NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Maths - Circles - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Math Chapter 10 - Circles solved by expert Math teachers on Vedantu as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 10 - Circles exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Math Solutions Chapter 10 – Circles is an important reference book that will help you in understanding every one of the significant topics of the chapter. Chapter 10 is one of the significant parts in Class 9 as per the CBSE. The NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Math questions and answers for this section give you the data on different subjects like angles subtended by the chords at a point, cyclic quadrilaterals and so on.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 10 – Circles
Multiple Choice Questions
Sample Question 1: In Fig. two congruent circles have centers $O$ and $O{\text{'}}$. Arc $AXB$ subtends an angle of $7{5^\circ }$ at the center $O$ and arc $A'YB{\text{'}}$ subtends an angle of $2{5^\circ }$ at the centre $O{\text{'}}$. Then the ratio of arcs $AXB$ and $A'YB{\text{'}}$ is:
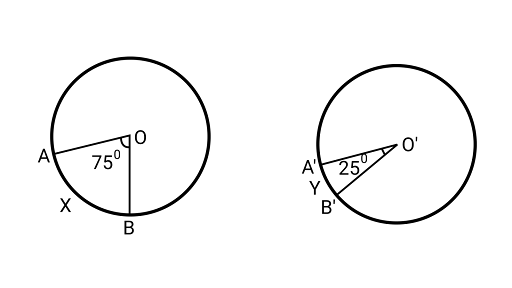
(A) $2:1$
(B) $1:2$
(C) $3:1$
(D) $1:3$
Ans: Correct option is (C).
For the case 1:
Substituting the values of $\theta$
${\text{Area }}(AXB) = \dfrac{1}{2}{r^2}\left( {{{75}^\circ }} \right)$
For the case 2:
Substituting the values of $\theta$
${\text{Area }}\left( {A'YB'} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}{r^2}\left( {{{25}^\circ }} \right)$
Now, finding ratio
$\dfrac{{{\text{ Area }}(AXB)}}{\text{Area }\left( {A'YB'} \right)}$
$={\text{ }}\dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{r^2}(75)}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}{r^2}(25)}} = \dfrac{{75}}{{25}} = \dfrac{3}{1}$
So, the ratio is $3:1.$
Sample Question 2: In Fig. $AB$ and $CD$ are two equal chords of a circle with center O. $OP$ and $OQ$ are perpendiculars on chords ${\text{AB}}$ and $CD$, respectively. If $\angle POQ = 15{0^\circ }$, then $\angle APQ$ is equal to
(A) $3{0^\circ }$
(B) $7{5^\circ }$
(C) $1{5^\circ }$
(D) $6{0^\circ }$
Ans: Correct option is (B).
Assume $\angle OPQ = \angle 1{\text{and}}\angle OQP = \angle 2$
$\because AB = CD$
$OP = OQ$ (Equal chords are equidistant from the centre)
$\angle 1 = \angle 2\quad $ (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
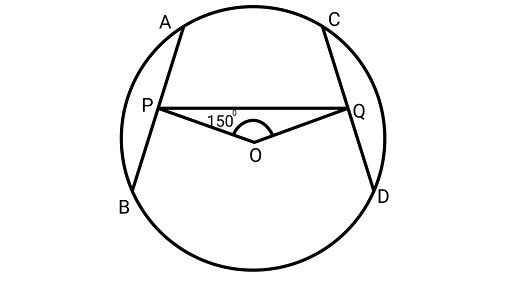
In POQ,
$\angle 1 + \angle 2 + \angle POQ = {180^\circ }$
$\angle 1 + \angle 1 + {150^\circ } = {180^\circ }$
$ 2\angle 1 = {180^\circ } - {150^\circ }$
$2\angle 1 = {30^\circ }$
$\angle 1 = {15^\circ }$
${\text{APB}}$ is a line segment
$\angle BPO + \angle 1 + \angle APQ = {180^\circ }$
${90^\circ } + {15^\circ } + \angle APQ = {180^\circ }$
$\angle APQ = {75^\circ }$
EXERCISE 10.1
1. $AD$ is the diameter of a circle and $AB$ is a chord. If $AD = 34cm,AB = 30cm$, the distance of $AB$ from the center of the circle is
(A) $17cm$
(B) $15cm$
(C) $4cm$
(D) $8cm$
Ans: Correct option is (D).
Drawing ${\text{OL}} \bot {\text{AB}}$.
$\because $ The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord.
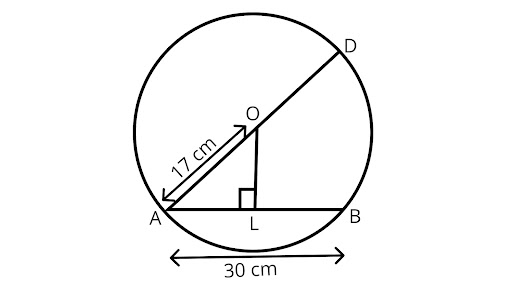
$\therefore AL = LB = \dfrac{1}{2}AB = 15cm$
Applying Pythagoras theorem in $\Delta OLA$
${OA}^{2} = {OL}^{2} + {AL}^{2}$
${(17)^2} = O{L^2} + {(15)^2}$
$289 = O{L^2} + 225$
$O{L^2} = 289 - 225 = 64$
$OL = 8cm$
2. In figure, if $OA = 5cm,AB = 8cm$ and OD is perpendicular to AB then CD is equal to
(A) 2cm
(B) 3cm
(C) 4cm
(D) 5cm
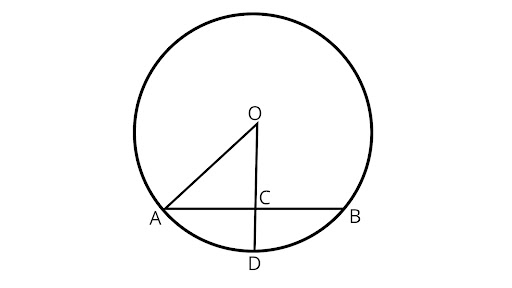
Ans: Correct option is (A).
From the figure
$AC = CB = \dfrac{1}{2}AB$
$ \dfrac{1}{2} \times 8 = 4cm$
Applying Pythagoras theorem in ${\Delta }ACO$
$A{O^2} = A{C^2} + O{C^2}$
${(5)^2} = {(4)^2} + O{C^2}$
$25 = 16 + O{C^2}$
$O{C^2} = 25 - 16 = 9$
$OC = 3cm$
Hence,
$CD = OD - OC$
$= 5 - 3 = 2cm$
3. If $AB = 12cm,BC = 16cm$ and $AB$ is perpendicular to $BC$, then the radius of the circle passing through the points $A,B$ and $C$ is
(A) $6cm$
(B) $8cm$
(C) $10cm$
(D) $12cm$
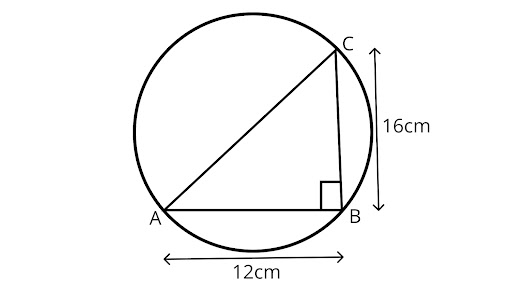
Ans: Correct option is (C)
Here, ${\text{BC}} \bot {\text{AB}}$, which implies it is a circle.
Applying Pythagoras theorem for calculating diameter ${\text{AC}}$
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
$A{C^2} = {(12)^2} + {(16)^2}$
$A{C^2} = 144 + 256$
$A{C^2} = 400$
$AC = \sqrt {400} = 20cm$
Radius of circle$ = \dfrac{1}{2}(AC)$
$\dfrac{1}{2} \times 20 = 10cm$
Hence, the radius of the circle is $10{\text{cm}}$.
4. In figure, if $\angle ABC = 2{0^\circ }$, then $\angle AOC$ is equal to
(A) $2{0^\circ }$
(B) $4{0^\circ }$
(C) $6{0^{^\circ }}$
(D) $1{0^\circ }$
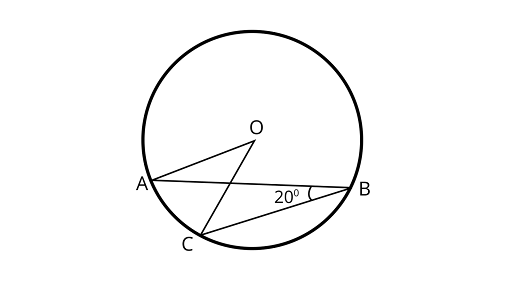
Ans: Correct option is (B)
From the theorem that the angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
$\angle AOC = 2\angle ABC$
$\angle AOC = 2 \times 2{0^\circ } = 4{0^\circ }$
5. In figure, if $AOB$ is a diameter of the circle and $AC = BC$, then $\angle CAB$ is equal to
(A) $3{0^\circ }$
(B) $6{0^\circ }$
(C) $9{0^\circ }$
(D) $4{5^\circ }$
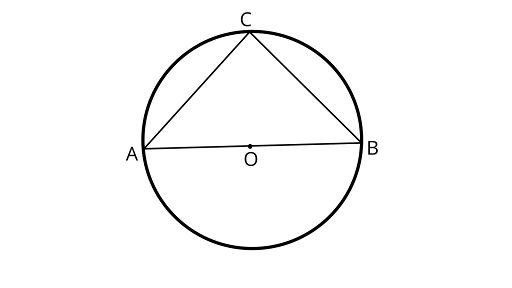
Ans: Correct option is (D)
Here, $\angle BCA = 9{0^\circ }$
$\angle ABC = \angle CAB$
$\because \text{[Angles opposite to equal sides are equal]}$
In ${\Delta }ABC$,
$\angle CAB + \angle ABC + \angle BCA = 18{0^\circ }$(Sum of angles of triangle)
$\angle CAB + \angle CAB + \angle 9{0^\circ } = 18{0^\circ }$
Now,
$2\angle CAB = 18{0^\circ } - 9{0^\circ }$
$\angle CAB = \dfrac{{9{0^\circ }}}{2}$
$\angle CAB = 4{5^\circ }$
6. In figure, if $\angle OAB = 4{0^\circ }$, and then $\angle ACB$ is equal to
(A) $50^\circ $
(B) $4{0^\circ }$
(C) $6{0^\circ }$
(D) $70^\circ $
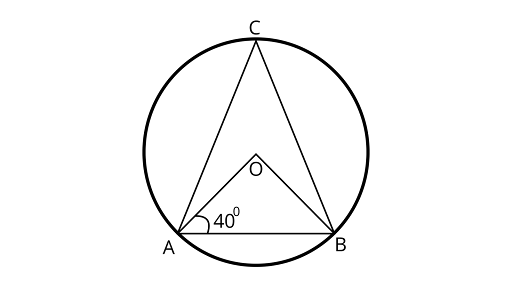
Ans: Correct option is (A)
Here, In ${{\Delta }OAB}$
$OA = OB$ (Radius of a circle)
$\because$ Angles opposite to equal sides are equal
$\angle OAB = \angle OBA$
$\angle OBA = 4{0^\circ }$
Also, $\angle AOB + \angle OBA + \angle BAO = 180^\circ $ (Sum of angles of triangle)
$\angle AOB + 4{0^\circ } + 4{0^\circ } = 18{0^\circ }$
$\angle AOB = 18{0^\circ } - 8{0^\circ }$
$\angle AOB = 10{0^\circ }$
$\because $ Angle subtended by an arc at the centre is twice the angle subtended by it at the remaining part of the circle.
$\angle AOB = 2\angle ACB$
$10{0^\circ } = 2\angle ACB$
$\angle ACB = \dfrac{{10{0^\circ }}}{2} = 5{0^\circ }$
$\angle ACB = 5{0^\circ }$
7. In figure, if $\angle DAB = 6{0^\circ },\angle ABD = 5{0^\circ }$, then $\angle ACB$ is equal to
(A) $6{0^\circ }$
(B) $5{0^\circ }$
(C) $7{0^\circ }$
(D) $8{0^\circ }$
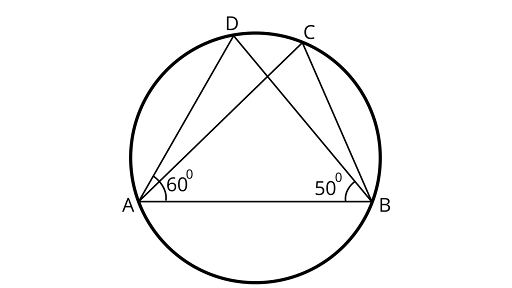
Ans: Correct option is (C)
From the theorem,
$\angle ADB = \angle ACB$ (Angles in same segment of a circle are equal)
In ${\Delta ABD}$ , using angle sum property of a triangle
$\angle ABD + \angle ADB + \angle DAB = 18{0^\circ }$
$5{0^\circ } + \angle ADB + 6{0^\circ } = 18{0^\circ }$
$\angle ADB = 18{0^\circ } - 11{0^\circ }$
$\angle ADB =\angle ACB= 7{0^\circ }$
8. ${\text{ABCD}}$ is a cyclic quadrilateral such that $AB$ is a diameter of the circle circumscribing it and $\angle ADC = 14{0^\circ }$, then $\angle BAC$ is equal to
(A) $8{0^\circ }$
(B) $5{0^\circ }$
(C) $4{0^\circ }$
(D) $3{0^\circ }$
Ans: Correct option is (B)
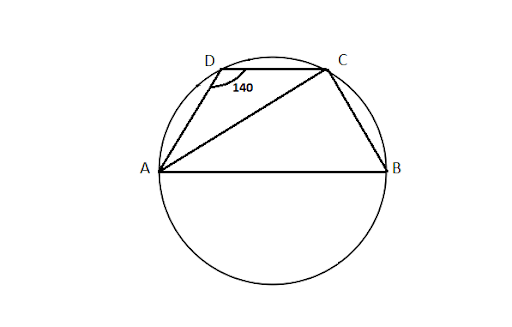
Using the property sum of the opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral is${180^\circ }$. $\angle ADC + \angle ABC = {180^\circ }$
$14{0^\circ } + \angle ABC = 18{0^\circ }$
$\angle ABC = 18{0^\circ } - 14{0^\circ }$
$\angle ABC = 4{0^\circ }$
$\because \angle ACB$ is an angle in a semi-circle.
$\therefore \angle ACB = 9{0^\circ }$
Using angle sum property of a triangle ${\Delta ABC}$
$\angle BAC + \angle ACB + \angle ABC = 18{0^\circ }$
$\angle BAC + 9{0^\circ } + 4{0^\circ } = 18{0^\circ }$
$\angle BAC = 18{0^\circ } - 13{0^\circ } = 5{0^\circ }$
$\angle BAC = 5{0^\circ }$
9. In figure, $BC$ is the diameter of the circle and $\angle BAO = 6{0^\circ }$. Then, $\angle ADC$ is equal to
(A) $3{0^\circ }$
(B) $4{5^\circ }$
(C) $6{0^\circ }$
(D) $12{0^\circ }$
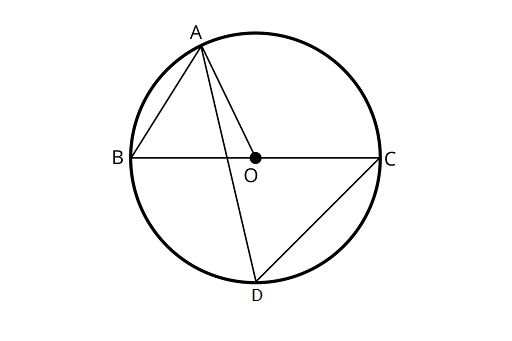
Ans: Correct option is (C)
Using the property angles opposite to equal sides are equal
Here, in ${{\Delta }AOB}$
$\angle OBA = \angle BAO$
$\angle OBA = 6{0^\circ }$
$\because $ Angles in the same segment AC are equal $\angle ABC = \angle ADC$
$\therefore \angle ADC = 6{0^\circ }$
10. In figure, if $\angle AOB = 9{0^\circ }$ and $\angle ABC = 3{0^\circ }$, then $\angle CAO$ is equal to
(A) $3{0^\circ }$
(B) $4{5^\circ }$
(C) $9{0^\circ }$
(D) $6{0^\circ }$
Ans: Correct option is (D)
In ${{\Delta OAB,}}$ Using angle sum property of a triangle
$\angle OAB + \angle ABO + \angle BOA = 18{0^\circ }$
$\angle OAB + \angle OAB + 9{0^\circ } = 18{0^\circ }$
$ 2\angle OAB = 18{0^\circ } - 9{0^\circ }$
$\angle OAB = \dfrac{{9{0^\circ }}}{2} = 4{5^\circ }$
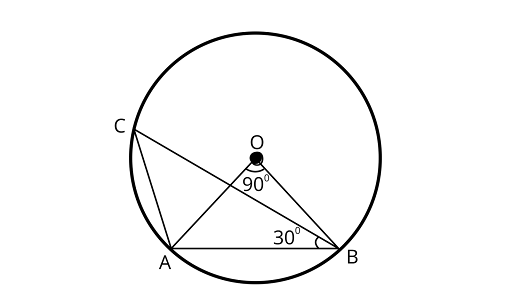
In ${{\Delta ACB,}}$ Using angle sum property of a triangle ${{\Delta ACB,}}$
$\angle ACB + \angle CBA + \angle CAB = 18{0^\circ }$
$\because \angle ACB=\dfrac{\angle A0B}{2}=\dfrac{9{0^\circ }}{2}=4{5^\circ }$
$4{5^\circ } + 3{0^\circ } + \angle CAB = 18{0^\circ }$
$\angle CAB = 18{0^\circ } - 7{5^\circ } = 10{5^\circ }$
Also,
$\angle CAO + \angle OAB = 10{5^\circ }$
$\angle CAO + 4{5^\circ } = 10{5^\circ }$
$\angle CAO = 10{5^\circ } - 4{5^\circ } = 6{0^\circ }$
Short Answer Questions with Reasoning
Write True or False and justify your answer.
Sample Question 1: The angles subtended by a chord at any two points of a circle are equal.
Ans: False
If two points lie in the same segment (major or minor) only, then the angles will be equal otherwise they are not equal.
Sample Question 2: Two chords of a circle of lengths $10{\text{ cm and }}8{\text{ cm}}$are at the distances $8.0{\text{ cm}}$ and $3.5{\text{ cm}}$, respectively from the centre.
Ans: False
Here, the larger chord is at a smaller distance from the center.
EXERCISE 10.2
Write True or False and Justify Your Answer in Each of the Following:
1. Two chords $AB$ and $CD$ of a circle are each at distances $4cm$ from the center. Then $AB = CD$.
Ans: The statement is True
The chords equidistant from the center of the circle are equal in length, so the statement two chords AB and CD of a circle are each at distances 4cm from the center. Then AB=CD.
2. Two chords $AB$ and $AC$ of a circle with center $O$ are on the opposite sides of $OA$. Then $\angle OAB = \angle OAC$.
Ans: The statement is False
Joining ${\text{OB}}$ and ${\text{OC}}$.
In ${\Delta OAB}$ and ${\Delta OAC}$,
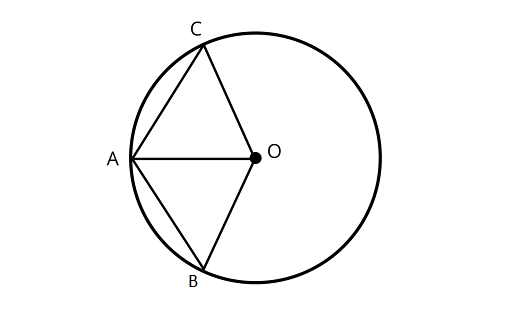
$OA = OA$ (Common side)
$OB = OC\quad$ (Radius of circle)
Here, either any angle or third side is not congruent to ${\Delta{ OAC}}$.
$\therefore $ $\angle OAB \ne \angle OAC$
3. Two congruent circles with centres $O$ and $O{\text{'}}$ intersect at two points $A$ and $B$. Then $\angle AOB = \angle A{O^\prime }B$.
Ans: The statement is True.
Joining ${\text{AB,}}{\text{OA}}$ and ${\text{OB,}}{\text{O'A}}$ and ${\text{BO'}}$.
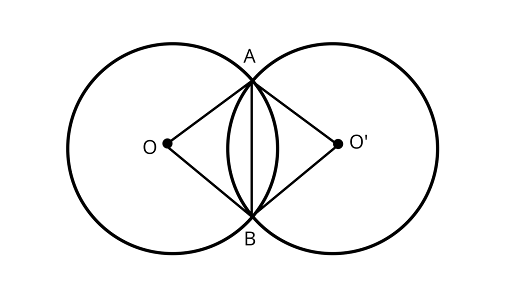
In ${{\Delta AOB}}$ and ${{\Delta AO'B}}$
$OA = A{O^\prime }$ (Same radius)
$OB = B{O^\prime }$ (Same radius)
$AB = AB$ (Common chord)
${{\Delta AOB}} \cong {{\Delta AO'B}}$ (by SSS congruence rule)
$\angle AOB = \angle A{O^\prime }B$ (by CPCT)
4. Through three collinear points a circle can be drawn.
Ans: The statement is False
The circle can pass through only two collinear points but not through three collinear points. So, the statement is false.
5. A circle of radius $3cm$ can be drawn through two points $A, B$ such that $AB = 6cm$.
Ans: The statement is True
diameter of a circle is $AB = 6cm$
radius of a circle$= \dfrac{{AB}}{2} = \dfrac{6}{2} = 3 cm$, which is true.
6. If $AOB$ is the diameter of a circle and ${\text{C}}$ is a point on the circle, then $A{C^2} + B{C^2} = A{B^2}$.
Ans: The statement is True
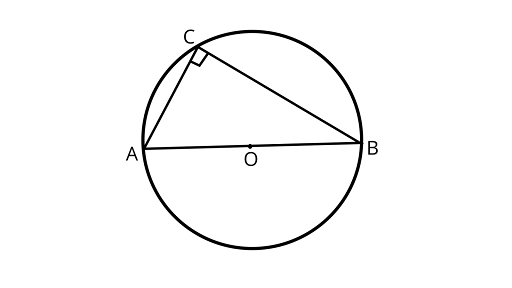
Because any diameter of the circle subtends a right angle to any point on the circle. AOB is the diameter of a circle and C is a point on the circle. C is a right angle here.
Using Pythagoras theorem
In right angled ${{\Delta ACB}}$
$A{C^2} + B{C^2} = A{B^2}$
7. $ABCD$ is a cyclic quadrilateral such that $\angle A = 9{0^\circ },\angle B = 7{0^\circ },\angle C = 9{5^\circ }$ and $\angle D = 10{5^\circ }$
Ans: The statement is False
For cyclic quadrilaterals, the sum of opposite angles is 180°.
Now calculating the sum of opposite angles of quadrilateral,
$\angle A + \angle C = 90^\circ + 95^\circ = 185^\circ \ne 180^\circ$
And $\angle B + \angle D = 70^\circ + 105^\circ = 175^\circ \ne 180^\circ$
So, it is not a cyclic quadrilateral.
8. If $A,B,C$ and $D$ are four points such that $\angle BAC = 3{0^\circ }$ and $\angle BDC = 6{0^\circ }$, then $D$ is the centre of the circle through $A,B$ and $C$.
Ans: The statement is False
Many points D can be there, such that $\angle BDC = 6{0^\circ }$ and each such point cannot be the center of the circle through $A, B$ and $C$. So, the statement is false.
9. If $A,B,C$ and $D$ are four points such that $\angle BAC = 4{5^\circ }$ and $\angle BDC = 4{5^\circ }$, then $A,B,C$ and $D$ are concyclic.
Ans: The statement is True.
$\because \angle BAC = 4{5^\circ }$ and $\angle BDC = 4{5^\circ }$
Angles in the same segment of a circle are equal. Hence, n $A,B,C$ and $D$ are Concyclic.
10. In Fig. , if $AOB$ is a diameter and $\angle ADC = 12{0^\circ }$, then $\angle CAB = 3{0^\circ }$.
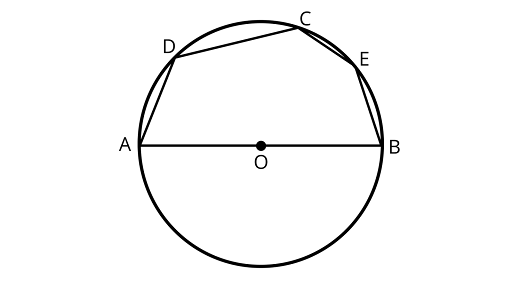
Ans: The statement is True
Since, ADCB is a cyclic quadrilateral.
$\angle \mathrm{ADC}+\angle \mathrm{CBA}=180^{\circ}$.
(sum of opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral is $180^{\circ}$ )
$\Rightarrow \angle C B A=180^{\circ}-120^{\circ}=60^{\circ}\left[\because \angle A D C=120^{\circ}\right]$
In $\triangle A C B, \angle C A B+\angle C B A+\angle A C B=180^{\circ}$
(by angle sum property of a triangle)
$\angle \mathrm{CAB}+60^{\circ}+90^{\circ}=180^{\circ}$
(triangle formed from diameter to the circle is $90^{\circ}$ i.e., $\angle A C B=90^{\circ}$ )
$\Rightarrow \angle C A B=180^{\circ}-150^{\circ}=30^{\circ} .$
Short Answer Questions
Sample Question 1: In Fig. AOC is the diameter of the circle and arc AXB = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ arc BYC. Find $\angle BOC$
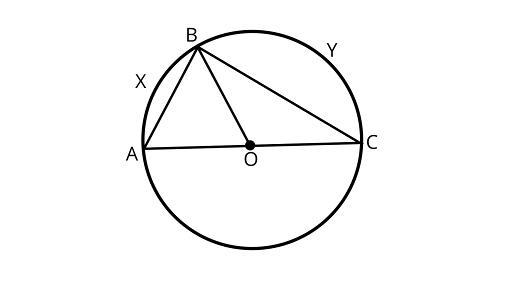
Ans: If two chords of a circle are equal, then their corresponding arcs are congruent and conversely, if two arcs are congruent, then their corresponding chords are equal.
As ${\text{arc}}AXB = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{arc}}BYC$
Also, $\angle AOB + \angle BOC = {180^\circ }$
$ \dfrac{1}{2}\angle BOC + \angle BOC = {180^\circ }$
$\angle BOC = \dfrac{2}{3} \times {180^\circ } = {120^\circ }$
Sample Question 2: In Fig. $\angle ABC = 4{5^\circ }$, prove that $OA \bot OC$.
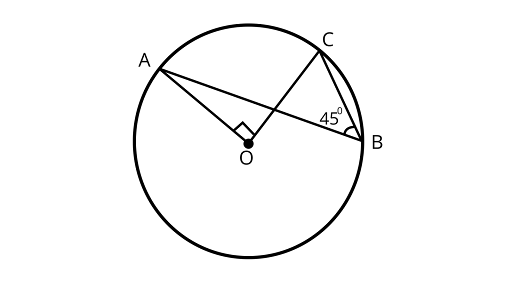
Ans: $\because \angle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle AOC$
$\angle AOC = 2\angle ABC = 2 \times {45^\circ } = {90^\circ }$
$\angle AOC = 2 \times {45^\circ } = {90^\circ }$
$ OA \bot OC$
EXERCISE 10.3
1. If arcs $AXB$ and $CYD$ of a circle are congruent, find the ratio of $AB$ and $CD$.
Ans: Assume ${\text{AXB}}$ and ${\text{CYD}}$ are arcs of circle
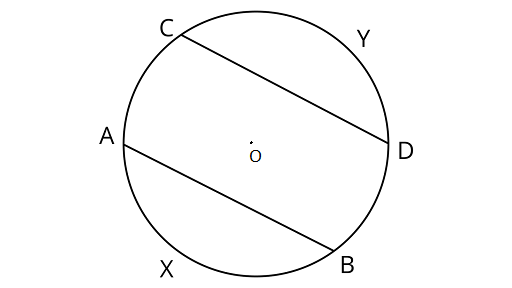
Centre and radius are ${\text{O}}$ and $r$ units,
Hence, the ratio of ${\text{AB}}$ and ${\text{CD}}$ is $1:1$
2. If the perpendicular bisector of a chord $AB$ of a circle $PXAQBY$ intersects the circle at $P$ and $Q$, prove that $arc PXA \cong arc PYB$.
Ans: If two chords of a circle are equal, then their corresponding arcs are congruent and conversely, if two arcs are congruent, then their corresponding chords are equal.
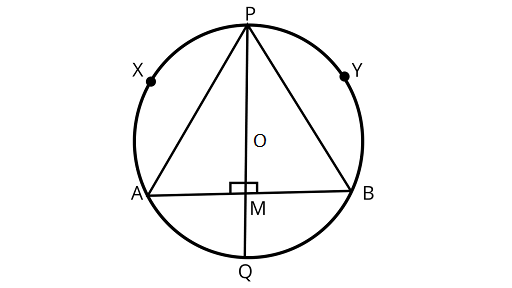
Assume $AB$ be a chord of a circle with a center at $O$. PQ is the perpendicular bisector of the chord $AB$ which intersects at ${\text{M}}$ passing through $O$.
Joining $AP{\text{ and }}BP$
In ${{\Delta APM}}$ and${{\Delta BPM}}$,
$AM = MB$
$\angle PMA = \angle PMB$
$PM = PM$ (Since, OM is the bisector of AB)
$\Delta {\text{APM}} \cong \Delta {\text{BPM}}$(SAS axiom of congruency)
$\therefore PA = PB$
$\therefore$ ${\text{arc }}PXA \cong {\text{arc }}PYB$
3. $A, B$, and $C$ are three points on a circle. Prove that the perpendicular bisectors of $AB, BC, and CA$ are concurrent.
Ans: If$A, B$ and $C$ are three points on a circle then the perpendicular bisectors of $AB, BC{\text{ and}}CA$ are concurrent.
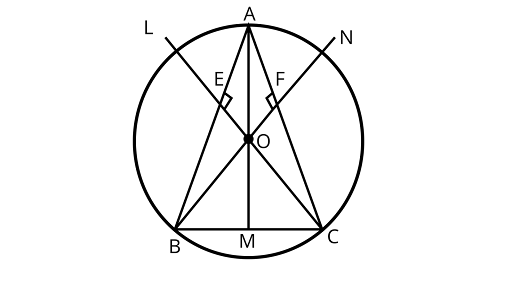
Drawing perpendicular bisectors of $AB$ meet at a point $O$.
Joining $OA,{\text{ }}OB{\text{ and }}OC$
$AE = BE$ ($E$ is the perpendicular bisector of ${\text{AB}}$ )
$\angle AEO = \angle BEO = {90^\circ }$
$OE = OE({\text{common}})$
$\Delta OEB \cong \Delta OEA$ (by SAS congruence rule)
$\therefore OA = OB$(By CPCT)
Similarly,
${\Delta OFA \cong \Delta OFB}$
${\therefore OA{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}OC}$
${{\text{So, }}OA = OB = OC = x{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{say}}} \right)}$
So, in ${{\Delta OMB and \Delta OMC}}$
$OB = OC$ (from above)
$OM = OM$ (common)
$\angle OMB = \angle OMC = 90^\circ$
$\therefore \Delta OEB \cong \Delta OEA$ (by RHS congruence rule)
$ BM = MC$ (by CPCT)
Therefore, $OM$ is the perpendicular bisector of $BC$
Hence, $OL,ON{\text{ and}}OM$ are concurrent
Hence, proved.
4. $AB$ and $AC$ are two equal chords of a circle. Prove that the bisector of the angle $BAC$ passes through the center of the circle.
Ans: Given: $A B$ and $C D$ are two equal chords of the circle.
Prove: Center O lies on the bisector of the $\angle B A C$.
Construction: Join BC. Let the bisector of $\angle B A C$ intersect $B C$ in $P$.
Proof:
In $\triangle \mathrm{APB}$ and $\triangle \mathrm{APC}$
$\mathrm{AB}=\mathrm{AC} \quad \ldots($ Given $)$
$\angle \mathrm{BAP}=\angle \mathrm{CAP} \quad \ldots($ Given $)$
$\mathrm{AP}=\mathrm{AP} \quad \ldots .($ common $)$
$\therefore \triangle \mathrm{APB} \cong \triangle \mathrm{APC} \quad \ldots \mathrm{SAS}$ test
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{BP}=\mathrm{CP}$ and $\angle \mathrm{APB}=\angle \mathrm{APC} \quad \ldots \mathrm{CPCT}$
$\angle \mathrm{APB}+\angle \mathrm{APC}=180^{\circ} \quad \ldots($ Linear pair $)$
$\therefore 2 \angle \mathrm{APB}=180^{\circ} \quad \ldots .(\angle \mathrm{APB}=\angle \mathrm{APC})$
$\Rightarrow \angle \mathrm{APB}=90^{\circ}$
$\therefore$ AP is a perpendicular bisector of chord BC.
Hence, AP passes through the center of the circle.
5. If a line segment joining midpoints of two chords of a circle passes through the center of the circle, prove that the two chords are parallel.
Ans: If a line segment joining midpoints of two chords of a circle passes through the center of the circle then the two chords are parallel.
Assume $AB{\text{ and}} CD$ are two chords of a circle.
Here, the centre is $O$ and $PQ$ is a diameter bisecting the chord $AB{\text{ and}}CD$ at $L$ and $M$.
Diameter $PQ$ passes through the center $O$ of the circle
Proof:
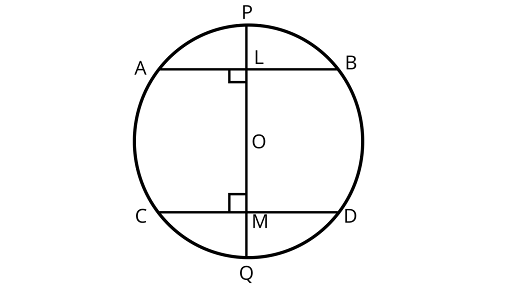
$\because L$ is the midpoint of $AB$
$\therefore $$OL \bot AB$ (the line joining the center of a circle to the midpoint of a chord is perpendicular to the chord)
$\angle ALO = {90^\circ }$
Similarly, $OM \bot CD$
$\therefore $$\angle OMD = {90^\circ }$
Hence, $\angle ALO = \angle OMD = {90^\circ }$
As alternating angles are equal that means chords are parallel.
6. $ABCD$ is such a quadrilateral that $A$ is the centre of the circle passing through $B,C$ and $D$. Prove that $\angle CBD + \angle CDB = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle BAD$
Ans: Join $AC{\text{ and }}BD$
$\because \operatorname{arc} DC$ subtends $\angle DAC$ at the centre and $\angle CBD$ at a point $B$ in the remaining part of the circle.
$\therefore \angle DAC = 2\angle CBD$$..................(i)$
Similarly,
$\because $ Arc $BC$ subtends $\angle CAB$ at the centre and $\angle CDB$ at a point $D$ in the remaining part of the circle.
$\therefore \angle CAB = 2\angle CDB.....................(ii)$
Adding ${\text{equations }}\left( i \right){\text{ and }}(ii)$, we get
$\angle DAC + \angle CAB = 2\angle CBD + 2\angle CDB$
$\angle BAD = 2(\angle CBD + \angle CDB)$
$\angle CDB + \angle CBD = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle BAD$
Hence proved.
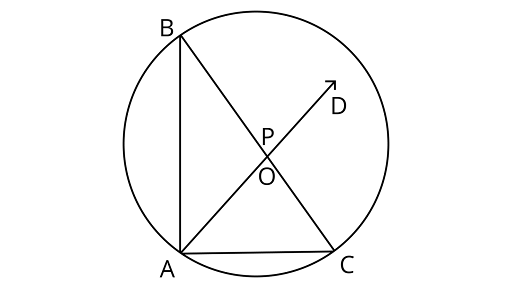
7. $O$ is the circumcentre of the ${{\Delta }}ABC$ and $D$ is the midpoint of the base $BC$. Prove that $\angle BOD = \angle A$.
Ans: Joining $OB,{\text{ }}OD{\text{ and }}OC$
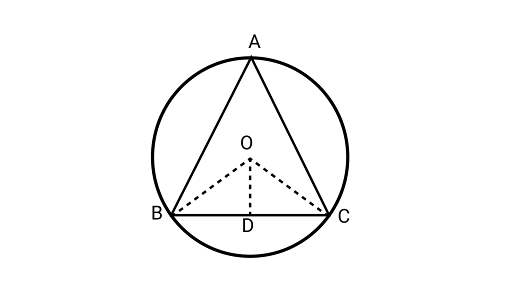
In ${{\Delta BOD}}{\text{ & }}{{\Delta COD}}$
$OB = OC\left( {{\text{radius of same circle}}} \right)$
$BD = DC\left( {\because OD{\text{ is the bisector of BC}}} \right)$
$OD = OD\left( {{\text{common}}} \right)$
$\Delta BOD \cong \Delta COD$
$\therefore \angle BOD = \angle COD{\text{( By}}{\text{CPCT)}}$
Using the property the angle subtended by an arc at the centre is twice the angle subtended by it at the remaining part of the circle.
$2\angle BAC = \angle BOC$
$\angle BAC = \dfrac{2}{2}\angle BOD$
$\because \angle BOC = 2\angle BOD$
$\angle BAC = \angle BOD$
Hence proved.
8. On a common hypotenuse $AB$, two right-angled triangles $ACBandADB$ are situated on opposite sides. Prove that $\angle BAC = \angle BDC$.
Ans: Joining $CD$.
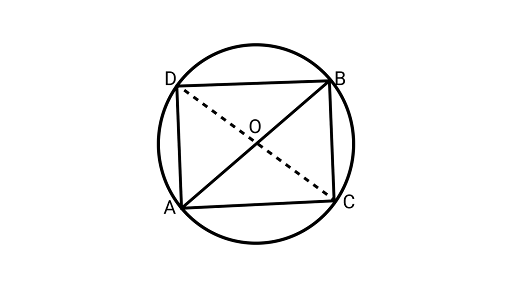
Assume O be the midpoint of AB.
$OA = OB = OC = OD$
$\because$ Mid-point of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equidistant from its vertices.
Now, drawing a circle to pass through the points $A,B,C$ and $D$.with $O$ as centre and radius equal to $OA$.
From the figure,
$\angle BAC$ and $\angle BDC$ ( angles of same segment $BC.$)
$\therefore $ $\angle BAC = \angle BDC\quad $
Hence proved.
9. Two chords $AB$ and $AC$ of a circle subtends angles equal to $9{0^\circ }$ and $15{0^\circ }$, respectively at the centre. Find $\angle BAC$, if $AB$ and $AC$ lie on the opposite sides of the centre.
Ans: In${{\Delta BOA}}$,
$OB = OA$ (Radius of circle)
$\therefore $$\angle OAB = \angle OBA$$ \ldots $(i) (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
Using angle sum property of a triangle
$\angle OAB + \angle OAB + {90^\circ } = {180^\circ }$
$ 2\angle OAB = {180^\circ } - {90^\circ }$
$\angle OAB = \dfrac{{{{90}^\circ }}}{2} = {45^\circ }$
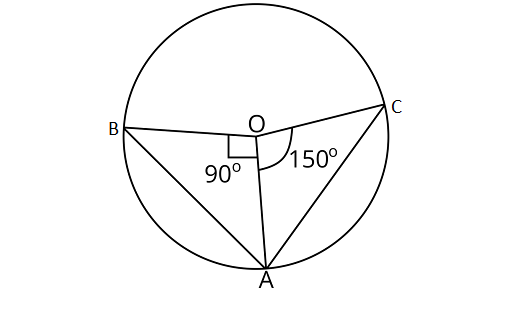
Now, in ${{\Delta AOC}}$,
$AO = OC$ (Radius of a circle)
$\angle OCA = \angle OAC\quad \ldots $(ii) (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
Using angle sum property of a triangle
$\angle AOC + \angle OAC + \angle OCA = {180^\circ }$
$ {150^\circ } + 2\angle OAC = {180^\circ }.$
$ 2\angle OAC = {180^\circ } - {150^\circ }$
$ 2\angle OAC = {30^\circ }$
$\angle OAC = {15^\circ }$
${\text{Also}}\angle BAC = \angle OAB + \angle OAC$
$\angle BAC = {45^\circ } + {15^\circ } = {60^\circ }$
10. If $BM$ and $CN$ are the perpendiculars drawn on the sides $AC$ and $AB$ of the ${{\Delta }}ABC$, prove that the points $B,C$, $M$ and $N$ are concyclic.
Ans: Drawing a circle passing through the points $B,C$, $M$ and $N$
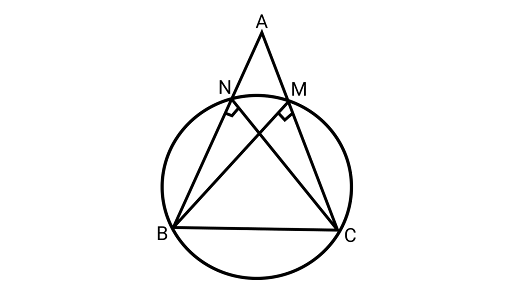
$\because \angle BNC = \angle BMC = {90}^{\circ} $
Angles subtended by the diameter in a semicircle $= {90}^{\circ}$
So, BC is the diameter of the circle.
points $M$ and $N$ should be on the same circle.
Hence, BCMN form a cyclic quadrilateral.
$\therefore $ The points B,C,M and N are concyclic.
11. If a line is drawn parallel to the base of an isosceles triangle to intersect its equal sides, prove that the quadrilateral, so formed, is cyclic.
Ans: Assume ${{\Delta ABC}}$ is an isosceles triangle with$AB = AC$.
Drawing a circle passing through the points $B,C,D$ and$E$.
In ${{\Delta ABC,}}$
$AB = AC$ (Equal sides of an isosceles triangle)
$\angle ACB = \angle ABC$ ………….... (i) (Angles opposite to the equal sides are equal)
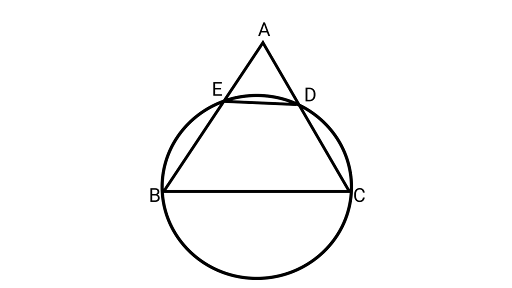
Since, $\angle ADE = \angle ACB\quad $ {Corresponding angles} …………... (ii)
Adding both sides by $\angle EDC$ in Eq. (ii),
$\angle ADE + \angle EDC = \angle ACB + \angle EDC$
$ {180^\circ } = \angle ACB + \angle EDC$
Here, $\angle ADE$ and $\angle EDC$ form linear pair
$\angle EDC + \angle ABC = {180^\circ }\quad $ {From Eq.(i)}
Hence, ${\text{BCDE}}$ is a cyclic quadrilateral, as the sum of the opposite angles is ${180^\circ }$.
12. If a pair of opposite sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are equal, and then prove that its diagonals are also equal.
Ans: Assume${\text{ABCD}}$ be a cyclic quadrilateral and $AD = BC$.
Joining $AC$ and $BD$
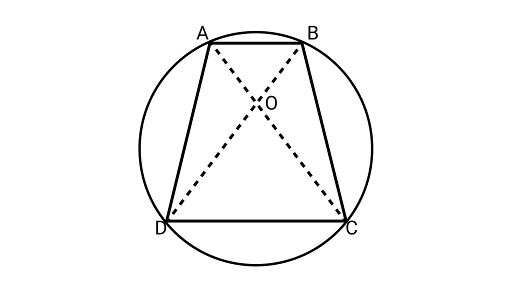
In ${{\Delta AOD}}$ and ${{\Delta BOC}}$,
$\angle OAD = \angle OBC$ and $\angle ODA = \angle OCB$(same segments subtends equal angle to the circle)
${\text{AD}} = {\text{BC}}$ (Given)
$\Delta AOD \cong \Delta BOC$ (By ASA congruence rule)
Adding ${\text{DOC}}$ on both sides
$\Delta AOD + \Delta DOC \cong \Delta BOC + \Delta DOC$
$ \Delta ADC \cong \Delta BCD$
$AC = BD{\text{ }}\left[ {{\text{by CPCT}}} \right]$
13. The circumcenter of the ${{\Delta }}ABC$ is O. Prove that $\angle OBC + \angle BAC = 90^\circ .$
Ans: Joining $BO{\text{ & }}CO$ .
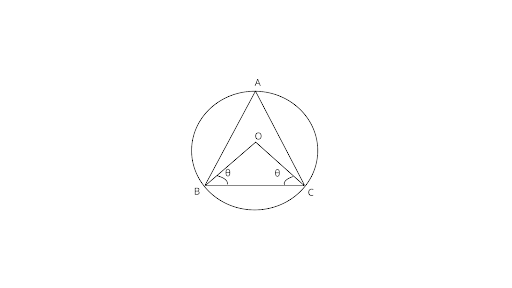
Assume $\angle OBC = \angle OCB = \theta $
In ${{\Delta OBC}}$ using angle sum property of a triangle
$\angle BOC + \angle OCB + \angle CBO = {180^\circ }$
$\angle BOC + \theta + \theta = {180^\circ }$
$\angle BOC = {180^\circ } - 2\theta $
Also, $\angle BOC = 2\angle BAC$
$\angle BAC = \dfrac{{\angle BOC}}{2}$
$\angle BAC = \dfrac{{{{180}^\circ } - 2\theta }}{2}$
$\angle BAC = {90^\circ } - \theta $
$\angle BAC + \theta = {90^\circ }$
$\therefore \angle BAC + \angle OBC = {90^\circ }$
Hence, proved.
14. A chord of a circle is equal to its radius. Find the angle subtended by this chord at a point in the major segment.
Ans: Assume $AB$ is a chord of a circle,
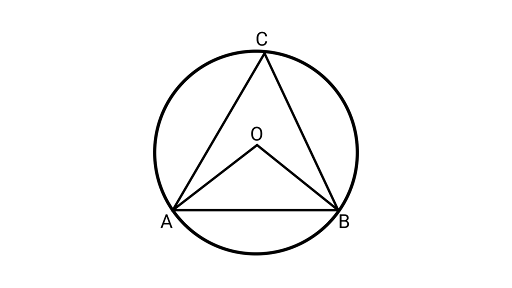
As chord is equal to the radius of the circle
$AB = BO \ldots $ (i)
Joining $OA,{\text{ }}AC{\text{ and }}BC$
$\because OA = OB = $ Radius of circle
$OA = AB = BO$
Thus, ${{\Delta OAB}}$ is an equilateral triangle.
As Each angle of an equilateral triangle is ${60^\circ }$
$\angle AOB = {60^\circ }\quad $
$\angle AOB = 2\angle ACB$
$\angle ACB = \dfrac{{{{60}^\circ }}}{2} = {30^\circ }$
15. In figure, $\angle ADC = 13{0^\circ }$ and chord $BC = $ chord $BE$. Find $\angle CBE$.
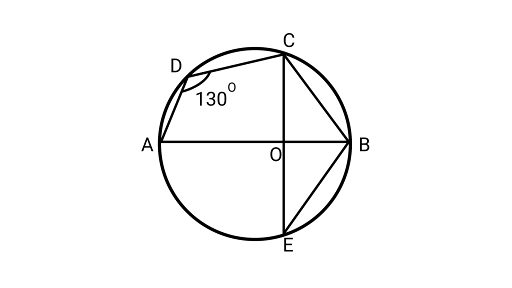
Ans: Using the property that the sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral ${{180}^{\circ} }$.
$\angle ADC + \angle OBC = {{180}^{\circ} }$
$ {130^\circ } + \angle OBC = {{180}^{\circ} }$
$\angle OBC = {{180}^{\circ} } - {{130}^{\circ} } = {{50}^{\circ} }$
$\angle OBC = {{50}^{\circ} }$
In ${{\Delta BOC}}$ and ${{\Delta BOE}}$,
$BC = BE$ (Given equal chord)
$OC = OE$ (Both are the radius of the circle)
$OB = OB$ (Common side)
$\Delta BOC \cong \Delta BOE$
Now, $\angle OBC = \angle OBE = {{50}^{\circ} }$ (by CPCT)
$\angle CBE = \angle CBO + \angle EBO$
$\angle CBE = {{100}^{\circ} }$
16. In Fig., $\angle ACB = 4{0^\circ }$. Find $\angle OAB$.
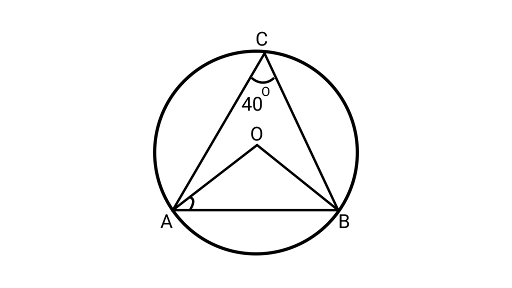
Ans: $\therefore \angle AOB = 2\angle ACB$
$\angle ACB = \dfrac{{\angle AOB}}{2}$
$ {40^\circ } = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle AOB$
$\angle AOB = {80^\circ }$ …………………….(i)
In ${{\Delta AOB,}}$
$AO = BO$ (Both are the radius of a circle)
$\angle OBA = \angle OAB$ …………………….(ii)
Using angle sum property of triangle
$\therefore \angle AOB + \angle OBA + \angle OAB = {180^\circ }$
${80^\circ } + \angle OAB + \angle OAB = {180^\circ }$ (From Eqs. (i) and (ii))
$ 2\angle OAB = {180^\circ } - {80^\circ }$
$ 2\angle OAB = {100^\circ }$
$\therefore \angle OAB = \dfrac{{{{100}^\circ }}}{2} = {50^\circ }$
17. A quadrilateral $ABCD$ is inscribed in a circle such that $AB$ is a diameter and $\angle ADC = 13{0^\circ }.$ Find $\angle BAC.$
Ans: Using the sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is ${180^\circ }$
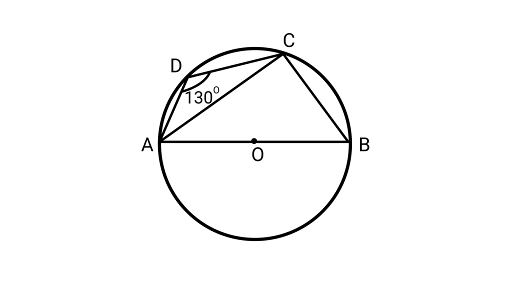
$\angle ADC + \angle ABC = {180^\circ }$
$ {130^\circ } + \angle ABC = {180^\circ }$
$\angle ABC = {50^\circ }$
AB is the diameter of a circle and AB subtends an angle to the circle's right angle.
$\angle ACB = {90^\circ }$
${\text{ In }}\Delta {\text{ABC,}}$ Using angle sum property of triangle
$\angle BAC + \angle ACB + \angle ABC = {180^\circ }$
$\angle BAC + {90^\circ } + {50^\circ } = {180^\circ }$
$\angle BAC = {180^\circ } - \left( {{{90}^\circ } + {{50}^\circ }} \right)$
$\angle BAC = {180^\circ } - {140^\circ } = {40^\circ }$
18: Two circles with centres $O$ and ${O^\prime }$ intersect at two points $A$ and $B$. A line $PQ$ is drawn parallel to $O{O^\prime }$ through $A$ (or $B$ ) intersecting the circles at $P$ and $Q$. Prove that $PQ = 2O{O^\prime }$.
Ans: $OP$ and $OB$ are the radii of the circle.
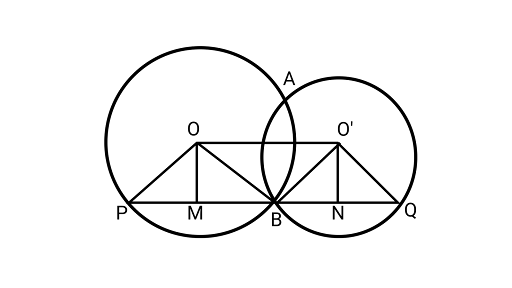
$PB$ is the chord with $OM$ as its perpendicular bisector.
$BM = MP \ldots .(1)$
${\text{ln}}{{\Delta OPB and \Delta O'BQ }}$
BN = NQ $\quad \ldots (2)$
From (1) and (2),
BM + BN = MP + NQ
$ (BM + BN) + (BM + BN) = (BM + BN) + (MP + NQ)$
$ 2(BM + BN) = (BM + BN) + (MP + NQ)$
$ 2\left( {O{O^\prime }} \right) = (BM + MP) + (BN + NQ)$
$ 2\left( {O{O^\prime }} \right) = BP + BQ$
$ 2O{O^\prime }^\prime = PQ$
19. In figure, $AOB$ is the diameter of the circle and $C, D, E$ are any three points on the semicircle. Find the value of $\angle ACD + \angle BED$.
Ans: Using property sum of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral is ${180^\circ }$
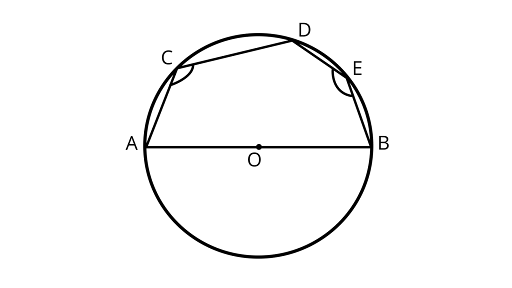
$\angle ACD + \angle AED = {180^\circ } \ldots $ (i) $\quad $
Now, $\angle AEB = {90^\circ }$.. (ii) (Diameter subtends a right angle to the circle)
Adding Equations (i) and (ii),
$(\angle ACD + \angle AED) + \angle AEB = {180^\circ } + {90^\circ } = {270^\circ }$
$\angle ACD + \angle BED = {270^\circ }$
20. In figure, $\angle OAB = 30^\circ$and $\angle OCB = 57^\circ .$Find$\angle BOC and\angle AOC$.
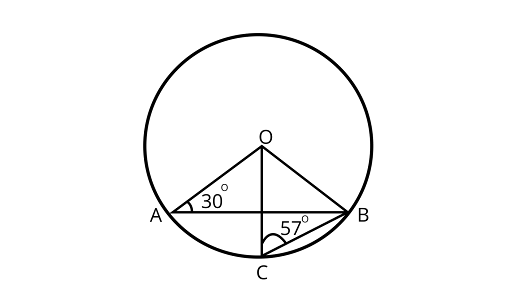
Ans: ${\text{ In }}\Delta {\text{AOB , }}$
$AO = OB\quad [{\text{ Radius of a circle }}]$
$\angle OBA = \angle BAO = {30^\circ }\quad [{\text{Angles opposite to equal sides are equal}}]{\text{ }}$
In $\Delta {\text{AOB }},{\text{ }}$
$\angle AOB + \angle OBA + \angle BAO = {180^\circ }$
$\angle AOB + {30^\circ } + {30^\circ } = {180^\circ }$
$\angle AOB = {180^\circ } - {30^\circ } - {30^\circ }$
$\therefore \angle AOB = {120^\circ }\quad \ldots \ldots (1)$
${\text{In }}\Delta {\text{OCB }},{\text{ }}$
$ OC = OB\quad [{\text{ Radius of a circle }}]$
$\angle OBC = \angle OCB = {57^\circ }.\quad [{\text{Angles opposite to equal sides are equal}}]{\text{ }}$
${\text{In }}\Delta {\text{OCB}}$
$\angle BOC + \angle OCB + \angle OBC = {180^\circ }$
$\angle BOC + {57^\circ } + {57^\circ } = {180^\circ }$
$\angle BOC = {180^\circ } - {114^\circ }$
$\therefore \angle BOC = {66^\circ }\quad \cdots - (2)$
$\angle AOB = {120^\circ }\quad [{\text{ From }}(1)]$
$\angle AOC + \angle COB = {120^\circ }$
$\angle AOC + {66^\circ } = {120^\circ }$
$\angle AOC = {120^\circ } - {66^\circ }$
$\therefore \angle AOC = {54^\circ }$
Long Answer Questions
Sample Question 1: Prove that two circles cannot intersect at more than two points.
Ans: Assume there are two circles which intersect at three points at ${\text{A}},{\text{B}}$ and ${\text{C}}$.
Also,${\text{A}},{\text{B}}$ and ${\text{C}}$ are not collinear.
$\because $ From three non-collinear points ${\text{A}},{\text{B}}$ and ${\text{C}}$ one and only one circle can pass.
Therefore, there cannot be two circles passing through ${\text{A}},{\text{B}}$ and ${\text{C}}$.
The two circles cannot intersect at more than two points.
Sample Question 2: Prove that among all the chords of a circle passing through a given point inside the circle that one is smallest which is perpendicular to the diameter passing through the point.
Ans: Assume ${\text{P}}$ be the given point inside a circle with center O. Drawing the chord, ${\text{AB}}$ perpendicular to the diameter ${\text{XY}}$ through ${\text{P}}$
Assume ${\text{CD}}$ be any other cord through ${\text{P}}$.
Drawing ${\text{ON }} \bot {\text{ CD}}$ from ${\text{O}}$
${\text{}}\Delta {\text{ONP}}$ is a right triangle (Fig.10.17).
$\therefore $ Hypotenuse ${\text{OP}}{\text{ > }}{\text{ON}}$
Since, the chord nearer to the center is larger than the chord which is farther to the center.
$\therefore {\text{CD}} > {\text{AB}}$
In other words, ${\text{AB}}$ is the smallest of all chords passing through ${\text{P}}$.
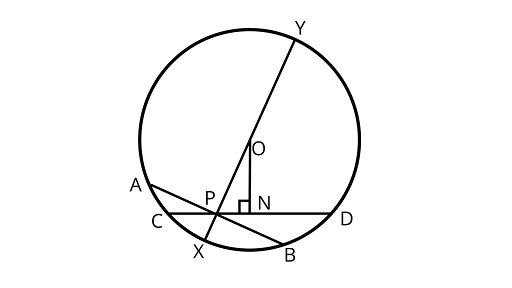
EXERCISE 10.4
1. If two equal chords of a circle intersect, prove that the parts of one chord are separately equal to the parts of the other chord.
Ans: Drawing ${\text{OM}} \bot {\text{AB}}$ and ${\text{ON}} \bot {\text{CD}}$ and joining ${\text{OE}}$&${\text{O}}$ is the centre of circle.
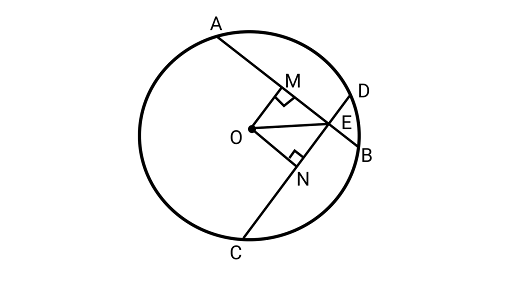
In $\Delta {\text{OME}}$ and ${{\Delta ONE}}$,
$OM = ON\quad $ (Equal chords are equidistant from the centre)
$OE = OE\quad $ (Common side)
$\angle OME = \angle ONE$ (As, each $90^\circ $)
By RHS congruence rule,
${{\Delta OME}} \cong$ ${{\Delta ONE}}$
EM = EN (By CPCT) ……………(1)
Now, AB = CD
Dividing both sides by 2,
$\dfrac{{AB}}{2} = \dfrac{{CD}}{2}$
$ AM = CN...........(2)$
$\because$ Perpendicular drawn from centre of circle to chord bisects the chord then,
$AM = MB$
$CN = ND$
Adding Equation (1) and (2),
EM + AM = EN + CN
AE = CE
Now, $AB = CD$
Subtracting both sides by ${\text{AE}}$
AB - AE = CD - AE
BE = CD - CE
BE = DE
Hence, proved.
2. If non-parallel sides of a trapezium are equal, prove that it is cyclic.
Ans: Joining ${\text{BE}}$ and the quadrilateral ${\text{ABED}}$ is a parallelogram
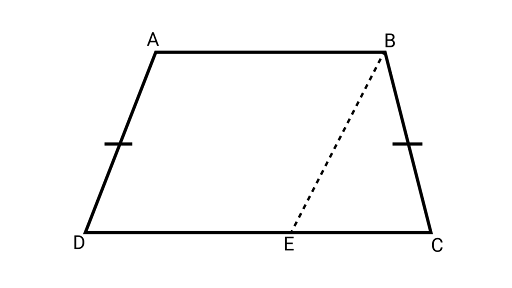
Opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal
$\angle BAD = \angle BED$ $ \ldots (1)$
$AD = BE$ ………….. (2) (Opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal)
$AD = BC$ ........... (3) (Given)
From Equation (2) and (3),
$BC = BE$
$\angle BEC = \angle BCE$ …………………. (4) (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
Also, $\angle BEC + \angle BED = {180^\circ }$ (linear pair axiom)
$\therefore $ $\angle BCE + \angle BAD = {180^\circ }$ (From Equation (1) and (4))
If the sum of opposite angles of a quadrilateral is${180^\circ }$, then the quadrilateral is cyclic.
Hence, trapezium ${\text{ABCD}}$ is cyclic.
Hence proved.
3. If $P,Q$ and $R$ are the mid-points of the sides, BC,CA and AB of a triangle and $AD$ is the perpendicular from $A$ on $BC$, then prove that $P, Q, R$, and $D$ are concyclic.
Ans:
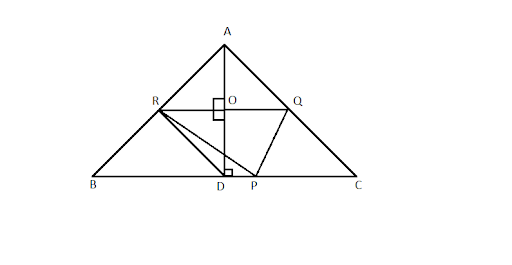
In $\Delta$ ABC, R and Q are the midpoint of AB and AC.
$\therefore$ RQ||BC (Midpoint theorem)
Similarly, PQ||AB and PR||CA.
In quadrilateral BPQR,
BP || RQ and PQ || BR (RQ || BC and PQ || AB)
∴ Quadrilateral BPQR is a parallelogram.
Similarly, quadrilateral ARPQ is a parallelogram.
$\angle A = \angle QPR$…………………(i) (Opposite angles of parallelogram are equal)
PR||AC and PC is the transversal.
$\angle C = \angle BPR$ (Corresponding angles)
$\angle DPQ = \angle DPR + \angle RPQ = \angle A + \angle C$ -------(i)
RQ || BC and BR is the transversal,
$∴ \angle ARO = \angle B$ (Corresponding angles) -------(ii)
In $ΔABD$, R is the mid point of AB and OR || BD.
∴ O is the midpoint of AD (Converse of mid point theorem)
$\Rightarrow OA = OD$
In $ΔAOR$ and $ΔDOR$
$OA = OD$ (Proved)
$\angle AOR = \angle DOR = {90}^{\circ}$ {$ \angle ROD = \angle ODP$ (Alternate angles) & $\angle AOR = \angle ROD = {90}^{\circ}$ (linear pair)}
$OR = OR$ (Common)
$∴ ΔAOR \cong ΔDOR$ (SAS congruence criterion)
$\Rightarrow \angle ARO = \angle DRO$ (CPCT)
$\Rightarrow \angle DRO = \angle B$ (Using (2))
In quadrilateral PRQD,
$\angle DRO + \angle DPQ =\angle B + ( \angle A + \angle C) = \angle A + \angle B + \angle C$ (Using (1))
$\Rightarrow \angle DRO + \angle DPQ = 180°$ ($\because \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = 180°$)
Hence, quadrilateral PRQD is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Thus, the points P, Q, R, and D are concyclic.
Hence proved.
4. $ABCD$ is a parallelogram. A circle through $A,B$ is so drawn that it intersects $AD$ at $P$ and $BC$ at $Q$. Prove that $P,Q,C$ and $D$ are concyclic.
Ans: Joining PQ
$\angle 1 = \angle A\quad $ (exterior angle property of cyclic quadrilateral)
But $\angle A = \angle C\quad $ (opposite angles of a parallelogram)
$\therefore \angle 1 = \angle C$
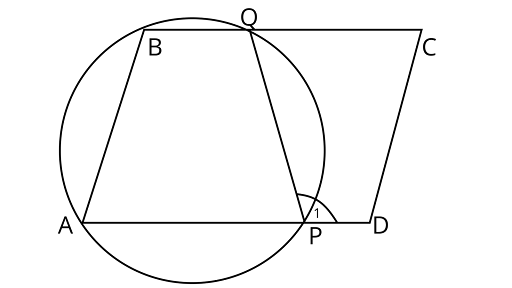
But $\angle C + \angle D = {180^\circ }\quad $ [sum of co-interior angles on the same side is $\left. {{{180}^\circ }} \right]$
$\angle 1 + \angle D = {180^\circ }\quad $ [From Eq. (i)]
Thus, the quadrilateral ${\text{QCDP}}$ is cyclic.
So, the points ${\text{P,}}{\text{Q,}}{\text{C}}$ and ${\text{D}}$ are concyclic.
Hence proved.
5. Prove that angle bisector of any angle of a triangle and perpendicular bisector of the opposite side, if intersect they will intersect on the circumcircle of the triangle.
Ans: Since, angles in the same segment are equal
$\angle BAP = \angle BCP$
$\because {\text{AP}}$ is a bisector of $\angle A$.
$\angle BAP = \angle BCP = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A \ldots (1)$
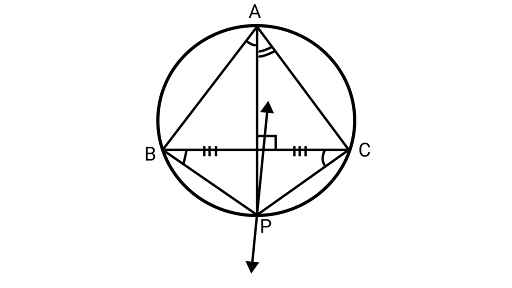
Similarly,
$\angle {\text{PAC}} = \angle {\text{PBC}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle {\text{A}} \ldots (2)$
From equations (1) and (2)
$\angle BCP = \angle PBC$
Using the property that the angles subtended by two Chords of a circle at the center are equal, the chords are equal.
So,${\text{BP}} = {\text{CP}}$
Here, ${\text{P}}$ is on perpendicular bisector of ${\text{BC}}$
Hence, angle bisector of $\angle A$ and perpendicular bisector of ${\text{BC}}$ Intersect on the circumcircle of ${{\Delta ABC}}$.
6. If two chords $AB and CD$ of a circle $AYDZBWCX$ intersect at right angles, then prove that $arcCXA + arcDZB = arcAYD + arcBWC =$ semi-circle.
Ans: Drawing a diameter ${\text{EF}}\parallel {\text{CD}}$ having centre ${\text{M}}$.
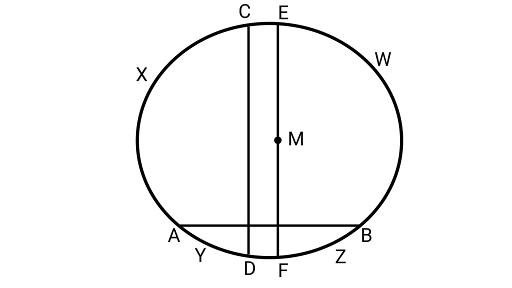
$\because {\text{EF}}\parallel {\text{CD}}$
${{arc}}{\text{EC}}{\text{ = }}{{arc}}{\text{DF}} \ldots (i)$
${{arc ECXA = arc EWB}}$ (Symmetrical about diameter of a circle)
${{arc AF = arc BF }}...\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)$
${{arc}}{\text{ECXAYDF = }}$Semi-circle
${{arc}}{\text{EA}}{\text{ + }}{{arc}}{\text{AF}}{\text{ = }}$ Semi-circle
${{arc}}{\text{EC}}{\text{ + }}{{arc}}{\text{CXA}}{\text{ + }}{{arc}}{\text{FB}}{\text{ = }}$ Semi-circle $\quad $ (from Eq. (ii))
${{arc}}{\text{DF}}{\text{ + }}{{arc}}{\text{CXA}}{\text{ + }}{\text{arcFB}}{\text{ = }}$ Semi-circle $\quad$ (from Eq. (i))
${{arc}}{\text{DF}}{\text{ + }}{{arc}}{\text{FB}}{\text{ + }}{{arcCXA}}{\text{ = }}$ Semi-circle
${{arc}}{\text{CXA}}{\text{ + }}{{arc}}{\text{DZB}}{\text{ = }}$ Semi-circle
Since, the circle divides itself in two semi-circles; therefore the remaining portion of the circle is also equal to the semi-circle.
$\therefore {{arc}}{\text{AYD}}{\text{ + }}{{arc}}{\text{BWC}}{\text{ = }}$ Semi-circle
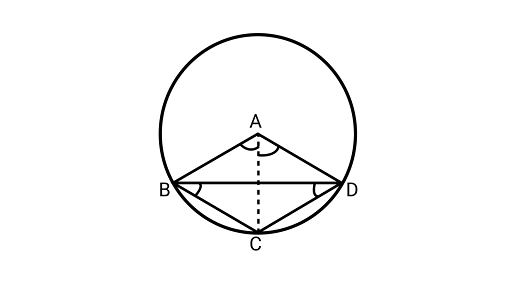
7. If $ABC$ is an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle and $P$ be any point on the minor $arcBC$ which does not coincide with $B$ or $C$, then prove that $PA$ is the angle bisector of $\angle BPC$.
Solution: Joining ${\text{PB and PC}}$
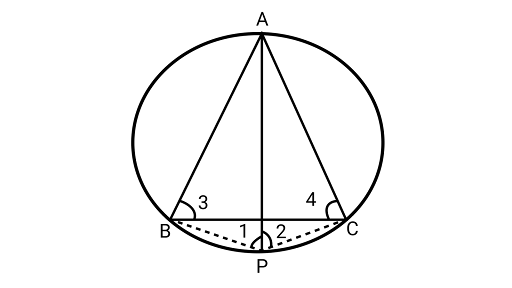
${{\Delta ABC}}$ is an equilateral triangle.
$\angle 3 = \angle 4 = {60^\circ }$(Angles in the same segment ${\text{AB}}$)
Now, $\angle 1 = \angle 4 = {60^\circ }$
$\angle 2 = \angle 3 = {60^\circ }$ (angles in the same segment AC)
$\therefore \angle 1 = \angle 2 = {60^\circ }$
Hence,${\text{PA}}$ is angle bisector of $\angle {\text{BPC}}$
8. In the figure, $AB$ and $CD$ are two chords of a circle intersecting each other at point$E$. Prove that $\angle AEC = \dfrac{1}{2}$ (angle subtended by arc CXA at center + angle subtended by arc $DYB$ at the center).
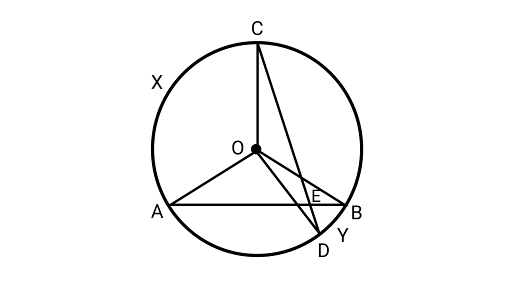
Ans: Extending the line ${\text{DO}}{\text{ and }}{\text{ BO}}$ at the points $I$ and $H$ on the circle. Also, joining ${\text{AC}}$
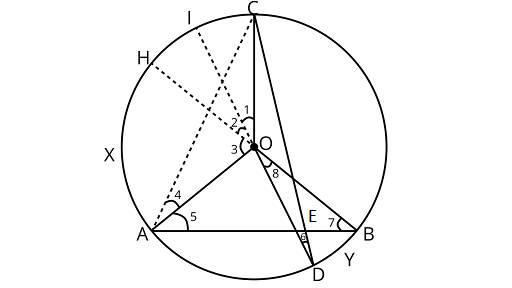
Using the property that the angle subtended by an arc at the centre is twice the angle subtended by it at the remaining part of the circle
$\therefore$ $\angle 1 = 2\angle 6$and $\angle 3 = 2\angle 7$
In ${{\Delta AOC}}$,
$\angle OCA = \angle 4\quad$ (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
Also, Using, angle sum property of triangle
$\angle AOC + \angle OCA + \angle 4 = {180^\circ }$
$\angle AOC + \angle 4 + \angle 4 = {180^\circ }$
$\angle AOC = {180^\circ } - 2\angle 4$
Now, in ${{\Delta AEC}}$
Using, angle sum property of triangle
$\angle AEC + \angle ECA + \angle CAE = {180^\circ }$
$\angle AEC = {180^\circ } - (\angle ECA + \angle CAE)$
$\angle AEC = {180^\circ } - [(\angle ECO + \angle OCA) + \angle CAO + \angle OAE]$
$ = {180^\circ } - (\angle 6 + \angle 4 + \angle 4 + \angle 5)$
$ = {180^\circ } - (2\angle 4 + \angle 5 + \angle 6)$ (In ${{\Delta OCD}},\angle 6 = \angle ECO$ angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
$ = {180^\circ } - \left( {{{180}^\circ } - \angle AOC + \angle 7 + \angle 6} \right)$
Now, ${{\Delta AOB,}}$,
$\angle 5 = \angle 7$
$ = \angle AOC - \dfrac{{\angle 3}}{2} - \dfrac{{\angle 1}}{2}$
Adding and subtracting $\dfrac{{\angle 2}}{2}$
$ = \angle AOC - \dfrac{{\angle 1}}{2} - \dfrac{{\angle 2}}{2} - \dfrac{{\angle 3}}{2} + \dfrac{{\angle 2}}{2}$
$ = \angle AOC - \dfrac{1}{2}(\angle 1 + \angle 2 + \angle 3) + \dfrac{{\angle 8}}{2}$ $(\because \angle 2 = \angle 8$ (Vertically opposite angles))
$= \angle AOC - \dfrac{{\angle AOC}}{2} + \dfrac{{\angle DOB}}{2}$
$\angle AEC = \dfrac{1}{2}(\angle AOC + \angle DOB)$
$\angle {\text{AEC}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ (Angle subtended by arc ${\text{CXA}}$ at centre + angle subtended by arc ${\text{DYB}}$ at the centre).
9. If bisectors of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral $ABCD$ intersect the circle, circumscribing it at the points $P$ and $Q$, prove that $PQ$ is a diameter of the circle.
Ans: Joining ${\text{QD}}$ and ${\text{QC}}$.
Using the property that the sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral ${180^\circ }$
$\therefore $$\angle CDA + \angle CBA = {180^\circ }$
Dividing both sides by 2,
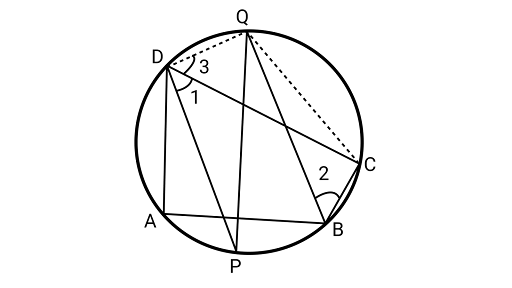
$\dfrac{1}{2}\angle CDA + \dfrac{1}{2}\angle CBA = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {180^\circ } = {90^\circ }$
Assume $\left[ {\angle 1 = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle CDA} \right.$ and $\left. {\angle 2 = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle CBA} \right]$
$\angle 1 + \angle 2 = {90^\circ }...............(1)$
But $\angle 2 = \angle 3\quad $ {angles in the same segment QC are equal}
$\angle 1 + \angle 3 = {90^\circ }..............(2)$
From Equation (1) and (2),
$\angle PDQ = {90^\circ }$
Hence, ${\text{PQ}}$ is the diameter of a circle, because the diameter of the circle subtends a right angle at the circumference.
10. A circle has a radius $\sqrt 2 cm$. It is divided into two segments by a chord of length $2cm$. Prove that the angle subtended by the chord at a point in the major segment is $4{5^\circ }$.
Ans: Drawing a circle having center ${\text{O}}$.
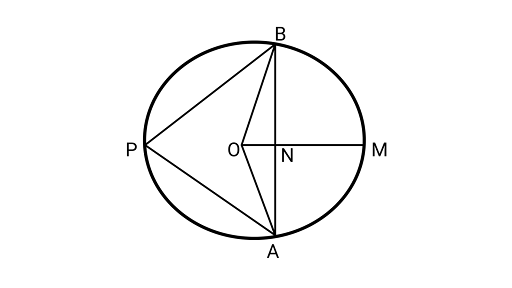
Assume $AB = 2{\text{cm}}$ be a chord of a circle.
$AN = NB = 1{\text{cm}}$
$OB = \sqrt 2 {\text{cm}}$
In $\Delta {\text{ONB}}$,
$O{B^2} = O{N^2} + N{B^2}$
${(\sqrt 2 )^2} = O{N^2} + {(1)^2}$
$ O{N^2} = 2 - 1 = 1$
$ ON = 1{\text{cm}}$
Also, $\angle ONB = {90^\circ }$ (${\text{ON}}$is the perpendicular bisector of the chord)
$\therefore $$\angle NOB = \angle NBO = {45^\circ }$
Similarly,$\angle AON = {45^\circ }$
Now,
$\angle AOB = \angle AON + \angle NOB$
$\angle AOB = {45^\circ } + {45^\circ } = {90^\circ }$
$\because $ Chord subtends an angle to the circle is half the angle subtended by it to the centre.
$\therefore \angle APB = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle AOB$
$\angle APB = \dfrac{{{{90}^\circ }}}{2} = {45^\circ }$
Hence proved.
11. Two equal chords $AB$ and $CD$ of a circle when produced intersect at a point $P$. Prove that $PB = PD$
Ans: Joining ${\text{OP}}$ and drawing, ${\text{OL}} \bot {\text{AB}}$ and ${\text{OM}} \bot {\text{CD}}$
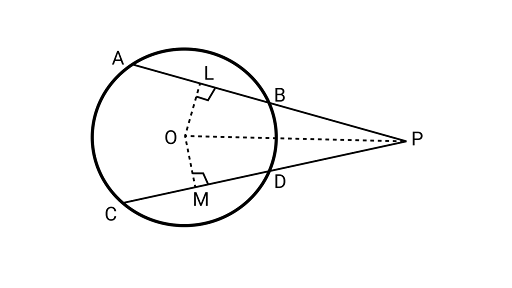
$AB = CD$
$OL = OM$ (Equal chords are equidistant from the centre)
In ${{\Delta OLP}}$ and${{\Delta OMP}}$,
$OL = OM$ (from above)
$\angle OLP = \angle OMP$ (each angle is ${90^\circ }$)
$OP = OP$ (common)
By RHS congruence rule,
${{\Delta OLP}} \cong {{\Delta OMP}}$
$LP = MP$ …………………(1)
Now, $AB = CD$
$ \dfrac{1}{2}(AB) = \dfrac{1}{2}(CD)$
$ BL = DM$...........(2)
Subtracting Eq. (2) from Eq. (1),
LP - BL = MP - DM
$ PB = PD$
Hence proved.
12. $AB$ and $AC$ are two chords of a circle of radius $r$ such that $AB = 2AC$. If $p$ and $q$ are the distances of $AB$ and AC from the centre, prove that $4{q^2} = {p^2} + 3{r^2}$
Ans: Assume ${\text{AC}} = a$, then ${\text{AB}} = 2a$
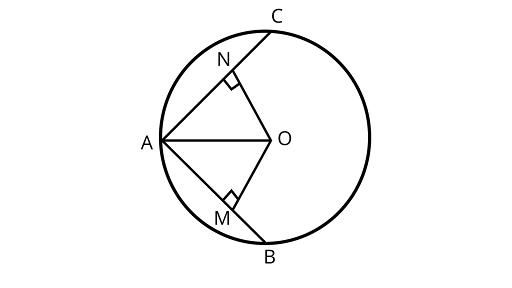
From center ${\text{O}}$, drawing a perpendicular to the chords ${\text{AB}}$ and ${\text{AC}}$ at ${\text{M}}$ and ${\text{N}}$
$\therefore {\text{AN}} = {\text{NC}} = \dfrac{a}{2}$
${\text{AM}} = {\text{MB}} = a$
In ${{\Delta OAM}}$ using Pythagoras theorem
$A{O^2} = A{M^2} + M{O^2}$
$ A{O^2} = {a^2} + {p^2}............(1)$
In ${{\Delta OAN}}$, using Pythagoras theorem
$A{O^2} = {(AN)^2} + {(NO)^2}$
$ A{O^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{a}{2}} \right)^2} + {q ^2}............(2)$
Solving equations (1) and (2)
$ {\left( {\dfrac{a}{2}} \right)^2} + {q^2} = {a^2} + {p^2}$
$ \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4} + {q^2} = {a^2} + {p^2}$
$ {a^2} + 4{q^2} = 4{a^2} + 4{p^2}$
$ 4{q^2} = 3{a^2} + 4{p^2}$
$ 4{q^2} = {p^2} + 3\left( {{a^2} + {p^2}} \right).....\left( 4 \right)$
In right angled ${{\Delta OAM}},$
${r^2} = {a^2} + {p^2}.....\left( 5 \right)$
On putting the value of equation 5 in 4, we get $4{q^2} = {p^2} + 3{r^2}$
Hence, Proved.
13. In figure, ${\text{O}}$ is the centre of the circle$\angle BCO = 30^\circ $. Find $x$ and $y$.
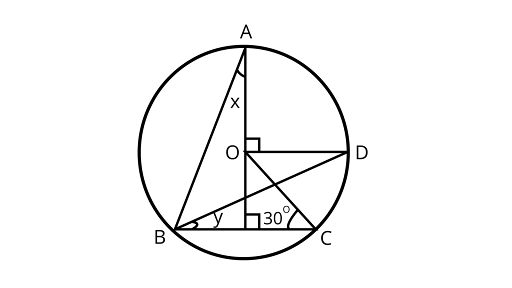
Ans: In the given figure
Joining ${\text{OB and AC}}$
In $\Delta {\text{BOC}}$,
$CO = BO$ (Radius of circle)
$\therefore$ $\angle OBC = \angle OCB = {30^\circ }$ (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
$\therefore $ $\angle BOC = {180^\circ } - (\angle OBC + \angle OCE)$ (By angle sum property of a triangle)
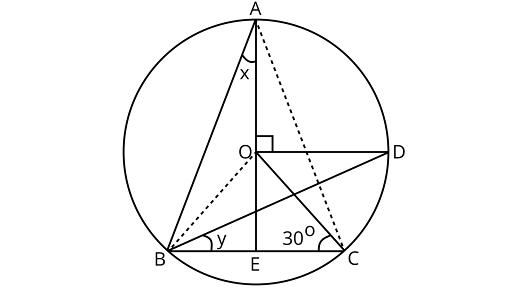
Using angle sum property of a triangle $ = {180^\circ } - \left( {{{30}^\circ } + {{30}^\circ }} \right) = {120^\circ }$
Using the property, the angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
$\because \angle BOC = 2\angle BAC$
$\angle BAC = \dfrac{{{{120}^\circ }}}{2} = {60^\circ }$
Also, $\angle BAE = \angle CAE = {30^\circ }$ (${\text{AE}}$ is an angle bisector of angle${\text{A}}$)
$\angle BAE = x = {30^\circ }$
In $\Delta {\text{ABE}}$,
Using angle sum property of a triangle
$\angle BAE + \angle EBA + \angle AEB = {180^\circ }$
$ {30^\circ } + \angle EBA + {90^\circ } = {180^\circ }$
$\angle EBA = {180^\circ } - \left( {{{90}^\circ } + {{30}^\circ }} \right)$
$\angle EBA = {180^\circ } - {120^\circ } = {60^\circ }$
Now, $\angle EBA = {60^\circ }$
$\angle ABD + y = {60^\circ }$
$ \dfrac{1}{2} \times \angle AOD + y = {60^\circ }$
$ \dfrac{{{{90}^\circ }}}{2} + y = {60^\circ }$
$ {45^\circ } + y = {60^\circ }$
$ y = {60^\circ } - {45^\circ }$
$ y = {15^\circ }$
14. In figure, $O$ is the centre of the circle, $BD = OD$ and $CD \bot AB$. Find $\angle CAB$.
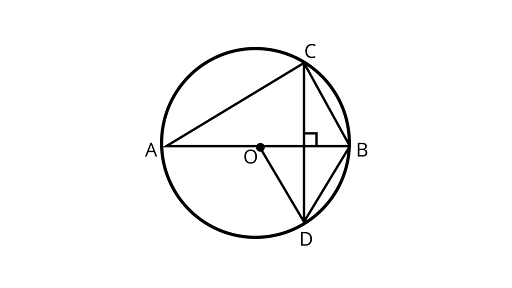
Ans: In ${{\Delta OBD}}$,
$BD = OD$ …..(1) (given)
$OD = OB$ …..(2) (Radius of circle)
$\therefore$ $OB = OD = BD$ (from equation 1 and 2)
${{\Delta OBD}}$ is an equilateral triangle.
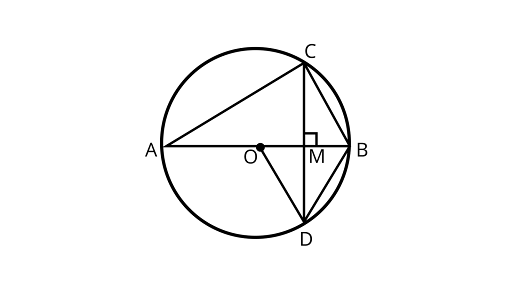
$\therefore \angle BOD = \angle OBD = \angle ODB = 60^\circ $
In ${{\Delta MBC}}$ and $\Delta {\text{MBD,}}$
$MB = MB$ (Common)
$\angle CMB = \angle BMD = {90^\circ }$
$CM = MD$ (Since, OM is the bisector of chord CD)
${{\Delta MBC}} \cong {{\Delta MBD}}$ (By SAS congruence rule)
$\therefore $$\angle MBC = \angle MBD\quad $ (By CPCT)
$\angle MBC = \angle OBD = 60^\circ \left[ {\because \angle OBD = 60^\circ } \right]$
Since, ${\text{AB}}$ is a diameter of the circle
$\therefore $ $\angle ACB = {90^\circ }$
In ${{\Delta ACB}}$, using angle sum property of a triangle
$\angle CAB + \angle CBA + \angle ACB = {180^\circ }$
$\angle CAB + {60^\circ } + {90^\circ } = {180^\circ }$
$\angle CAB = {180^\circ } - \left( {{{60}^\circ } + {{90}^\circ }} \right) = {30^\circ }$
Importance of NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Chapter 10 - Circle
NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 10 Circles prepares students for the end of the year tests. Addressing the model questions will assist students with understanding the essentials and progressed topics of the chapter. With the assistance of solutions, students can undoubtedly resolve their doubts while tackling the questions available in the NCERT book. These NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths questions are planned by our experts keeping in mind the CBSE prospectus for Chapter 10 based on these points:
Circles and their connected terms like curves, area, chords, semicircle, fragments, and so forth
The point is subtended by chords of a circle at a point and theorems dependent on it
The perpendicular from the Center to a Chord and hypotheses dependent on it
Circle through Three Points and its connected hypotheses
Point Subtended by an Arc of a Circle
Points in a similar portion of a circle
Cyclic Quadrilaterals and related hypotheses
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 - Circles (Book Solutions)
1. What are some important terms in NCERT Class 9 Math Chapter 10?
Circle – From a fixed point in a plane, there are a few arrangements of points at a decent distance at a proper point that makes a circle. This fixed point is known as the center of a circle.
Radius – The distance between a state of the edge on the circle just as the center of the circle is known as the radius.
Tangent and Secant– A line that contacts a circle at one point is known as a tangent, then again, a line that cuts a circle at 2 points is known as secant.
Chord – The line section inside a circle that joins any 2 places of the circle is known as a chord.
2. What is meant by diameter, arc, circumference and sector in a circle?
Diameter – A chord that goes through the center of a circle is known as a diameter. A Diameter is in every case double the radius and is known as the longest chord.
Arc – The part of a circle between 2 points is known as a curve {arc}. The longer one is known as the significant arc, then again, the shorter one is known as the minor arc.
Circumference – The circumference is known as the boundary of the circle that implies it is the distance covered by circumventing the boundary of the circle
Sector – A sector means the part of the circle that is encased by an arc and to radii. In this, the smallest area is known as a minor area and the bigger region is known as the major area.
3. What are the theorems mentioned in Chapter 10-Circle of Class 9 Maths?
The theorems mentioned in NCERT Chapter 10-Circle of Class 9 Maths are:
Equivalent chords subtend equivalent points at the center.
If the angles subtended by the chords of the circle at the middle are equivalent then the chords are approaches.
The perpendicular from the center of a circle to the line divides up the chord.
A line is drawn through the center of a circle to cut up a line opposite to the chord.
Equivalent chords of a circle are equidistant from the middle.
4. What are questions asked at the end of NCERT Math Class 9 Math Chapter 10?
Practice 10.1 comprises of 10 NCERT Exemplar Class 9 problems identified with the diameter of a circle, the chords of a circle, point suspended by chords and so on
Practice 10.2 comprises 10 Exemplar problems in which you have to justify assuming the given assertion is right or not, identified with collinear points, the center of the circle and angles suspended by chords.
Practice 10.3 comprises 20 Exemplar issues in which you will either need to find the angles or to prove the event that the angles are equivalent, to demonstrate assuming the chords are equal.
Practice 10.4 comprises around 14 Exemplar problems in which you need to prove hypotheses with the help of point bisectors, symmetrical triangles, cyclic quadrilaterals and so forth.
5. Why opt for Vedantu when preparing for NCERT Maths Class 9 Chapter 10- Circle?
Vedantu is one of the renowned learning platforms which aims at making studying simple and fun for you by utilizing state of the art innovation and content from subject experts. The experts have planned the in-depth answers for the NCERT Exemplar questions for CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 10. Along these lines, presently you can make the study of math simple with the team of Vedantu by just visiting the website and signing up for free of cost! Download all the NCERT Class 9 Maths Solutions for free.





































