
Write two examples of plants with taproots.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Taproots are seen in plants that are dicotyledonous ( having two cotyledons in seed). Taproots are the roots in which the radicle grows primarily with branching into secondary tertiary roots etc. A prominent example of the taproot is mustard (Brassica).
Complete answer:
Taproots are defined as roots in which there is one long thick root known as the primary root from which other roots grow laterally. Two examples of taproots are:
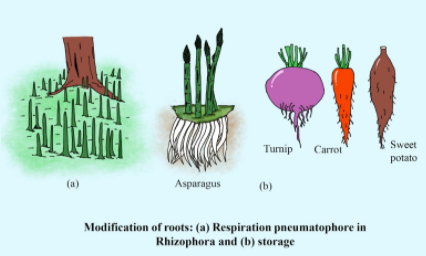
Carrot: Carrot is an example of modification in roots for the storage of food. The root type is known as fusiform as its top is broad and tapers as we go down.
Sweet potato: Sweet potato is also a type of root modification for the storage of food. It is not to be confused with potato which is a modification of stem for food storage.
Additional information:
Other types of roots are mentioned below :
Fibrous roots: This type of root system is found in monocotyledonous plants. Here the radicle is short-lived and is replaced by several small roots arising from the base of the stem. An example includes wheat.
Stilt roots: These roots arise from the base of the stems and provide support to it. Eg- sugarcane
Prop roots: There are the aerial roots of the Banyan tree that come to the ground to give support to the heavy branches of the banyan.
Pneumatophores: These roots come out vertically from the soil for respiration in mangroves. Example- Rhizophora
Note: -The proof to show potato is a stem medication is that potato has buds on it which are only seen in stems.
-Adventitious roots such as prop roots, stilt roots, etc are the roots that arise from a part of the plant that is not radicle.
-The main functions of the root system are the absorption of water and minerals, proper anchorage to the plant, synthesis of plant growth regulators, etc.
Complete answer:
Taproots are defined as roots in which there is one long thick root known as the primary root from which other roots grow laterally. Two examples of taproots are:
Carrot: Carrot is an example of modification in roots for the storage of food. The root type is known as fusiform as its top is broad and tapers as we go down.
Sweet potato: Sweet potato is also a type of root modification for the storage of food. It is not to be confused with potato which is a modification of stem for food storage.
Additional information:
Other types of roots are mentioned below :
Fibrous roots: This type of root system is found in monocotyledonous plants. Here the radicle is short-lived and is replaced by several small roots arising from the base of the stem. An example includes wheat.
Stilt roots: These roots arise from the base of the stems and provide support to it. Eg- sugarcane
Prop roots: There are the aerial roots of the Banyan tree that come to the ground to give support to the heavy branches of the banyan.
Pneumatophores: These roots come out vertically from the soil for respiration in mangroves. Example- Rhizophora
Note: -The proof to show potato is a stem medication is that potato has buds on it which are only seen in stems.
-Adventitious roots such as prop roots, stilt roots, etc are the roots that arise from a part of the plant that is not radicle.
-The main functions of the root system are the absorption of water and minerals, proper anchorage to the plant, synthesis of plant growth regulators, etc.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




