NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology - Transport in Plants - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 - Transport in Plants solved by expert Biology teachers of Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 11 - Transport in Plants exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths from Vedantu, which are curated by master teachers. Science Students who are looking for Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions will also find the Solutions curated by our Master Teachers really Helpful.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 - TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
Multiple Choice Questions(MCQs)
1. Which of the following statements does not apply to reverse osmosis?
(a) It is used for water purification.
(b) In this technique, pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied to the system
(c) It is a passive process
(d) It is an active process
Ans: (c) It is a passive process
Explanation: Osmosis is a passive process so the water follows down the gradient , but reverse osmosis water molecules go against osmotic pressure due to cumulative pressure gradient, so reverse osmosis requires energy to transport molecules, hence it is an active process. So the correct answer is (c) it is a passive transport
2. Which one of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
(a) Temperature
(b) Light
(c) Wind speed
(d) Chlorophyll content of leaves
Ans: (d) Chlorophyll content of leaves
Explanation: Chlorophyll has no role to play in transpiration. Temperature, light, and wind speed all affect the rate of transpiration because it is determined by evaporation.
3. The lower surface of leaf will have more number of stomata in a
(a) Dorsiventral leaf
(b) Isobilateral leaf
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a) Dorsiventral leaf
Explanation: Dorsiventral leaves face a high rate of transpiration and the transpiration occurs through stomata, so to avoid the percentage of transpiration rate lower surface of the dorsiventral leaves contain more number of stomata and lesser number of stomata in upper surface but In the isobilateral leaf, the number of stomata is the same on both surfaces.
4. The form of sugar transported through phloem is
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Sucrose
(d) Ribose
Ans: (c) Sucrose
Explanation: Sucrose is a disaccharide. It is the most inactive form of sugar so used in transport through phloem to all parts of the plant body.
5. The process of guttation takes place
(a) When the root pressure is high and the rate of transpiration is low.
(b) When the root pressure is low and the rate of transpiration is high
(c) When the root pressure equals the rate of transpiration
(d) When the root pressure, as well as rate of transpiration, are high.
Ans: (a) When the root pressure is high and the rate of transpiration is low
Explanation: Guttation occurs in the absence of transpiration, especially in low light conditions (early morning). Guttation leads to the formation of water droplets on the tips of leaves while transpiration releases water vapour.
6. Which of the following is an example of imbibition?
(a) Uptake of water by root hair
(b) Exchange of gases in stomata
(c) Swelling of seed when put in soil
(d) Opening of stomata
Ans: (c) swelling of seed when put in the soil
Explanation: In fact, the seeds increase enormously in their volume by absorbing water in which the process is referred as imbibition, and the seeds germinate.
7. When a plant undergoes senescence, the nutrients maybe
(a) Accumulated
(b) Bound to cell wall
(c) Translocated
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c) Translocated
Explanation: Nutrient resources are withdrawn or translocated from senescenced parts and are then relocated to other parts of the plant body for optimum use.
8. Water potential of pure water at standard temperature is equal to
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) Zero
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c) Zero
Explanation: Water potential is the free energy present in water. The water potential of pure water at standard temperature is traditionally assumed to be zero.
9. Choose the correct option mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of a fungus with the root system, which helps in
(a) Absorption of water
(b) Mineral nutrition
(c) Translocation
(d) Gaseous exchange
Options:
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) both A and B
(d) both B and C
Ans: (c) both A and B
Explanation: In the higher plant roots association of fungal mycelia is present, this association is called mycorrhiza.. Mycorrhiza plays no role in translocation and gaseous exchange.
10. Based on the figure given, which of the following statements is not correct?
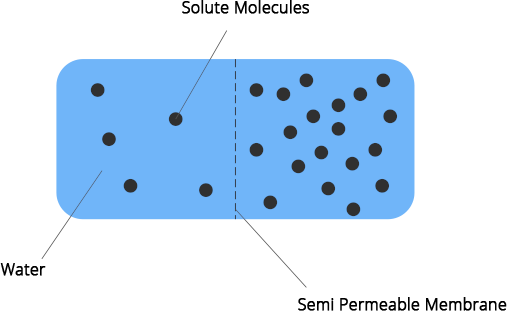
(a) Movement of solvent molecules will take place from chambers A to B.
(b) Movement of solute will take place from A to B.
(c) Presence of a semipermeable is a prerequisite for this process to occur.
(d) The direction and rate of osmosis depend on both the pressure gradient and concentration gradient.
Ans: (b) Movement of solute will take place from A to B
Explanation: The movement of solvent always takes place from high solvent concentration to low solvent concentration. Solute never moves through a semipermeable membrane.
11. Match the following and choose the correct option
Column A | Column B |
A. Leaves | (i) Anti-transpirant |
B. Seed | (ii) Transpiration |
C. Roots | (iii) Negative osmotic potential |
D. Aspirin | (iv) Imbibition |
E. Plasmolyzed cell | (v) Absorption |
(a) A-(ii), B-(iv), c-(v), D-(i), E-(iii)
(b) A-(iii), B-(ii), c-(iv), D-(i), E-(v)
(c) A-(i), B-(ii), c-(iii), D-(ii), E-(v)
(d) A-(v), B-(iv), c-(iii), D-(ii), E-(i)
Ans: (a) A-(ii), B-(iv), c-(v), D-(i), E-(iii)
Explanation: Transpiration mainly takes place through stomata present on the surface of the leaves. 'A' is being matched only with 'ii' only in this option; so the option 'a' is the correct answer.
12. Mark the mismatched pair.
(a) Amyloplast: store protein granule
(b) Elaioplast: store oils or fats
(c) Chloroplasts: contain chlorophyll pigments
(d) Chromoplasts: contain colored pigments other than chlorophyll
Ans: (a) Amyloplast: store protein granules
Explanation: Amyloplasts are the non-pigmented organelles present in only some of the plant cells and their function is to produce and store starch granules by glucose polymerization.
Very Short Answer Questions
1. Smaller, lipid-soluble molecules diffuse faster through the cell membrane, but the movement of hydrophilic substances are facilitated by specific transporters which are chemically _________.
Ans: Proteins
Explanation: Smaller, lipid-soluble molecules diffuse faster through the cell membrane, but the movement of hydrophilic substances are facilitated by specific transporters which are chemically Proteins
2. In a passive transport across a membrane, when two protein molecules move in opposite directions and are independent of each other, it is called as -------.
Ans: Antiport
Explanation: In a passive transport across a membrane, when two protein molecules move in opposite directions and are independent of each other, it is called as Antiport
3. Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion, in which water diffuses across the cell membrane. The rate and direction of osmosis depend upon both ______________.
Ans: Pressure gradient and concentration gradient
Explanation: Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion, in which water diffuses across the cell membrane. The rate and direction of osmosis depend upon both Pressure gradient and concentration gradient
4. A flowering plant is planted in an earthen pot and irrigated. Urea is added to make the plant grow faster, but after some time the plant dies. This may be due to -------.
Ans: Exosmosis
Explanation: A flowering plant is planted in an earthen pot and irrigated. Urea is added to make the plant grow faster, but after some time the plant dies. This may be due to Exosmosis.
5. Absorption of water from soil by dry seeds increases the-------, thus helping seedlings to come out of soil.
Ans: Pressure
Explanation: Absorption of water from soil by dry seeds increases the pressure, thus helping seedlings to come out of soil Pressure.
6. Water moves up against gravity, and even for a tree of 20m height, the tip receives water within two hours. The most important physiological phenomenon which is -------
Ans: Transpiration pull
Explanation: Water moves up against gravity, and even for a tree of 20m height, the tip receives water within two hours. The most important physiological phenomenon which is Transpiration pull
7. The plant cell cytoplasm is surrounded by both cell wall and cell membrane. The specificity of transport of substances are mostly across the cell membrane, because-------.
Ans: Cell membrane is selectively permeable.
Explanation: The plant cell cytoplasm is surrounded by both cell wall and cell membrane. The specificity of transport of substances are mostly across the cell membrane, because Cell membrane is selectively permeable.
8. The $C_4$ plants are twice as efficient as $C_3$ plants in terms of fixing CO₂ but lose only-------as much water as $C_3$ plants for the same amount of CO₂ fixed.
Ans: Half
Explanation: The $C_4$ plants are twice as efficient as $C_3$ plants in terms of fixing $CO_2$ but lose only Half as much water as $C_3$ plants for the same amount of $CO_2$ fixed.
9. Movement of substances in xylem is unidirectional while in phloem it is bidirectional. Explain.
Ans: Leaves carry out photosynthesis and act as a source of food for plants during growth. The phloem supplies food from source to sink, the food stored in the sink are transported toward the growing buds through phloem during spring season. So phloem shows bidirectional movement of food but the transport of water in Xylem is from root to leaves only so the transport in xylem is unidirectional
10. Identify the process occurring in I, II and III
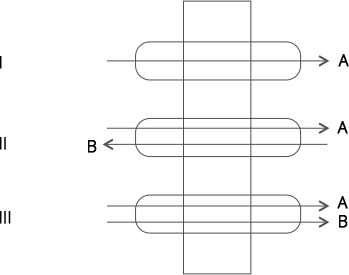
Ans: (I) Uniport, (II) Antiport, (III) Symport
11. Given below is a table. Fill the gaps.
Property Simple diffusion facilitated transport Active Transport
Property | Simple diffusion | Facilitated transport | Active transport |
Highly selective | ………. | Yes | ……. |
Uphill transport | ………. | ……. | Yes |
Requires ATP | ……….. | …….. | ……... |
Ans:
Property | Simple diffusion | Facilitated transport | Active transport |
Highly selective | No | Yes | Yes |
Uphill transport | No | No | Yes |
Requires ATP | No | No | Yes |
12. Define water potential and solute potential.
Ans: The kinetic energy of water is called water potential. Water potential reduces when a solute is dissolved in it. The magnitude of lowering of water potential because of solute is called solute potential.
13. Why is solute potential always negative? Explain $y_w = y_s + y_p$
Ans: When a solute is dissolved in water, it reduces the water potential because water concentration in a solution is less than that in pure water. The measure of reduction in water pollution because of solute is called solute potential. Since solute potential always has a negative impact on water potential, its value is always negative.
$y_w = y_s + y_p$
Here, $y_w$- water potential, $y_s$ - solute potential, and $y_p$ - pressure potential.
14. An onion peel was taken and
(a) Placed in a salt solution for five minutes.
(b) After that it was placed in distilled water.
When seen under the microscope what would be observed in a and b?
Ans: In the case of 'a', the cells of the onion peel would lose water. This will show shrunk cells in the microscope.
In the case of 'be, the cells of onion peel would gain water. This will show normal cells in the microscope.
In both the cases, movement of water takes place because of an osmotic gradient.
15. Differentiate between Apoplast and Symplast pathways of water movement. Which of these would need active transport?
Ans:
Apoplast Pathway | Symplast Pathway |
(i) The intercellular gaps and cell walls are the only places where water can travel apoplastically. | (i) The symplastic movement of water occurs through the cells—their cytoplasm, intercellular movement is through the plasmodesmata. |
(ii) The apoplast pathway does not provide any barrier to water movement. | (ii) The symplast pathway provides a little barrier to water movement. |
(iii) It consists of the nonliving parts of the plant body. | (iii) It consists of living parts of the plant body. |
(iv) Movement of water in this pathway is faster. | (iv) Movement of water in this pathway is relatively slower. |
Active transport is not required by any of these pathways.
16. How does most of the water move within the root?
Ans: Water moves within the root through the apoplast pathway as the cortical cells are loosely packed. Only a small portion of water moves through the symplast pathway. The Casparian strip prevents water movement through the apoplast pathway.so here, the symplast pathway is the preferred pathway for movement of water.
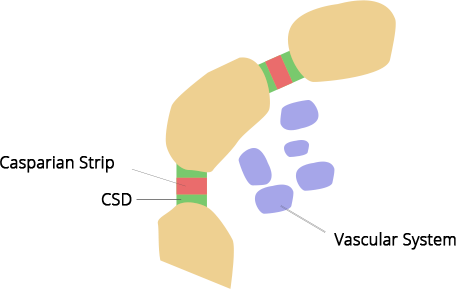
17. Give the location of the Casparian strip and explain its role in the water movement.
Ans: The Casparian strip is present at the boundary of the endodermis. It is made up of suberin. The Casparian strip is impervious to water, and thus, water cannot enter it through the apoplast pathway. Water needs to enter the vascular bundle through the symplast pathway.
18. Differentiate between guttation and transpiration.
Ans:
Transpiration | Guttation |
(i) Loss of water through the stomata is called transpiration. | (i) Loss of water through leaf apex is called guttation. |
(ii) Facilitated by evaporation. | (ii) Facilitated by root pressure. |
(iii) Takes place in most of the plants. | (iii) Takes place in grasses only. |
(iv) Takes place throughout the day; in the sunshine. | (iv) Takes place early in the morning. |
19. Transpiration is a necessary evil in plants. Explain.
Ans: Transpiration even though it causes loss of a large amount of water from the plant body, stopping of growth and also causes leaves wilting, if occurs in more than a required quantity but also helpful and necessary in removing excess amount of water from the plant body, to maintain negative pressure for the ascent of sap in xylem by producing suction pressure, to help in cooling of plant body, to make minerals and water available for all parts of plant body and also very important for the proper growth of the plant. Considering all these we can say that even though the transpiration is affecting the plant on the same hand it is necessary for the plant for their development,Hence transpiration is called as necessary evil
20. Describe briefly the three physical properties of water which helps in ascent of water in xylem.
Ans: Following are the three physical properties of water that help in the ascent of water in the xylem.
Cohesion: It is the ability of water molecules to stick to each other.
Adhesion: It is the ability of water molecules to stick to a surface.
Surface Tension: The property of any liquid that tends to occupy the smallest possible surface area is called surface tension. Water makes a continuous column of water in the xylem vessels by adhesion cohesion and surface tension. Transpiration pull, pulls this water as a column .
21. A gardener forgot to water a potted plant for a day during summer, what will happen to the plant? Do you think it is reversible? If yes, how?
Ans: In the days of summer, watering is not done for a day for a potted plant, it will show wilting of leaves. This condition occurs because of excess water loss by transpiration. Yes this process is reversible only by watering the plant within a certain period of time. If the watering is delayed for a longer period of time, it cannot be reversible.
22. Identify a type of molecular movement which is highly selective and requires special membrane proteins, but does not require energy.
Ans: Highly selective,requirement of special membrane protein and does not require energy, this type of molecular movement is called facilitated diffusion. Any substance diffusion across a membrane depends on its soluble ability in lipids. The substance with hydrophilic moiety cannot diffuse through a membrane. So special membrane proteins are present to facilitate the diffusion of such molecules, here also diffusion occurs from higher to lower concentration and so ATP. Facilitated diffusion depends on transporter proteins as it is highly selective.
23. Correct the statements
(a) Cells shrink in hypotonic solutions and swell in hypertonic solutions.
Ans: Cells swell in hypotonic solutions and shrink in hypertonic solutions.
(b) Imbibition is a special type of diffusion when water is absorbed by living cells.
Ans: Imbibition is a particular type of diffusion when water is absorbed by solids – colloids.
(c) Most of the water flow in the roots occurs via the symplast.
Ans: Most of the water flow in the roots occurs via the apoplast.
Short Answer Questions
1. Minerals absorbed by the roots travel up the xylem. How do they reach the parts where they are needed most? Do all the parts of the plant get the same amount of the minerals?
Ans: Minerals are transported to the required parts of the plant body. Once when the minerals enter the xylem, transpiration pull helps in their transportation. These minerals are transported passively and they enter the cell by active transport. More minerals are transported to the young and growing parts of the plant as they require more minerals for their growth
Minerals are also translocated from the senescent or old parts of the plant to required parts or to the young storage parts of the plant body, Hence optimum use of minerals takes place.
2. If one wants to find minerals and in the form, they are mobilized in the plant, how will an analysis of the exudate help?
Ans: The form and ways of mineral transport in plants were recognized by the analysis of xylem exudates. For an example the xylem exudate analysis has shown that nitrogen is carried out as inorganic ions but much of it is carried as organic form as amino acids and related compounds. Similarly, organic compounds are also carried as phosphorus and sulphur in smaller amounts. There is some amount of materials exchanged between xylem and phloem. Hence it is not respectively that Xylem and phloem transport only inorganic and organic compounds.
3. From your knowledge of physiology can you think of some method of increasing the life of cut plants in a vase?
Ans: The life of a cut plant can be increased by following methods:
(a) Put the cutted plant immediately in the water .
(b) Adding the required mineral nutrients to the water containing cutted plant.
(c) Cytokine(hormone) spray helps in extending the life of the cutted plant.
4. Do different species of plants growing in the same area show the same rate of transpiration at a particular time? Justify your answer.
Ans: Transpiration takes place through stomata. Transpiration factor is mainly dependent on the number of stomata, percent of open stomata, water availability and structure of canopy etc. these factors may differ in different plants. So the different plant species in the same area cannot show the same transpiration rate. It may differ in different species at a particular time.
5. Water is indispensable for life. What properties of water make it useful for all biological processes on the earth?
Ans: The properties of water make it useful for all biological processes on the earth are:.
(i) Water can dissolve most of the substance and hence it is Universal Solvent and also water is a major component of the cells so it is an important ingredient of the cells.
(ii) In some of the animals like frogs and fishes which conduct external fertilization, water is the main source of medium for the male gamete to reach the female gamete.
(iii) Aquatic organisms also require oxygen for breathing So water helps them by dissolving the oxygen
(iv) In aquatic plants, water acts as the pollination agent.
(v) Water also helps in maintaining the temperature in living beings by attaining a cooling effect .
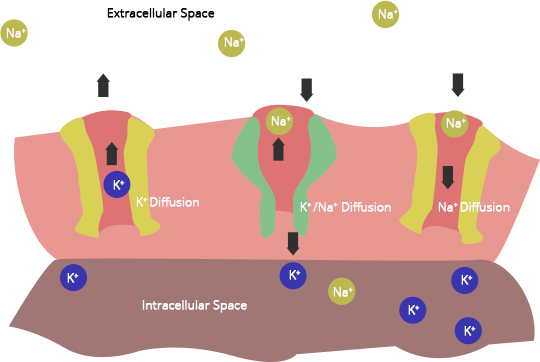
6. How is it that the intracellular levels of ${K}^{+}$ are higher than extracellular levels in animal cells?
Ans: If the membrane potential of a quiescent cell is relatively static which is called resting potential. When a cell membrane is in resting potential, then intracellular levels of ${K}^{+}$ are higher than extracellular levels in animal cells. This is brought about by ${Na}^{+}/{K}^{+}$ - ATPase, which is also called sodium/proton pump. This pump makes ${2K}^{+}$ ions enter the cell for every 3 ${Na}^{+}$ ions leaving the cell. Thus, for every three positive charges going out; only 2 positive charges go in. This results in a higher concentration of ${K}^{+}$ inside the cell than outside it.
7. Cut pieces of beetroot that do not leave colour in cold water but do so in hot water. Explain
Ans: The cut piece of beetroot in hot water leads to the plasma membrane leakage and this results in release of pigment in water which makes the water color. If in case, the beetroot piece place in cold water plasma membrane do not leak as the temperature is not enough and hence pigment are not released out and water color doesn't change
8. In a girdled plant, when water is supplied to the leaves above the girdle, leaves may remain green for some time, then wilt and ultimately die. What does it indicate?
Ans: In a girdled plant leaves remain green for sometime when water supplied is above the girdle in leaves. This is because leaves carry on photosynthesis in the presence of water. But leaves will not be able to translocate the food prepared by them as the girdling also damages the phloem. This finally results in the death of the leaves above the girdle, even if there is regular supply of water..
9. Various types of transport mechanisms are needed to fulfill the mineral requirements of a plant. Why are they not fulfilled by diffusion alone?
Ans: The concentration of minerals in the roots is always more than concentration of soil, hence diffusion cannot lead to the movement of mineral ions across walls of root and charged particles cannot move across cell membranes. Hence, diffusion alone cannot meet the plant mineral requirements.
10. How can plants be grown under a limited water supply without compromising on metabolic activities?
Ans: In the condition of limited water supply, transpiration rate will be decreased by closing of stomata but the important process like photosynthesis, respiration and transport of food will be taking place.
11. Will the ascent of sap be possible without the cohesion and adhesion of the water molecules? Explain.
Ans: In plants, ascent of sap involves factors like root pressure, capillary action, adhesion-cohesion and transpiration. Movement of water upto the base of the stem is resulted only by root pressure. Water can raise only a few centimeters by capillary action so it is effective only in herbs.when there is a water column underneath which is to be pulled only then transpiration pull works. Hence, without adhesion-cohesion of water molecules ascent of sap is not possible
12. Keep some freshly cut flowers in a solution of food colour. Wait for some time for the dye to rise in flower, when the stem of the flower is held up in light; coloured strands can be seen inside. Can this experiment demonstrate which tissue is conducting water up the stem?
Ans: Coloured strands represent the continuous column of water through the stem. We have seen that water molecules make continuous columns because of adhesion-cohesion. We have also seen that water moves through the xylem in plants. Hence, this experiment can demonstrate that xylem is conducting water up the stem.
13. When a freshly collected Spirogyra, the filament is kept in a 10% potassium nitrate solution, it is observed that the protoplasm shrinks in size:
(a) What is this phenomenon called?
Ans: This phenomenon is called plasmolysis.
(b) What will happen if the filament is replaced in distilled water?
Ans: When the filament is replaced in distilled water, water enters the cell and cell can attain again its original shape and size
14. Sugar crystals do not dissolve easily in ice-cold water. Explain.
Ans: The temperature reduction reduces the kinetic energy of water. So hot water can quickly dissolve sugar crystals but it takes much more time to dissolve in room temperature water and also takes very longer period to dissolve in ice water
15. Salt is applied to tennis lawns to kill weeds. How does salting tennis lawns help in killing weeds without affecting the grass?
Ans: Applying salt may not only lead to the death of weeds but also the grass. Applying salt for plants leads to osmosis and water comes out of the cell. It is a misconception that applying salt may lead to the death of only weed plants.
Plant cells losing excess water may lead to its death and later death of the plant. Some gardeners practiced applying salt but it had drawbacks. The only solution to protect useful plants is to sprinkle weeds only, but it is not a full-proof method to avoid weeds without affecting useful plants.
16. What is the chemical composition of xylem and phloem sap?
Ans: The xylem sap mainly consists of inorganic compounds. Inorganic compounds are mostly sulphur and potassium and organic compounds are mostly nitrogen. Also in phloem sap we can find both organic and inorganic compounds. As the phloem carries food it contains more organic compounds but also contain inorganic compounds for exchange of materials between Xylem and phloem
17. If you are provided with two tubes (A and B), where one is narrow and the other is relatively wider and if both are immersed in a beaker containing water as shown in the given figure. Why does B show higher water rise than A?
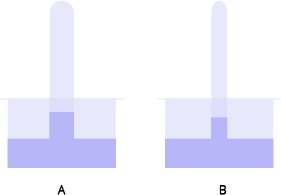
Ans: The lumen of tube B is smaller than that of A. Tube B creates a more capillary effect than tube A because of the smaller lumen. Due to this, the water rises higher in tube B than in tube A.
18. What are 'aquaporins'? How does the presence of aquaporins affect osmosis?
Ans: Integral membrane proteins are nothing but Aquaproteins. They belong to a large family of Major Intrinsic Proteins (MIP). Aquaporins form pores in membranes of biological cells. Aquaporins hasten the rate of osmosis.
19. ABA (Abscisic acid) is called a stress hormone.
(a) How does this hormone overcome stress conditions?
Ans: During water scarcity, stomata is given a signal by ABA. This results in closing of stomata. Hence transpiration cannot take place and water is conserved. This is how ABA helps out in stress conditions
(b) From where does this hormone get released in leaves?
Ans: Leaf apex releases ABA
20. We know that plants are harmed by excess water. But plants survive under water. Condition. How are they able to manage excess water?
Ans: Some varieties of rice are adapted to survive in the flooded condition also. These types of plant can show quick growth in their stem during flood and ensure that some foliage parts are always above the water. They have hollow stems which helps in gaseous exchange and hence we can see some rice plant varieties survive even 1 month in the flood
21. Differentiate between diffusion and translocation in plants.
Ans: Difference between diffusion and translocation in plants are :
Diffusion | Translocation |
(i) This is a passive process. | (i) This is an active process. |
(ii) Energy is not required. | (ii) Energy is required. |
(iii) Facilitates the movement of water and gases. | (iii) Facilitates movement of organic compounds. |
22. How is facilitated diffusion different from diffusion?
Ans:
Diffusion | Facilitated diffusion |
(i) During diffusion, movement is along an osmotic gradient. | (i) During facilitated diffusion, movement is against the osmotic gradient. |
(ii) It is a slow process. | (ii) It is a fast process. |
(iii) It is not dependent on a living system. | (iii) It is dependent on a living system. |
23. Explain the mass flow hypothesis of transport in phloem.
Ans: The mass flow hypothesis is also known as Pressure flow hypothesis, this theory is most accepted for the food movement in phloem. Ernst Munch proposed this theory in the 1930s. Osmotic gradient is set up in the phloem by the high concentration of glucose in the cells. This results in transfer of water from xylem to phloem. This proceeds and the sugar is moved from the source to sink in phloem sap due to turgor pressure. As the pressure is involved it is called pressure flow hypothesis and also the bulk movement of substance refers the mass flow hypothesis
24. Observe the diagram and answer the following;

(I) (II)
(a) Are these types of guard cells found in monocots or dicots?
Ans: These are found in dicots, as they are bean-shaped
(b) Which of these shows a higher water content (i) or (ii)?
Ans: Stomata in fig. (i) shows higher water content as it is turgid and open, and that in fig. (ii) shows lower water content as it is flaccid and close.
(c) Which element plays an important role in the opening and closing of stomata?
Ans: Potassium
25. Define Uniport, Symport and Antiport. Do they require energy?
Ans: Some carrier proteins allow movement only when two types of molecules move Together. Based on this criterion, such a movement can be of three types:
(a) Uniport: When both the molecules move across a membrane independent of each other, this is called uniport.
(b) Antiport: When both types of molecule move in opposite directions; this is called antiport.
(c) Symport: When both types of molecule move in the same direction, this is called symport.
These are types of facilitated diffusion and hence do not require energy.
Long Answer Questions
1. Minerals are present in the soil in sufficient amounts. Do plants need to adjust the types of solutes that reach the xylem? Which molecules help to adjust this? How do plants regulate the type and quantity of solutes that reach xylem?
Ans: Soil contains a sufficient amount of minerals in it but solutes received by the xylem need to be adjusted by the plant. Soil contains minerals in the form of ions, some minerals are absorbed passively by the root hairs from the soil and some actively, this active transport of mineral ions are controlled by the special membrane proteins in root hairs. The transport proteins are also present in endodermal proteins. Mineral ions are selected by these transport proteins for the uptake, that means these transport proteins select the mineral ions for uptake not all ions are allowed to enter. These transport proteins act as gatekeepers where they permit the quantity and type of solute enter the xylem, and just one way ion transport is allowed by epidermis of suberin layer
2. Plants show temporary and permanent wilting. Differentiate between the two. Do any of them indicate the water status of the soil?
Ans:
Temporary Wilting | Permanent Wilting |
(i) There is a temporary loss of turgidity in cells. | (i) There is permanent loss of turgidity in cells. |
(ii) This happens when the rate of | (ii) This happens when the rate of transpiration is more than the rate of water supply Then the rate of water supply. But the difference is below a critical level. |
(iii) Wilting disappears as soon as the water supply resumes to normal. | (iii) Wilting does not disappear even after the water supply resumes to normal. |
(iv) Plant recovers its normal activity. | (iv) Plant eventually dies. |
3. Which of these is a semipermeable membrane (S.P) and which is selectively permeable (S.L)
(a) Animal Bladder
Ans: Semi-permeable
(b) Plasmalemma
Ans: Selectively permeable
(c) Tonoplast
Ans: Selectively permeable
(d) Parchment membrane
Ans: Semi-permeable
(e) Egg membrane
Ans: Semi-permeable
4. Halophytes may show precell pressure very much higher than atmospheric pressure. Explain how this can happen?
Ans: The plants that are adapted to live in saline water are called Halophytes. In this condition, the water potential of the plant cell is more than the soil. So the plant can face the low water availability condition and proceeds to water stress. However, these plants are adapted in such a way that they can sustain this condition. Mainly the sodium and potassium in the excess salt are stored in the vacuoles of these plants. So the purcell pressure and ambient pressure is sustained by the plant
5. The radiolabeled carbon in carbon dioxide supplied to potato plants in an experiment was seen in the tuber eventually. Trace the movement of the labeled carbon dioxide.
Ans: To observe the following movement of starch and the creation of Carbohydrate from various parts of the plant to the others, the radiolabeled carbon dioxide is supplied.Leaves perform photosynthesis; the radioactive carbon dioxide is received by the leaves .
Following the photosynthesis process, Carbohydrate in the leaves is the radioactive carbon. The presence of starch which is the by-product of photosynthesis is also proved. The carbohydrates transform into starch and are moved to the other organs to store. Hence, in the tubers there are radioactive carbons, as starch present in tubers.
Leaves →Phloem in veins→ Phloem in stem→ Tuber
6. Water molecules are very polar. The polar end of the molecule attracts opposite charges on another water molecule (acts like a magnet). How will you explain this property of water with reference to the upward movement of water? Comment on the upward movement of water given the intermolecular hydrogen bonding in water.
Ans: Water molecules are polar. There is a formation of hydrogen bonds between slightly negative and slightly positive charged oxygen and hydrogen bonds respectively when the two water molecules approach each other. The surface tension of liquid is the one of the principle factors of attractive force along with other intermolecular forces. It also helps in dragging of water from xylem to the leaf
Cohesion between water molecules helps in making a continuous column of water in the xylem. This, along with adhesion and surface tension, helps the transpiration pull to pull up the water column in plants. Thus, a multitude of factors is working during the ascent of sap in plants.
7. Comment on the experimental setup
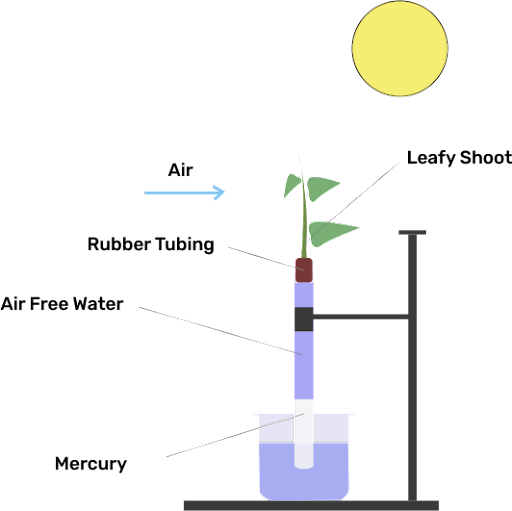
(a) What does the setup demonstrate?
Ans: The setup demonstrates the effect of wind speed on the rate of transpiration.
(b) What will happen to the level of water if a blower is placed close to setup?
Ans: If the blower is placed close to the setup, this will decrease the level of water. This happens because increased wind speed increases the rate of transpiration.
(c) Will the mercury level fluctuate (go up/down) if phenylmercuric acetate is sprayed on leaves?
Ans: Phenyl mercuric acetate will reduce the rate of transpiration. As a result, mercury levels would go down.
This chapter comes under the unit of Physiology of Plants. The lessons includes topics like
Simple Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Symport, antiport and uniport
Active transport
Comparison between transport mechanisms
Plant water relationship
Potential and Osmosis
Absorption of Plants by Water
Ascent of Saps
Uptake and Transport of Mineral Nutrients
Phloem Transport
Pressure Flow or Mass Flow Hypothesis
Important Topics:
Different means of transport
Difference between active and passive transport
Isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic solutions and behavior of cells placed inside them
Apoplast and symplast pathway
Ascent of sap
Mass flow hypothesis
Effective Tips for Biology Preparation
Class 11 Biology is very important. There are lots of scientific terminologies that have to be remembered properly.
This can be done only through proper revision and reading the terms every day.
Prepare the notes with all the definitions and the important terminologies. Revise every day so that you will remember.
You can also use flashcards to make them prominent so that it becomes easier to revise.
The diagrams will fetch you marks easily. So practice drawing neat and labelled diagrams.
Practice writing the answers relevantly and according to the marks.
This can be best practiced by solving the previous year’s question paper.
To make your preparation for biology better, log on to Vedantu and find out the best NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chapter 11 solutions right away. Focus on the conceptual answers given by the top experts and learn how to score more in the final exams.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 (Book Solutions) For Fast Query Resolution
1. Where can I find the NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 with solutions?
The students of Class 11 need not worry about collecting the study material for Class 11 Science NCERT Exemplar from one place to another. Because at Vedantu.com we have all NCERT book solutions, NCERT Exemplar Solutions which are made in PDF format for you to easily download from the Vedantu website or app. Chapter-wise solutions are available that will help students whenever they face any problem in their lesson. The students can study these PDFs in any form they like, whether hard copy, soft copy, online or offline for them their study to be more interesting and less stressful. Vedantu also provides various other learning resources, all for free.
2. How can I prepare better for Class 11 Biology?
The students of Class 11 should understand every concept of Biology Class 11. These include the Different means of transport, Difference between active and passive transport, Isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic solutions and behavior of cells placed inside them, Apoplast and symplast pathway, Ascent of sap, Mass flow hypothesis, etc. To do this, the students should practice from proper notes which are simplified and comprehensible. These are available at Vedantu for free of charge. The students should also attempt questions from NCERT Exemplar to make sure they leave nothing behind which will be beneficial for Class 12 and other exams.
3. Why is the NCERT Exemplar needed for Class 11 Biology?
The NCERT Exemplar is a must for the preparation of a Class 11 student. It helps you to understand the chapter in detail and solve the questions from NCERT Exemplar and NCERT textbook Class 11 Biology better your concepts and also have some important questions which can come in the Class 11 examinations. This ensures that each student gets better grades in their Class 11 Biology examinations. This book along with the NCERT textbook also helps the students who are going to attempt medical-based examinations in the future.
4. What are the concepts mentioned in NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 11?
The concepts mentioned in Class 11 Biology Chapter 11, Transport in Plants mentions terms like Translocation, Diffusion, Facilitated diffusion, porins, aquaporins, Passive symports and antiports, uniports, active transport, comparison of different transport processes, plant-water relations, transpiration, water potential, solute potential, pressure potential, Osmosis, pressure gradient, concentration gradient, plasmolysis, isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic, turgor pressure, Imbibition, apoplast, symplastic system, endodermis, Casparian strip, mycorrhiza, guttation, cohesion-tension-transpiration pull model, Uptake of Mineral Ions, etc knowing all these terms and details related to them is necessary for every Class 11 student.
5. Is it necessary to solve the NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Transport in plants?
It is very crucial for a Class 11 student to solve all the questions in NCERT Exemplar as it tests your knowledge regarding chapter 11 Transport in plants from the unit Plant physiology. It also helps you in the preparation of competitive examinations such as NEET, etc. If a student studies from NCERT Exemplar and solves it with the help of the solutions provided by Vedantu which are prepared with care for your practice then surely any student can get good marks and have a better practice of Class 11 biology for the future.

























