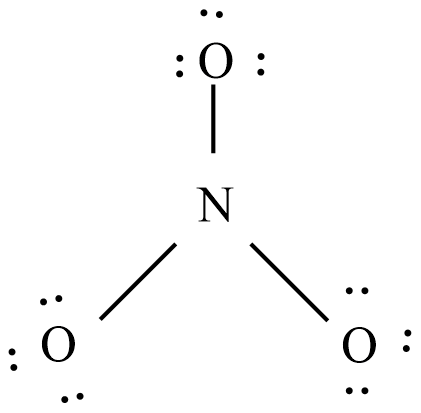
Add multiple bonds to check if the central atom can achieve an octet.
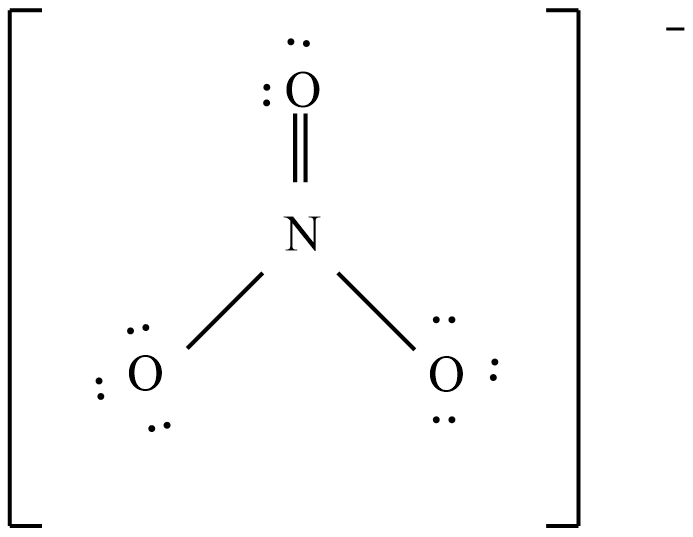
And the possible resonance structures are:
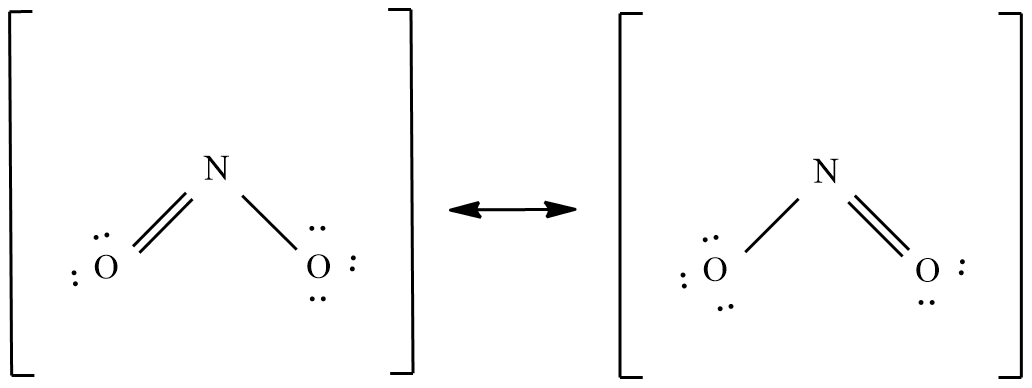
Nitrogen dioxide ( $N{{O}_{2}}$ ):
Nitrogen dioxide contains an odd number of 17 valence electrons and it behaves as a typical odd molecule. It exhibits a resonance structure on dimerization, Nitrogen dioxide converted to stable dinitrogen tetraoxide molecule with an even number of molecules.
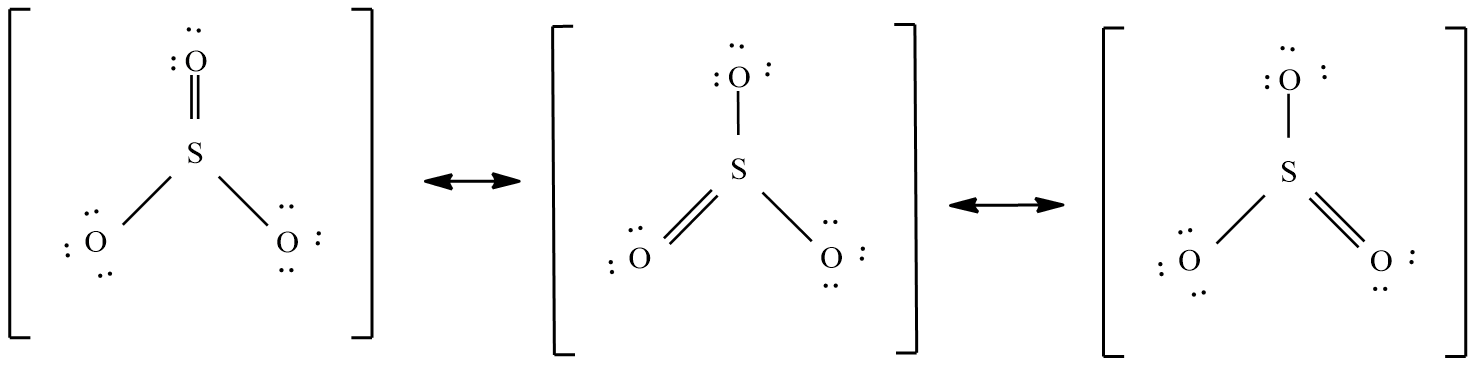
Sulphur trioxide ( $S{{O}_{3}}$ ):
The valence electrons in this molecule = 24 electrons.
The molecular shape is trigonal planar and the possible resonance structure are:
Note: Sometimes Lewis structure is not enough for explaining bonding in some molecules or ions and a single Lewis formula is not sufficient to describe the delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several structures. For example, ozone is an allotrope of oxygen with a V-shaped structure with an O-O-O bond angle of ${{117.5}^{o}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Based on resonance structures of single polyatomic species are capable of describing delocalized electrons that cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula with an integer number of covalent bonds.
The nitrate ( $N{{O}_{3}}^{-}$ ) ion:
Count the valence electrons
= no of nitrogen atoms x 5 electrons + no of oxygen atoms x 6 electrons + one electron.
= 1 x 5 + 3 x 6 + 1 = 24 electrons
The below diagram shows the bond connectivity and octet electrons to the atoms bonded to the central atom which is the trigonal planar.

Add multiple bonds to check if the central atom can achieve an octet.

And the possible resonance structures are:

Nitrogen dioxide ( $N{{O}_{2}}$ ):
Nitrogen dioxide contains an odd number of 17 valence electrons and it behaves as a typical odd molecule. It exhibits a resonance structure on dimerization, Nitrogen dioxide converted to stable dinitrogen tetraoxide molecule with an even number of molecules.

Sulphur trioxide ( $S{{O}_{3}}$ ):
The valence electrons in this molecule = 24 electrons.
The molecular shape is trigonal planar and the possible resonance structure are:

Note: Sometimes Lewis structure is not enough for explaining bonding in some molecules or ions and a single Lewis formula is not sufficient to describe the delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several structures. For example, ozone is an allotrope of oxygen with a V-shaped structure with an O-O-O bond angle of ${{117.5}^{o}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




