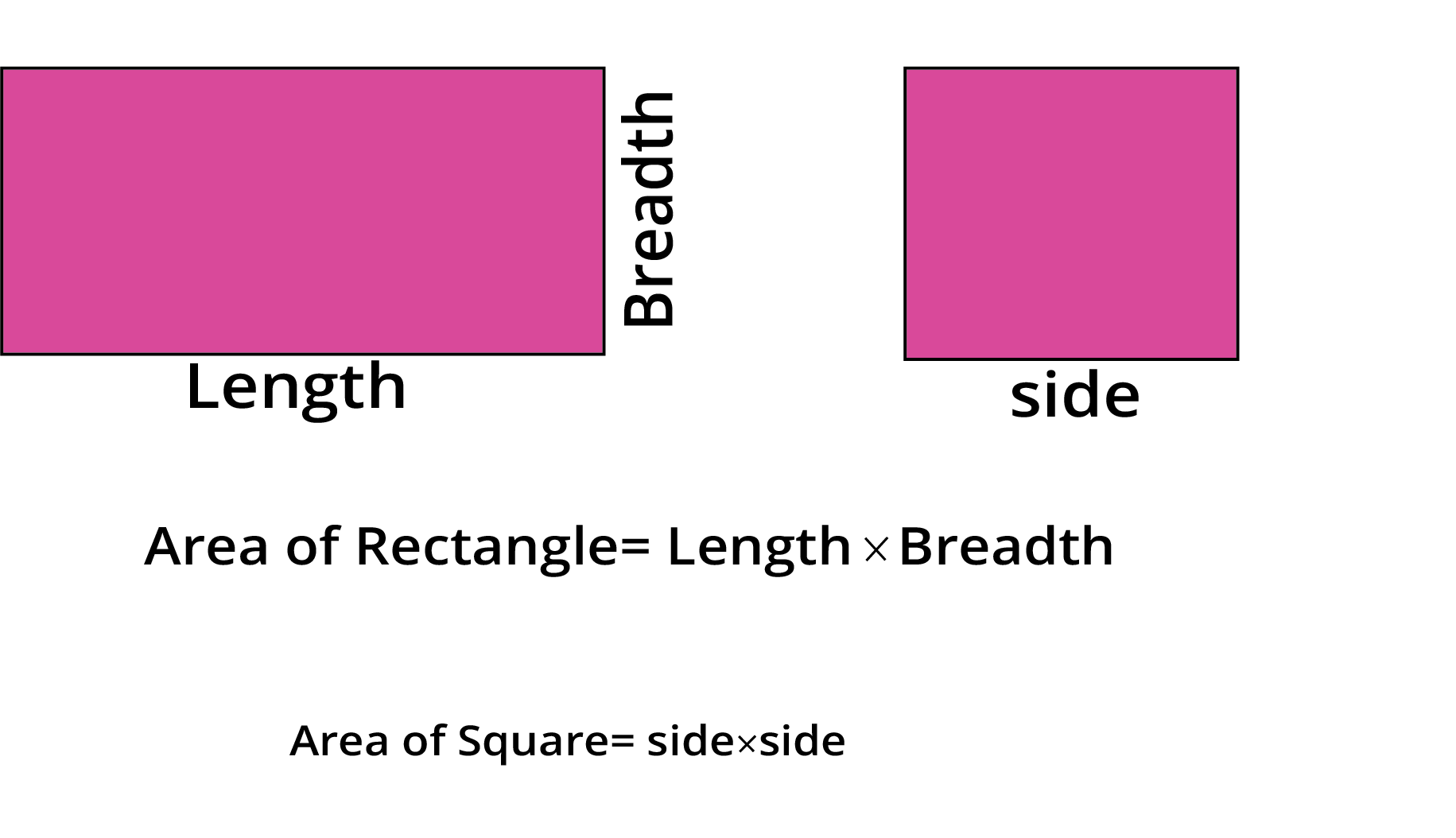Maths Notes for Chapter 11 Area and Its Boundary Class 5 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Area and Its Boundary Class 5 Maths Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the most important concepts to remember from the 'Area and Its Boundary' chapter for a quick revision?
For a quick recap, focus on understanding three main ideas: perimeter (the length of the boundary), area (the space inside the boundary), and the simple formulas for calculating these for basic shapes like squares and rectangles.
2. What is the easiest way to understand the area of a shape?
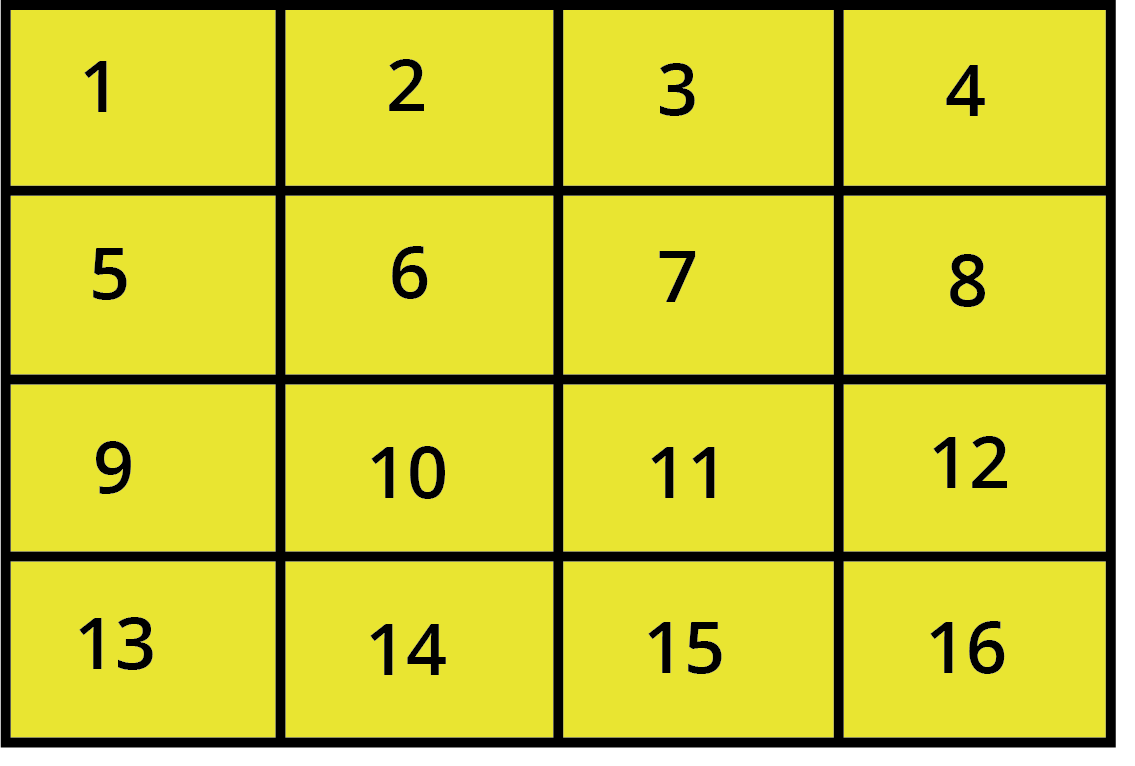
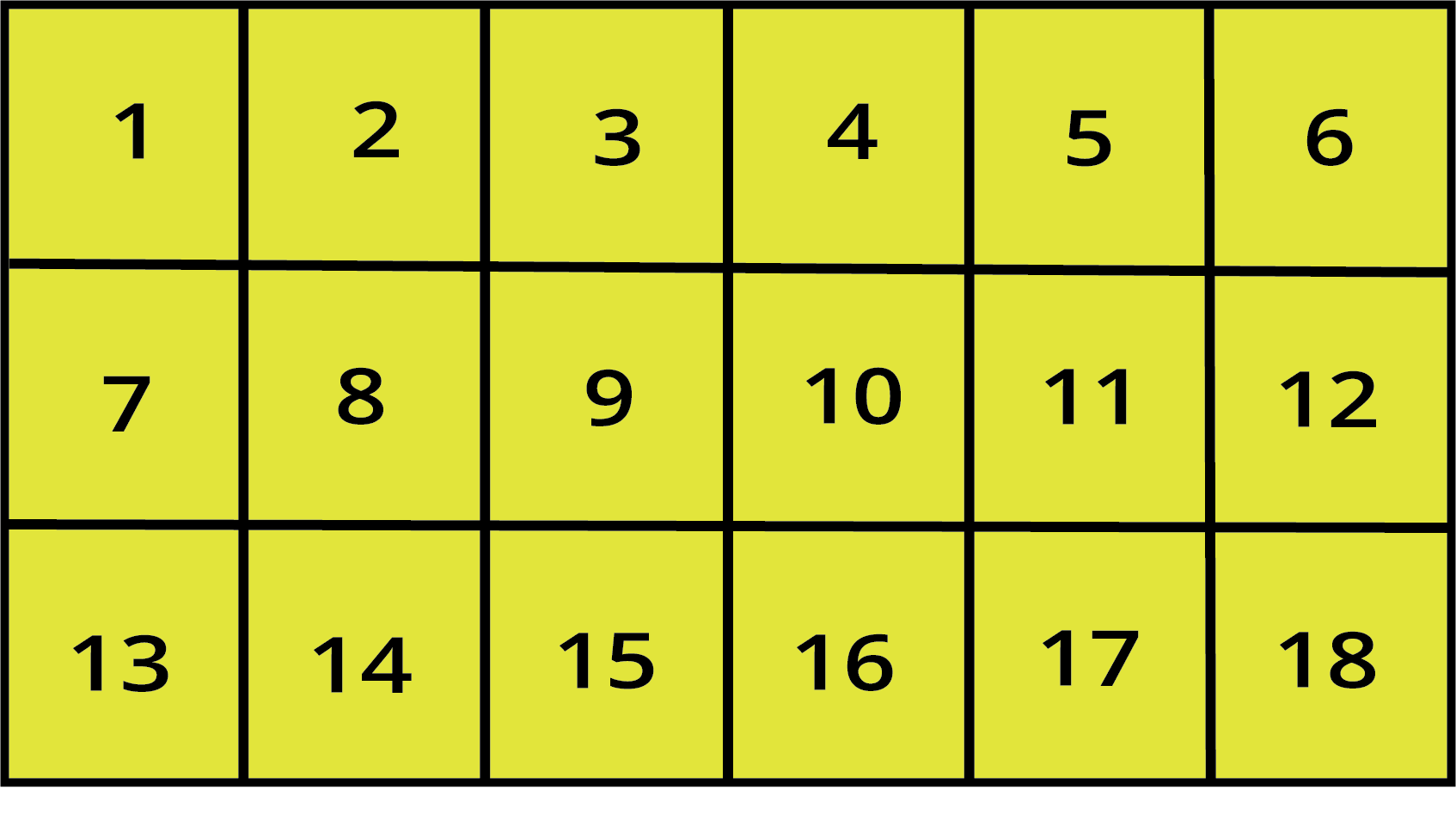
Think of area as the number of small squares that can fit perfectly inside a shape. For a rectangle, you can find this by multiplying its length and breadth. For a square, you multiply the side by itself.
3. How do you find the perimeter of any shape?
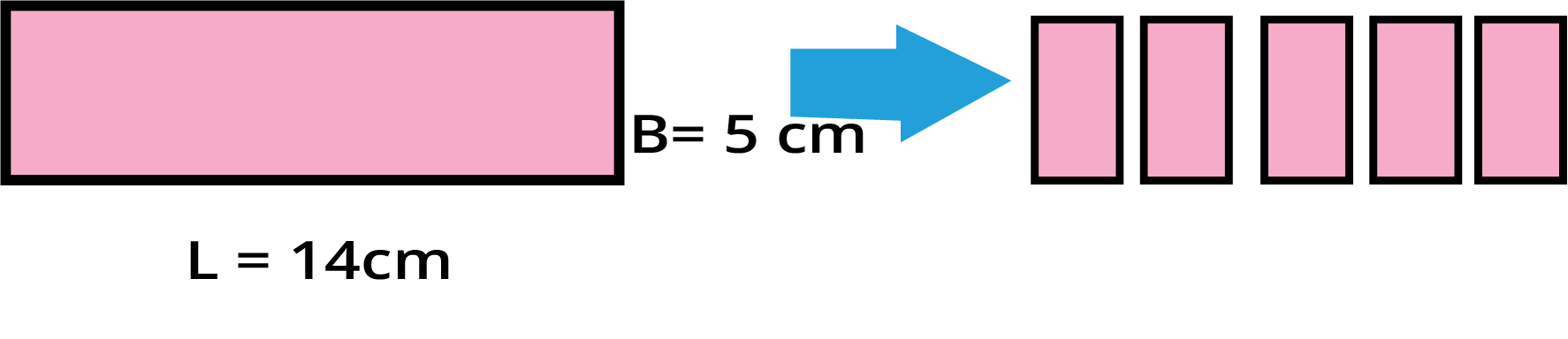
To find the perimeter of any straight-sided shape, you simply add up the lengths of all its sides. For a square, a quick way is to use the formula 4 × length of one side, and for a rectangle, use 2 × (length + breadth).
4. What's the main difference between area and perimeter?
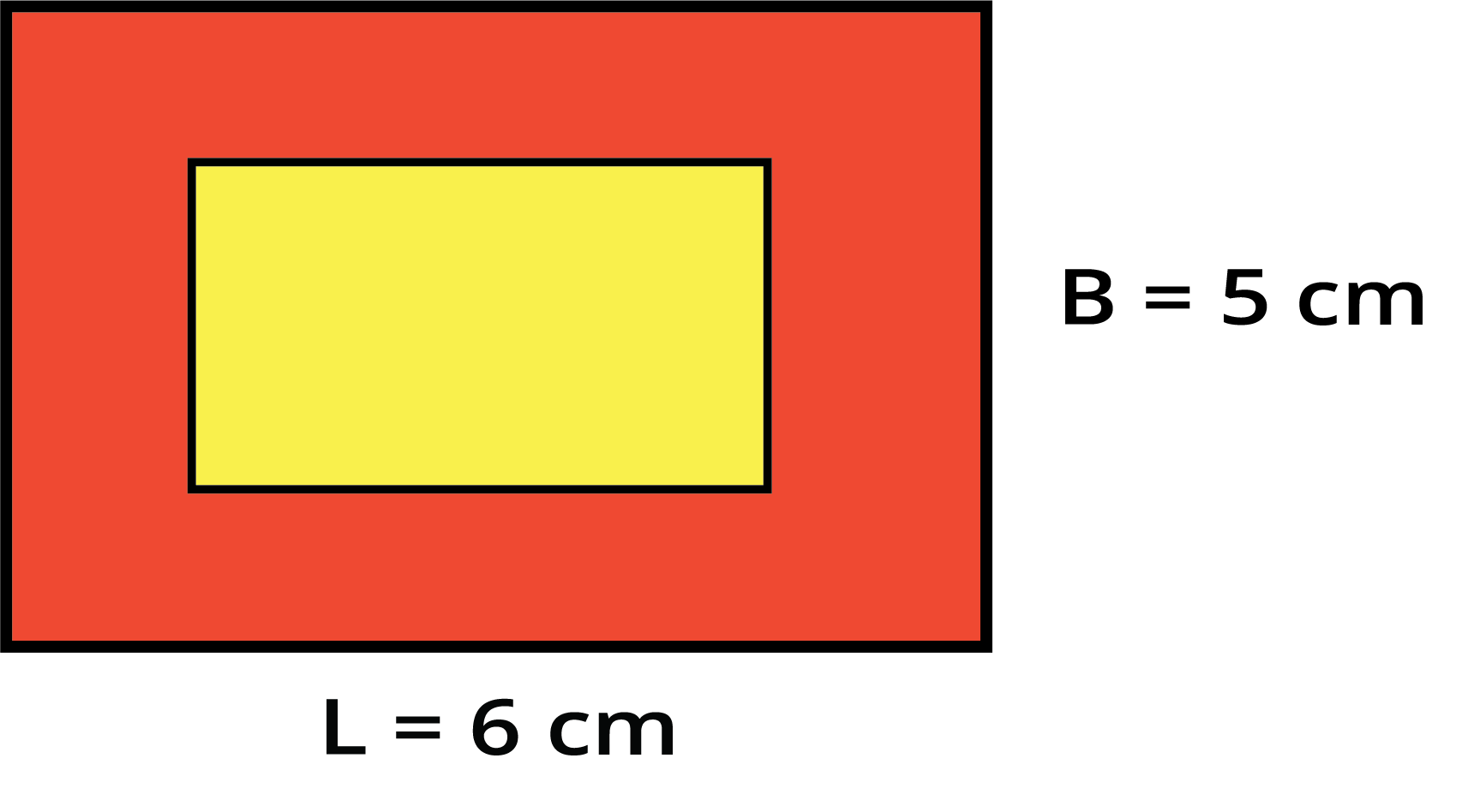
The key difference is what you are measuring. Perimeter measures the total distance around a shape, like a fence around a garden. Area measures the total space inside the shape, like the grass inside the garden. This is why perimeter is in units (cm, m) and area is in square units (sq. cm, sq. m).
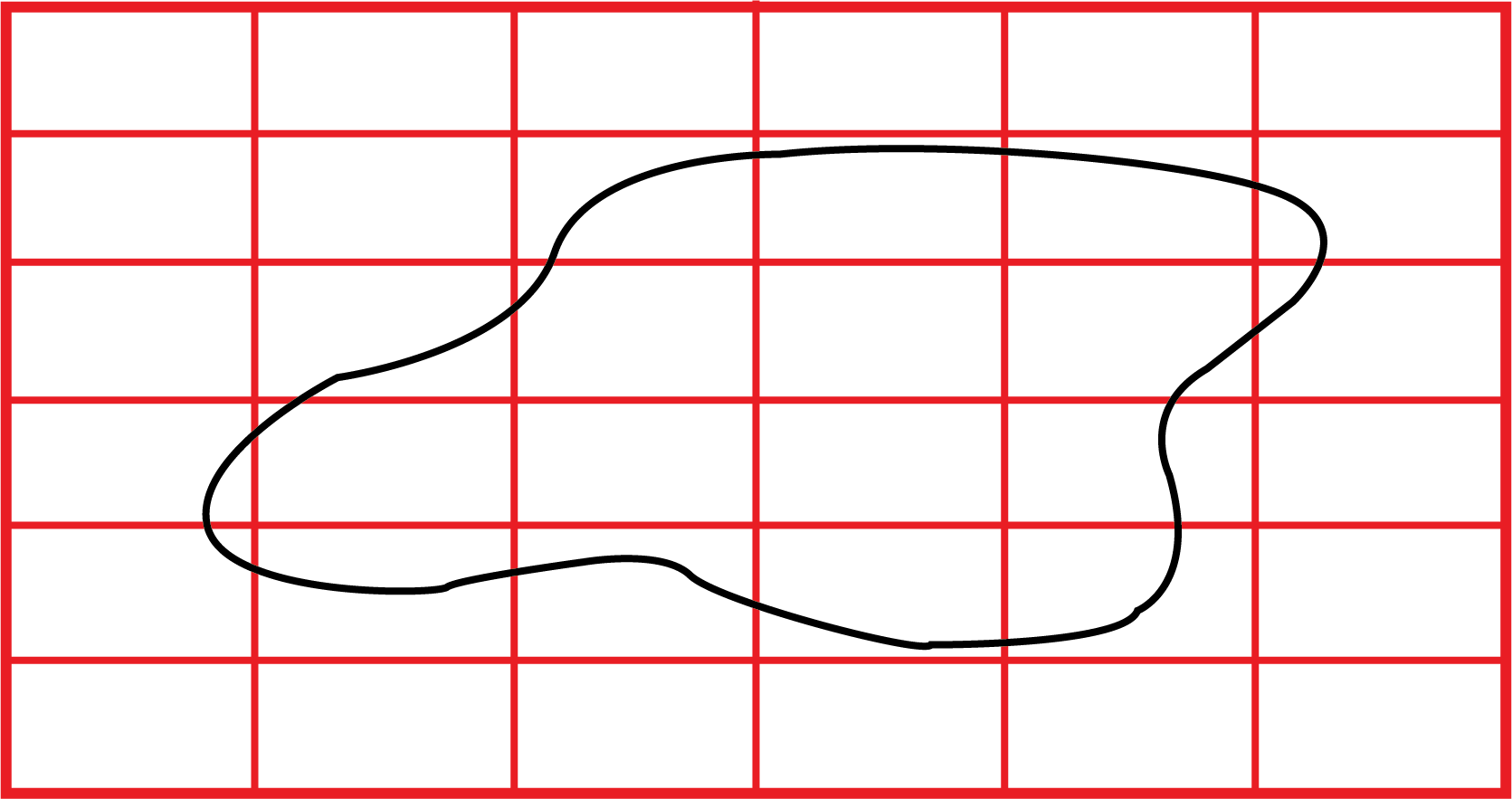
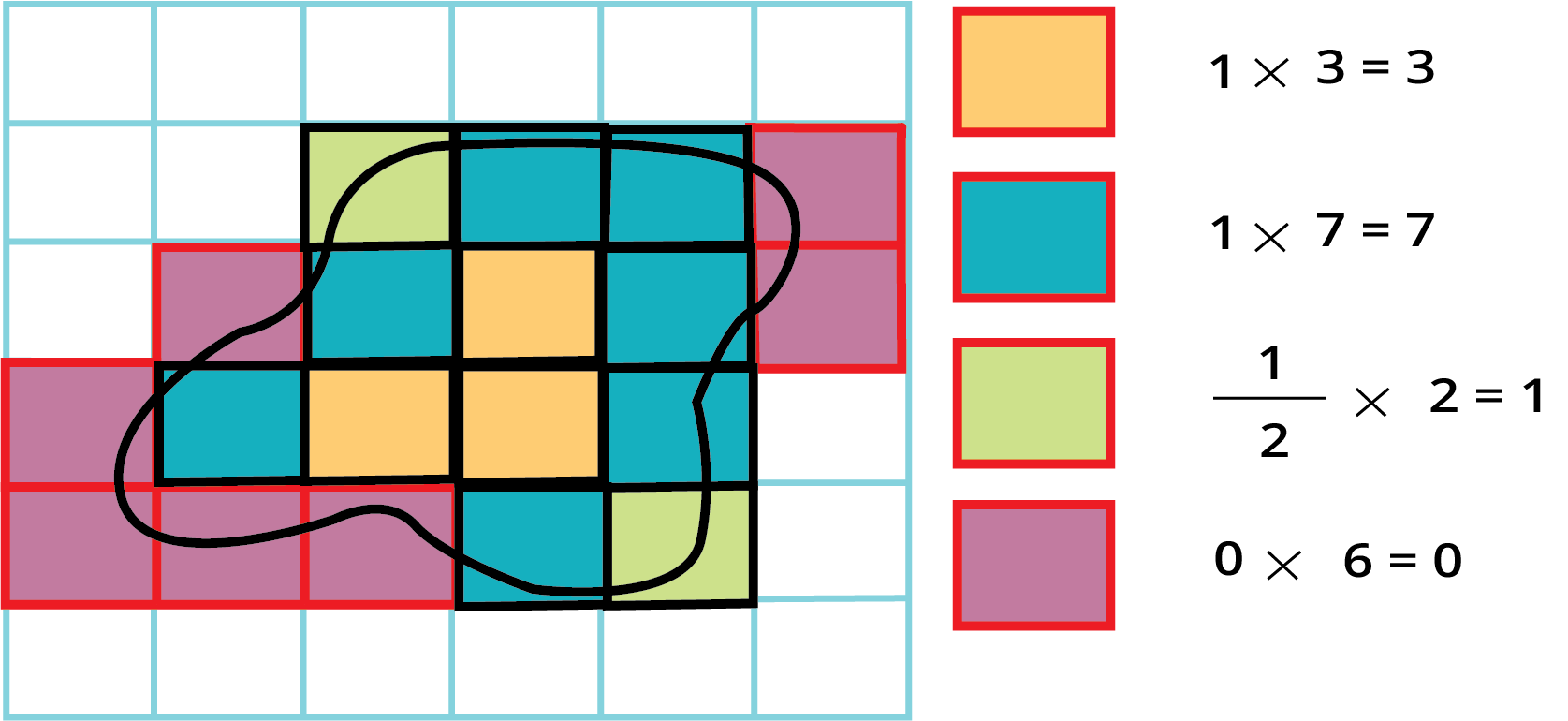
5. How can I find the area of an irregular shape, like a leaf, using the method in this chapter?
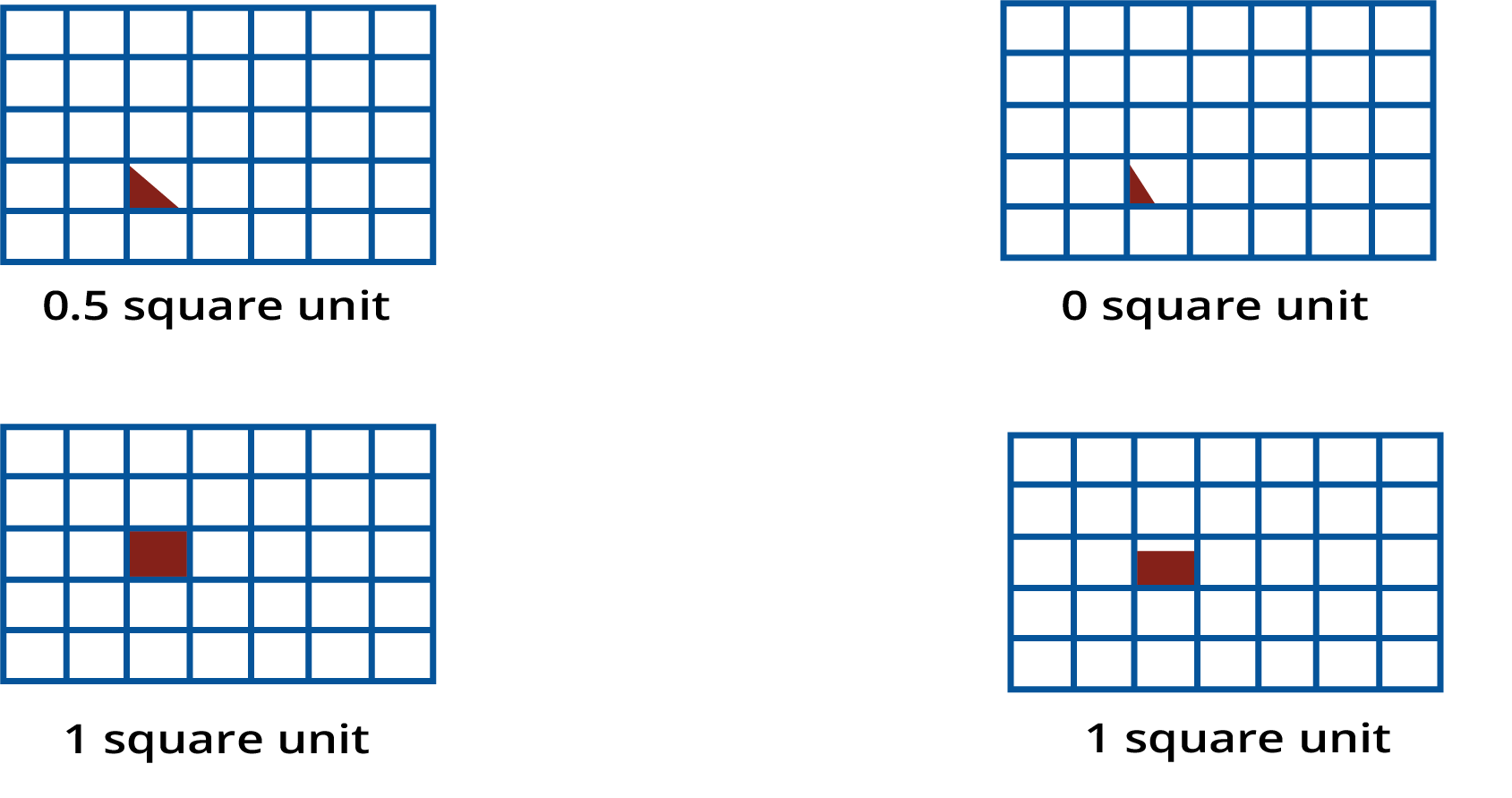
The best way to estimate the area of an irregular shape is by using a square-gridded paper. Place the shape on the grid and count the squares it covers. A simple rule is to count full squares as 1, squares that are more than half-filled as 1, and ignore any squares that are less than half-filled.
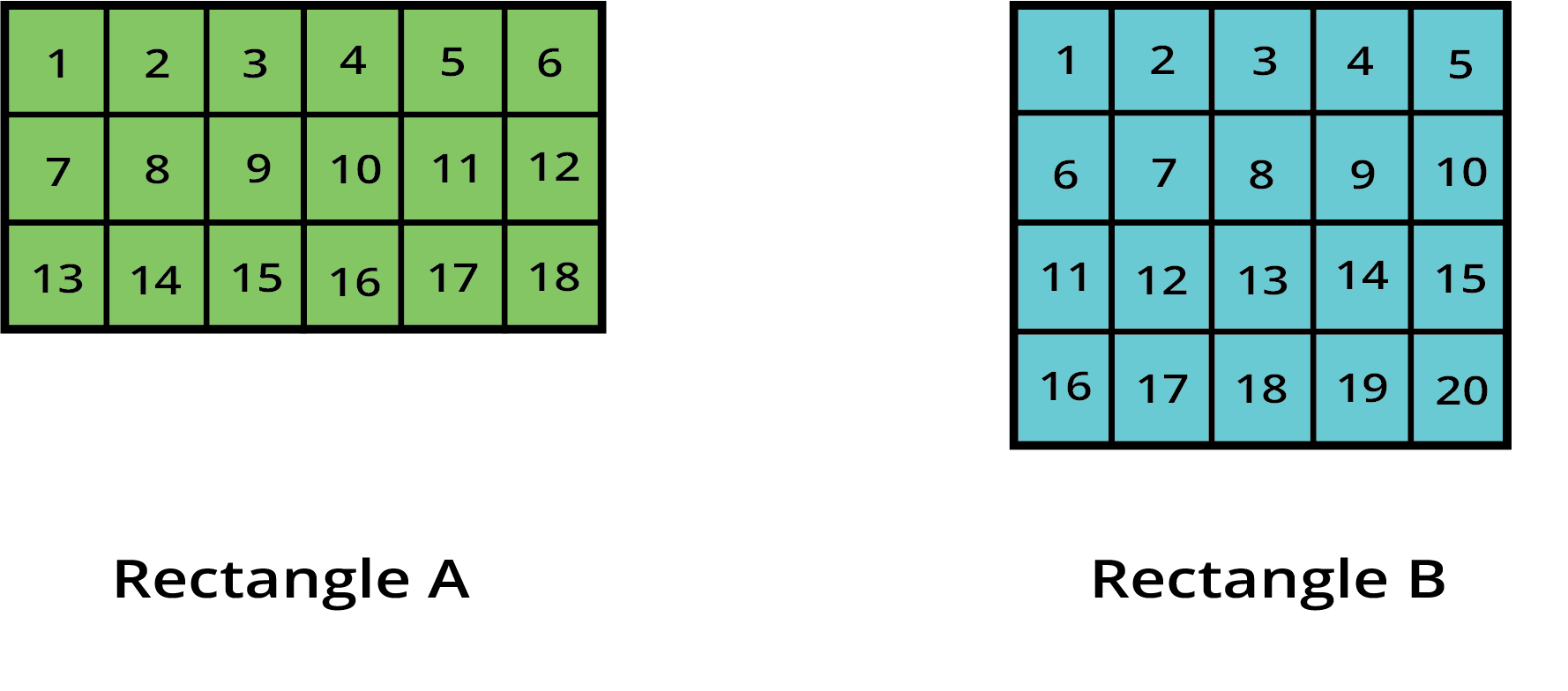
6. If two different rectangles have the same perimeter, will they always have the same area?
No, this is a common point of confusion. Two rectangles can have the same perimeter but very different areas. For example, a long, thin rectangle (like 10 cm by 2 cm) and a more square-like rectangle (like 6 cm by 6 cm) can both have a perimeter of 24 cm, but their areas will be 20 sq. cm and 36 sq. cm, respectively.
7. Why is it so important to use the correct units like 'sq. cm' for area?
Using the correct units is crucial because it shows what you are measuring. Writing 'cm' refers to a simple length (like the perimeter), while 'sq. cm' refers to a two-dimensional space (the area). Getting this wrong can mean your answer is conceptually incorrect, even if the number is right.
8. What is a good strategy to revise this chapter effectively before an exam?
A great way to revise is to first review the definitions of area and perimeter. Then, write down the formulas for squares and rectangles and solve a few practice problems for each. Finally, try drawing a few shapes on paper and finding their area and perimeter to confirm you have understood the concepts well.