Maths Notes for Chapter 11 Surface Areas and Volumes Class 9 - FREE PDF Download
Surface Areas and Volumes Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
FAQs on Surface Areas and Volumes Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts to revise in Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 – Surface Areas and Volumes?
The main concepts to focus on while revising Surface Areas and Volumes Class 9 include:
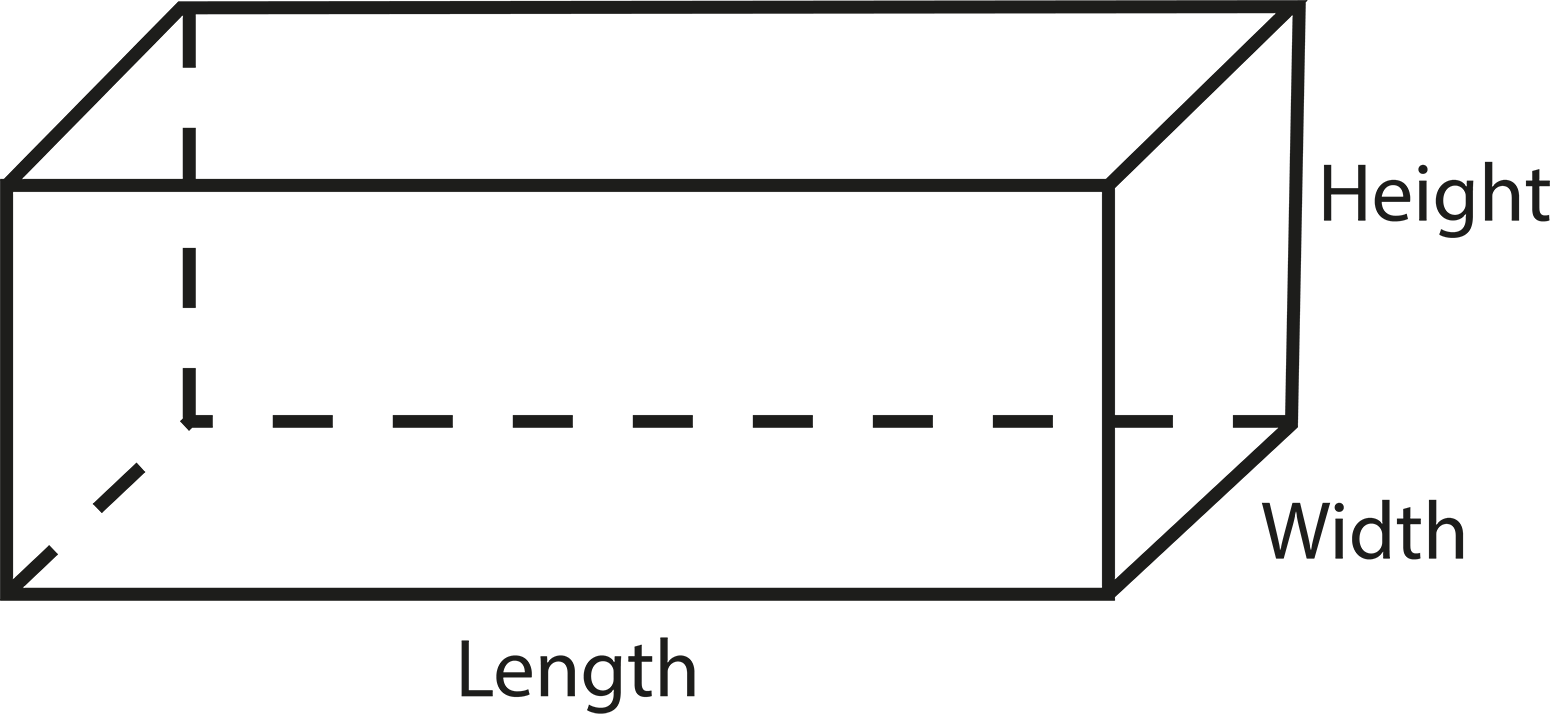
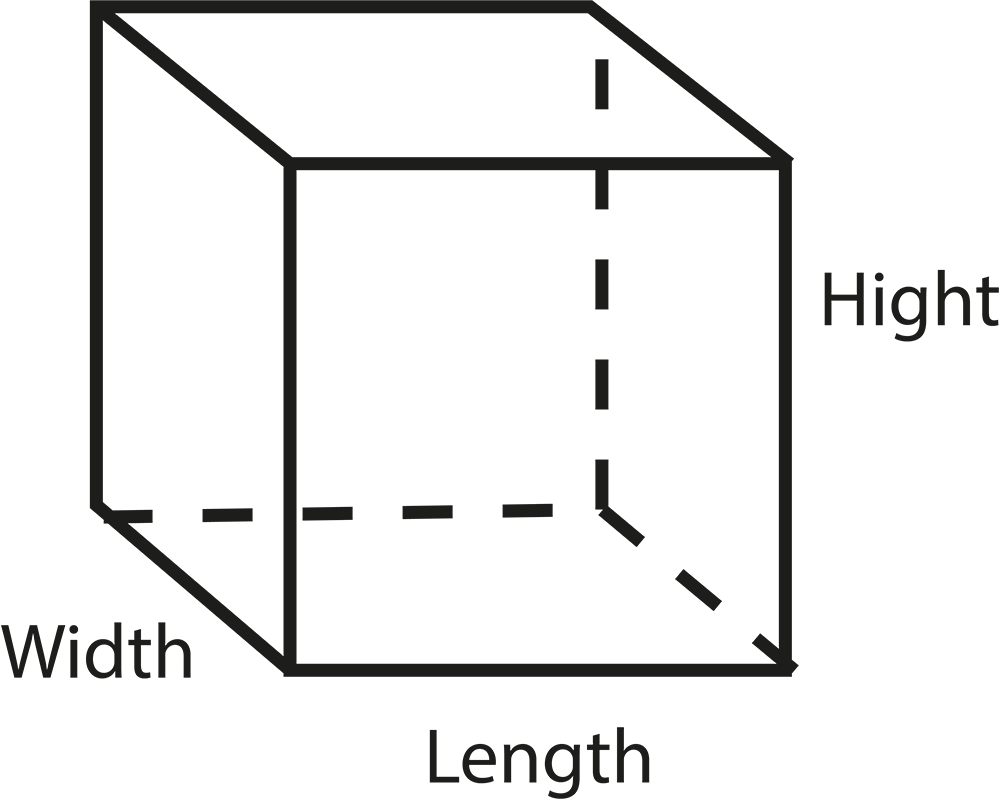
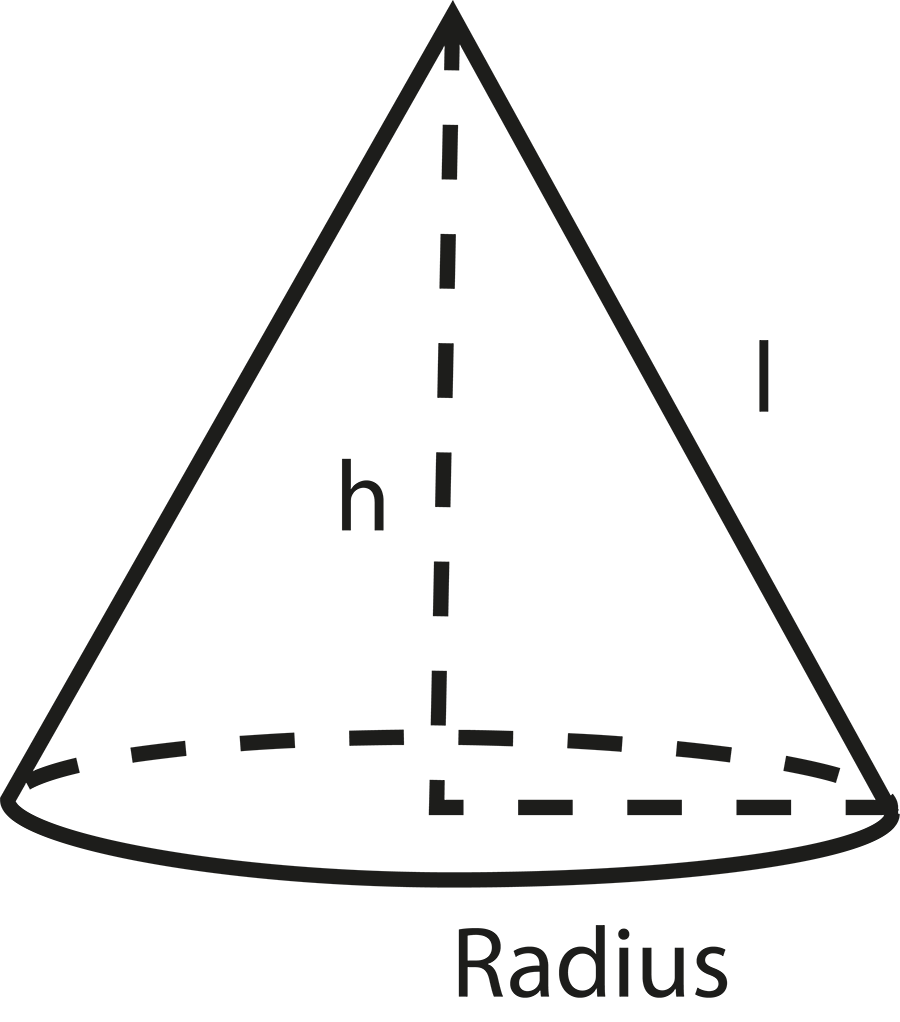
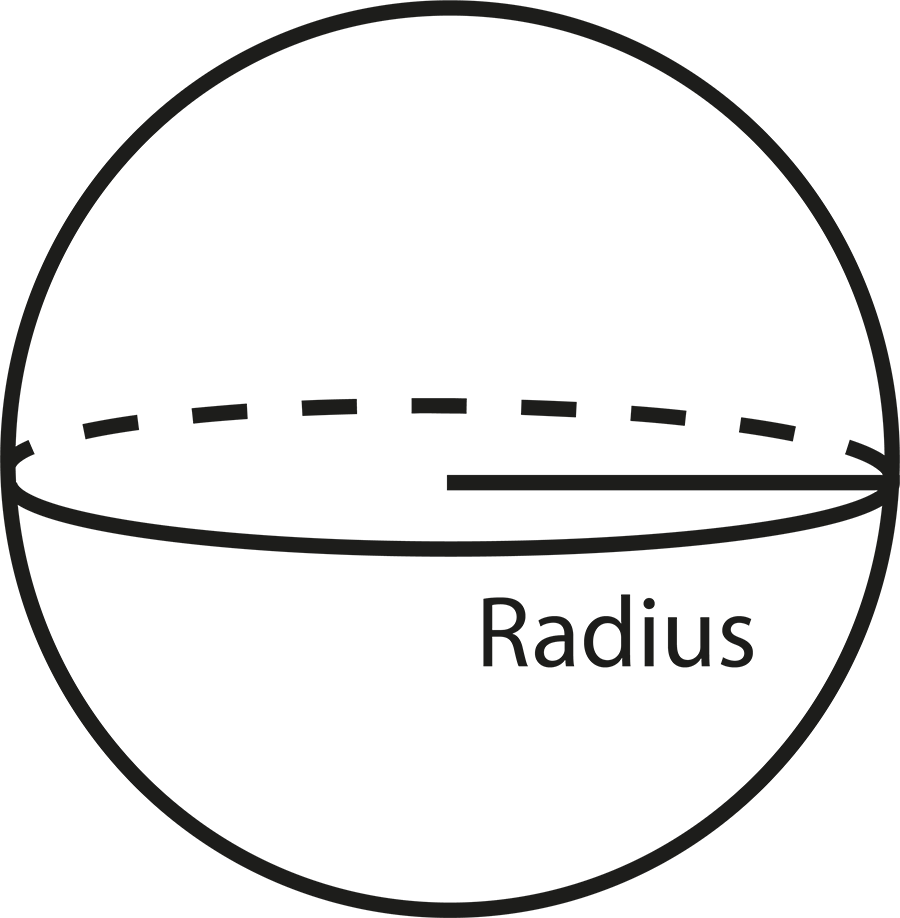
- Definitions of solid shapes: cuboid, cube, cylinder, cone, sphere, hemisphere
- Surface area and volume formulas for each shape
- Difference between lateral/curved surface area (LSA/CSA) and total surface area (TSA)
- Understanding volume as space occupied and surface area as the area covering the object
- Application-based questions involving combinations of solids
2. How can I quickly summarize all the important formulas for surface areas and volumes for revision?
To efficiently revise formulas, create a concept map grouping each shape with its surface areas (CSA/LSA, TSA) and volume. Memorize standard units: surface area in square units and volume in cubic units. Practice by writing the formulas for cube, cuboid, cylinder, cone, sphere, and hemisphere in a table for quick recall before exams.
3. What is the best way to structure my revision for Chapter 11 – Surface Areas and Volumes?
Start by reviewing key terms and definitions. Next, list down all the major formulas for surface area and volume. Then, revise solved examples and important NCERT exercise questions. Lastly, attempt a quick summary sheet and practice a variety of problems to ensure thorough understanding before your exam.
4. What are the connections between surface area and volume in 3D shapes?
Surface area is related to how much material covers a solid, while volume describes the space inside it. Both depend on the measurements of the shape but have different units and applications. For example, a cube with a larger side length will have a surface area that increases as the square of its length and a volume that increases as the cube of its length. Recognizing this helps in solving comparison and application problems.
5. Why is it important to differentiate between curved/lateral surface area and total surface area during revision?
Distinguishing between curved/lateral surface area (CSA/LSA) and total surface area (TSA) is vital because many problems ask specifically for one or the other. CSA/LSA includes only the side, while TSA adds the base(s) or ends. Accurately identifying which surface areas are required prevents calculation errors in competitive and board exams.
6. How can concept maps help in quick revision for Surface Areas and Volumes?
Concept maps visually organize formulas, properties, and relationships between different solids. They help students see connections, improve recall, and revise efficiently before exams. Drawing a concept map for all key formulas and properties makes revision faster and more effective.
7. What types of questions are most likely to appear in exams from this chapter?
Common question types include:
- Direct formula-based calculation of surface area or volume
- Word problems combining two or more shapes
- Questions involving unit conversions
- Problems requiring differentiation between TSA & LSA/CSA
- Application-based HOTS questioning (higher-order thinking)
8. How should I deal with common mistakes while revising Surface Areas and Volumes?
To avoid mistakes:
- Always check units (cm2 vs. m2, cm3 vs. m3)
- Write formulas before substituting values
- Be clear on which surface area is needed
- Practice typical problems where solids are combined or hollow
- Revise by solving previous years’ exam questions
9. What are the most important key terms to know when revising Chapter 11?
Key terms include: surface area, total surface area (TSA), curved/lateral surface area (CSA/LSA), volume, solid, base area, slant height, radius, height, and different 3D shapes such as cube, cuboid, cylinder, cone, sphere, hemisphere, and formulae related to each. Understanding these ensures thorough subject grasp for exams.
10. How can I make revision effective for practical and application-based questions in Class 9 Surface Areas and Volumes?
To revise practical questions, focus on understanding how to interpret real-life scenarios into mathematical models. Practice converting word problems into equations using the right surface area or volume formulas. Attempt questions where objects are combined or hollow, and pay close attention to the units and what is being asked.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video