Class 8 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 8 Cell—Structure and Functions
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 8 Cell—Structure and Functions
1. What do you mean by prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
Bacterial cells and blue-green algae lack the well-defined nuclei (plural of nucleus) that multicellular creatures have. Nuclear components are present in the cells of such creatures, but the nuclear membrane is absent. These cells are known as prokaryotic cells, with pro denoting "primitive" and karyon denoting "nucleus."
Prokaryotes are organisms that have prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells are plant and animal cells having a well-organized nucleus and nuclear membrane. ‘ Eu' and 'karyon' stand for 'truth' and 'nucleus,' respectively.
Eukaryotes are organisms that have eukaryotic cells.
2. What is the basic functioning of the cell, and how are they formed?
Cells make up living beings, and various bodily sections are made up of a variety of cells. Cells are responsible for forming all plant components, including roots, stems, fruit, and leaves. Similarly, cells construct the many organs of an animal. Cells are responsible for the basic functioning of any creature, regardless of its structure. Cells come in various forms and sizes, and each organism has its own set of characteristics. In unicellular organisms, the form of a cell is not fixed. Amoeba is one such example.
3. Where can I get NCERT Solutions-based revision notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8?
Even for Chapter 8 of Class 8 Science, Vedantu offers you comprehensive revision notes based on NCERT Solutions. NCERT Solutions contains questions and solutions for every NCERT textbook question. Vedantu offers a free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Chapter 8 of Class 8 Science. Experts explain the topics, assisting you in better understanding the Chapter and assessing you in your school projects. Practice papers and previous year's examinations are also available from NCERT Solutions to assist you in acing the test.
4. What is the mechanism through which molecules enter and exit the cell?
Molecules move in and out of cells using two primary ways of passive transport Osmosis and Diffusion. The process of 'Osmosis' occurs when a solvent travels from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution across a semipermeable membrane to equalize the concentration levels of both solutions. Roots, for example, take water from the soil via osmosis. The process of 'diffusion' occurs when particles of any material migrate from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration until equilibrium is established. For example, when you spray perfume, the smell diffuses into the air.
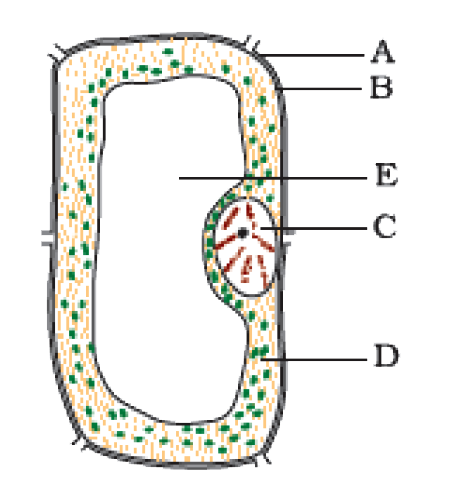
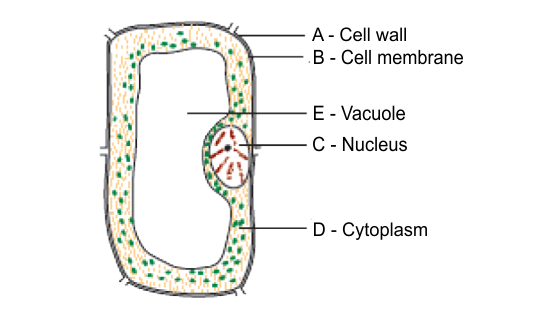
5. What are Organelles and Nucleus?
Cell organelles are the numerous components found within the cell. All of these components are unique and tailored to their respective tasks.
For instance, mitochondria, lysosomes, and so on.
It is spherical and is found in the cell's center. A membrane termed the nuclear membrane separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. It decides what each organelle should perform and how the cell should operate based on information stored in the chromosomes. The nucleolus is a more minor acting concentrated substance found in the nucleus.