NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology - Neural Control and Coordination - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter-21 (Book Solutions)
1. What is the weightage of Chapter 21 - Neural Control and Coordination in Class 11 Biology?
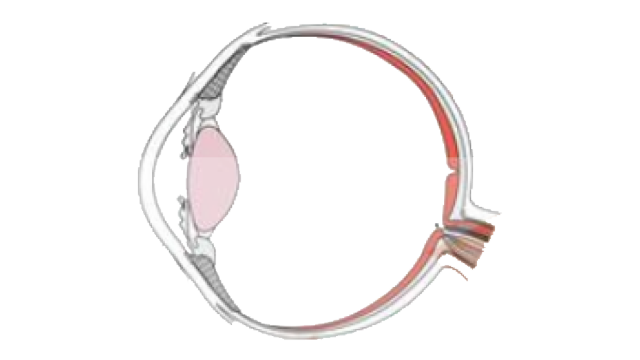
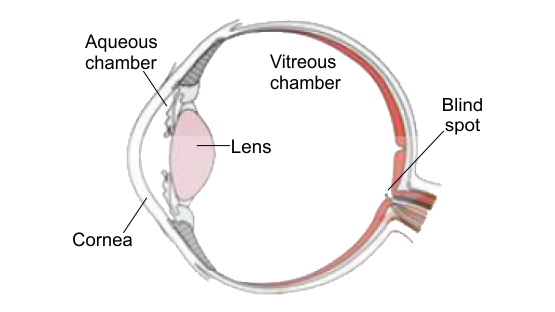
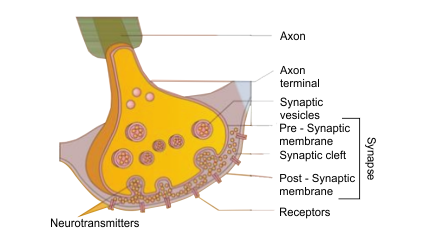
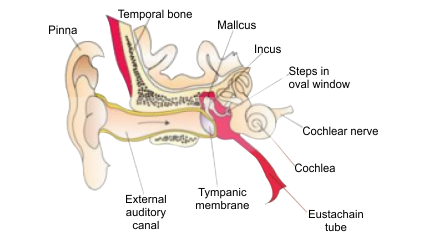
Chapter 21 - Neural Control and Coordination is important in Class 11 biology. However, for the NEET exam, its weightage is 2-3% according to the past few years’ question papers. Class 11 students should, however, give equal importance to this chapter as other chapters can easily be understood if they have a clear understanding of the concepts in this chapter. The reason is that neural control and coordination decide all major functions of the body including metabolism. Also, this topic is easy to understand and score. So, when more questions come from this chapter, one can easily score higher marks.
2. Why is solving NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 - Neural Control and Coordination necessary?
NCERT Exemplar is designed to check your progress. They are good practice books with a lot of practice questions of much higher level, specially designed to crack tough competitive exams. NCERT Exemplar solutions are not easily available. So Vedantu experts have taken this task of providing Exemplar solutions to the students, which they can download from the Vedantu website. Solving NCERT Exemplar gives the students the extra advantage of cracking competitive exams as these books take them to a higher level of study where conceptual study can stand, not simply memorizing text can help.
3. What does Vedantu provide on Chapter 21 - Neural Control and Coordination of Class 11 Biology?
Vedantu subject experts have tried to design every chapter and topic in such a way that it is easily understandable by students. Experts have made a concise chapter guide that focuses on all important points. Students can get NCERT Exemplar PDF and their solutions prepared by the subject experts in the Vedantu website, which they can freely download when they think necessary. Vedantu provides sample question papers and solutions of each chapter and topic, which makes the students confident about the topic.
4. Is it enough to study from Vedantu without attending any offline coaching classes for Class 11?
Yes, definitely. Vedantu is a platform that can prepare a student confident enough to face any competitive exam. However, it depends upon the students, how sincerely and dedicatedly they follow the study materials of Vedantu and how well they have planned their daily routine to go through each chapter and topic from Vedantu apart from their main textbook. Students should also regularly practice the sample questions and Exemplar to develop their confidence and overcome weak points, which becomes evident only when they solve a variety of questions.