NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter-12 (Book Solutions)
1. Why is it necessary to solve through the Vedantu NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download?
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download via Vedantu tends to provide a lot of information regarding the topic itself making it much easier for students to prepare for their Class 12 board exams. This book also consists of a lot of possible questions that could be asked in the Class 12 board exams hence making it easier for students to work on their preparation with the book obtained via Vedantu. This book will also help students to get a good knowledge database about the topics involved.
2. What are the important topics that are covered in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download?
Some of the important topics that are covered in teh NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download can be provided as follows:
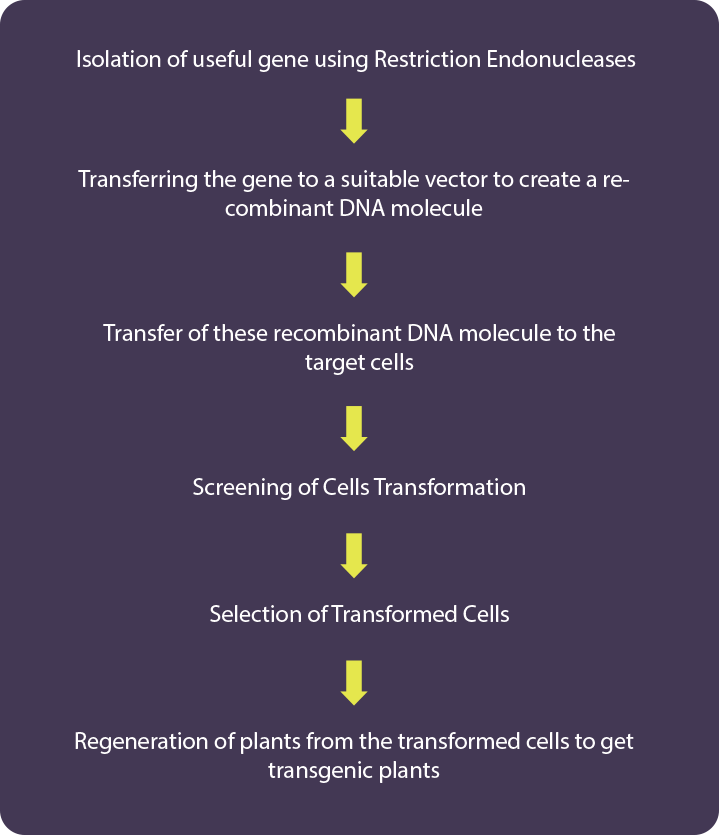
Biotechnology: This field uses the studies of biological aspects for the development of technologies and products which will help in the better welfare of humans. It is highly used in various diagnostic purposes and other medical fields.
Application of Biotechnology in Medicines: Biotechnology tends to contribute a lot to the medicines that are used in our daily life. Usage of biotechnology in medicines can also be termed medicinal biotechnology. Due to this advancement, it is possible to generate genetically modified insulin or humulin which are used for the treatment of diabetic patients.
Molecular Diagnosis: The process involving diagnosis of various diseases which will be done by recombinant DNA technology and PCR is called molecular diagnosis.
Gene Therapy: This process is highly used for the correction of hereditary diseases where defected genes are corrected via gene therapy.
3. How many exercises are present in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download and how many should students solve?
There are in total 57 questions that are indirectly asked which are of high aptitude and are also a bit difficult and tricky. These questions have been divided into various other questions such as MCQs, short-form questions and long answer questions. Below is a list of all the questions that are included in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download:
There are in total 15 MCQs which will consist of 4 options. You need to choose the correct options but this will need you to have good knowledge about the topic.
There are VSAs which are also called the very short answers with about 17 in number. These will need you to answer the question in about one or two words.
There are 15 SAs or short answer questions along with 10 long answer or LA questions.
4. Are there any other Vedantu study materials that are available apart from the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download?
Vednatu makes sure to provide a lot of study materials for students of Class 12 as it is important that they completely understand the concepts that are involved in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications - Free PDF Download. Students will also be able to summarize the topic well if they have understood the concepts that are involved which will hence help them write well during the exams. As it is important to also practise these concepts students can access the Vedantu sample questions papers for Biology which is available for free and can be solved for better knowledge.
5. Is it possible to download the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications via Vedantu?
Yes, Vedantu makes sure that the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and its Applications is available for free and can be downloaded by anyone who wants to refer to the book. Students will also be able to find the solutions to the questions that are asked in the book and hence work on their skills by referring to the solutions. While some may get a good internet connection it is not necessarily the case for every student and hence this facility is a boon for all the students as they can access the book anytime they need.