Physics Notes for Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Thermal Properties of Matter Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the core topics covered in the Class 11 Physics Chapter 10: Thermal Properties of Matter Revision Notes?
The Class 11 Physics Chapter 10: Thermal Properties of Matter Revision Notes cover the core topics of temperature, heat, thermal expansion, measurement of temperature, heat transfer methods (conduction, convection, and radiation), specific and latent heat, change of state, Newton’s law of cooling, the ideal gas equation, and practical applications of thermal properties. These concepts are structured to align with the latest CBSE syllabus, providing a concise yet comprehensive summary for quick revision.
2. How are revision notes structured to help with last-minute exam preparation for Thermal Properties of Matter?
Revision notes are arranged according to concept clusters—starting from fundamental properties like temperature and heat, moving to heat transfer mechanisms, followed by key laws and formulae, and ending with application-based points. They provide condensed key points, important formulas, and quick summaries of each section. This order enables students to revise efficiently, connect related ideas, and prioritize high-yield topics, making last-minute preparation focused and effective.
3. What is the best sequence to revise the key concepts in Thermal Properties of Matter Class 11 Notes?
The recommended revision sequence is:
- Start with basic definitions (temperature, heat, heat capacity).
- Review modes of heat transfer (conduction, convection, radiation).
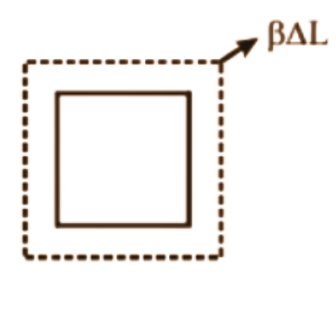
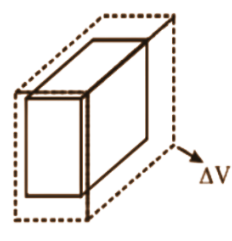
- Move to thermal expansion (linear, area, and volume expansion).
- Cement understanding of fundamental laws like Newton’s Law of Cooling, Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and relevant thermometry.
- Finish with important formulas and application-based examples.
This order builds conceptual understanding before moving to practical problem-solving.
4. Which key formulas should every student revise thoroughly in this chapter for CBSE exams?
Essential formulas include:
- Q = mcΔT (Heat gained or lost)
- c = Q / (mΔT) (Specific heat capacity)
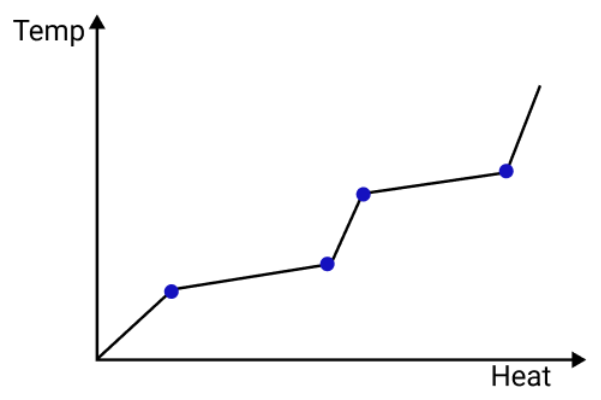
- Q = mL (Latent heat for state change)
- ΔL = αL₀ΔT (Linear expansion)
- Q = kA(T₁-T₂)t/d (Fourier’s Law for conduction)
- P = σAT⁴ (Stefan-Boltzmann Law for radiation)
- dT/dt = -k(T - Tambient) (Newton’s Law of Cooling)
These formulas are frequently tested in numerical and conceptual CBSE exam problems.
5. Why is it important to understand the different methods of heat transfer when revising this chapter?
Knowing the distinct mechanisms of conduction, convection, and radiation allows students to correctly apply theoretical models to practical scenarios and solve exam questions accurately. Each method has unique characteristics, formulae, and real-world relevance, so clarity on these ensures strong conceptual and problem-solving skills for CBSE and entrance exams.
6. How can students connect the chapter's concepts to real-life applications for better retention?
Students should relate concepts such as thermal expansion (e.g., expansion joints in rails), insulation (thermos flasks, bird feathers), and latent heat (steam burns vs. boiling water burns) to everyday phenomena. This contextual understanding aids memory, enhances comprehension, and equips students to answer applied reasoning questions in exams.
7. What common misconceptions should be avoided while revising Class 11 Thermal Properties of Matter?
Students often incorrectly believe that:
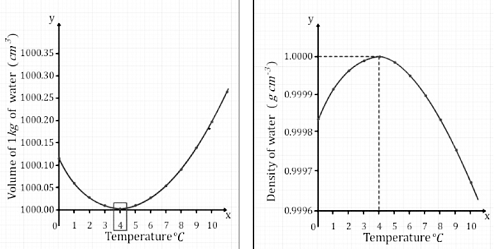
- All substances expand uniformly with temperature (exceptions like water’s anomalous expansion exist).
- Heat and temperature are the same (heat is energy transfer; temperature is a measure of hotness).
- Heat only flows through conduction (convection and radiation are also key, depending on the medium).
Avoiding these misconceptions is essential for mastering both conceptual and numerical CBSE questions.
8. What strategies can help in quickly revising important concepts before the Physics exam?
Use concise summaries, flashcards for formulae, mind maps for connecting concepts, and solve previous years’ short questions. Focus on areas with high exam weightage, inter-link definitions with formulae, and clarify common doubts by discussing with peers or tutors. Regularly self-test using chapter summaries and concept maps to strengthen retention.
9. How do Thermal Properties of Matter Revision Notes differ from NCERT Solutions or Important Questions?
Revision notes provide synopses, concept maps, and key-point summaries for quick understanding and recap, while NCERT Solutions offer stepwise answers to official textbook questions, and Important Questions focus on probable board exam queries. Revision notes connect concepts, highlight interrelations, and serve as a rapid revision aid rather than detailed answer scripts or exam-focused question banks.
10. What areas in this chapter are frequently emphasised for CBSE competitive entrance tests like JEE or NEET?
Exam patterns indicate frequent emphasis on heat transfer numericals, derivations related to Newton’s law of cooling, latent heat applications, and questions connecting the ideal-gas equation to thermal phenomena. Problem-solving involving real-life scenarios and conceptual traps around expansion and heat flow are also common. Prioritising these in revision can give students a competitive edge.